Abstract
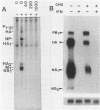
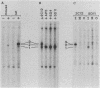
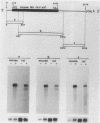
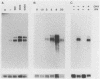
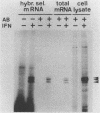
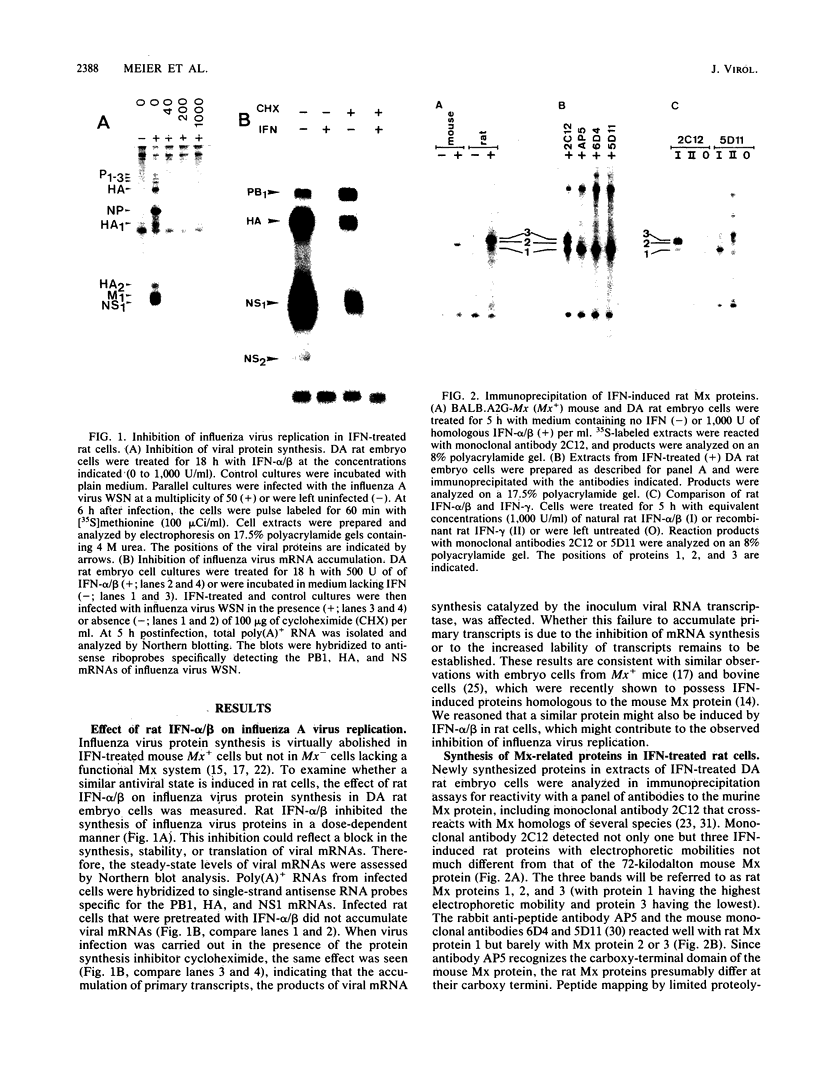
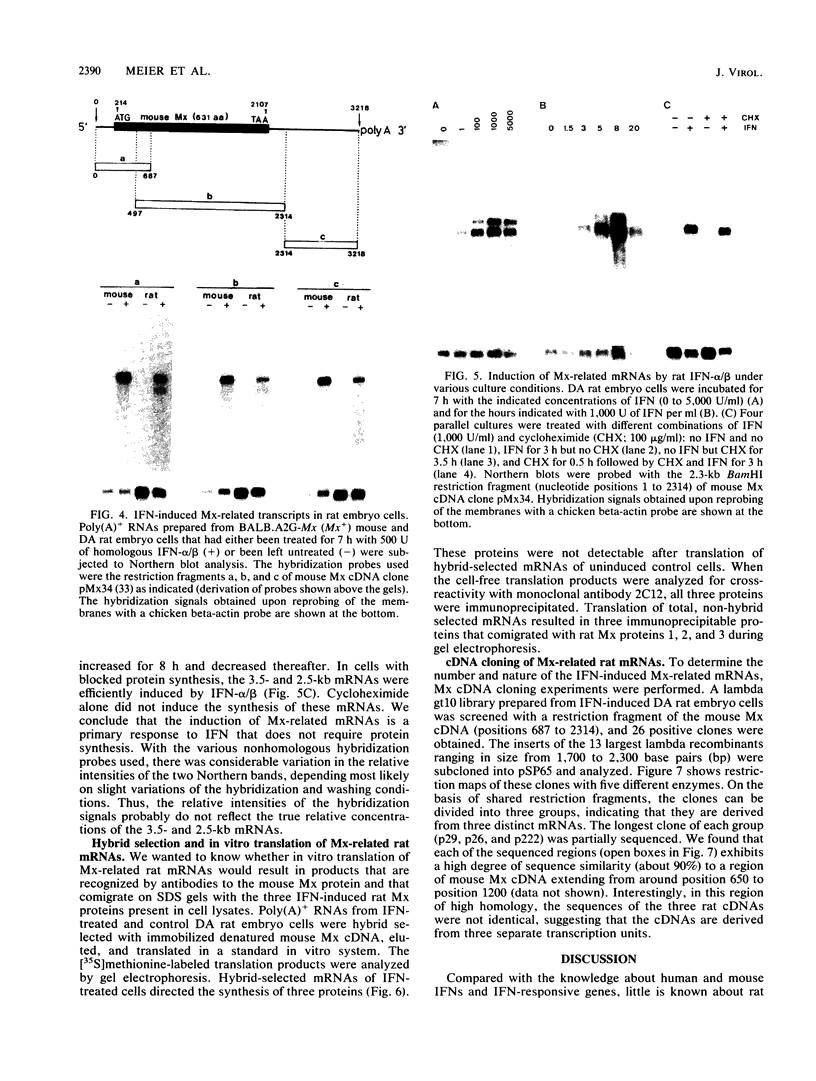
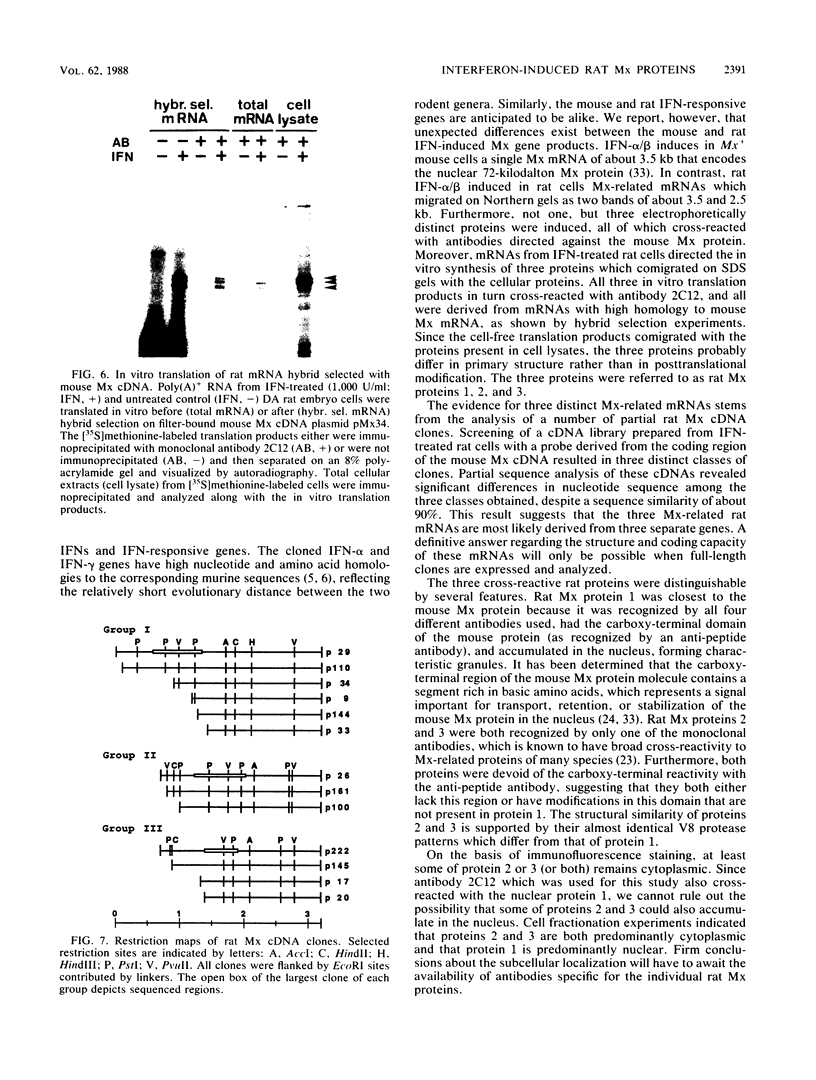
Mouse Mx protein, an interferon (IFN)-induced nuclear protein, confers selective resistance to influenza virus. We show here that, as with influenza virus-resistant Mx+ mouse embryo cells, influenza virus mRNA accumulation and protein synthesis are strongly inhibited in rat embryo cells treated with IFN-alpha/beta. IFN-alpha/beta induced in rat cells the synthesis of Mx-related mRNAs migrating on Northern (RNA) gels as two bands of about 3.5 and 2.5 kilobases which directed the synthesis of three electrophoretically distinct proteins called rat Mx proteins 1, 2, and 3. The three rat proteins were antigenically related to the mouse Mx protein but differed in molecular weight and intracellular location. Rat Mx protein 1 was found predominantly in the nucleus and, on the basis of several criteria, resembled the nuclear mouse Mx protein. It was induced by IFN-alpha/beta in all 28 inbred rat strains tested. Rat Mx proteins 2 and 3 differed from protein 1 at the carboxy terminus and were predominantly cytoplasmic like the human Mx homolog. Sequence data of partial cDNA clones indicate that three Mx-related genes, rather than one, exist in the rat.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheiter H., Haller O. Antiviral state against influenza virus neutralized by microinjection of antibodies to interferon-induced Mx proteins. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1315–1320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheiter H., Staeheli P. Expression of interferon dependent resistance to influenza virus in mouse embryo cells. Arch Virol. 1983;76(2):127–137. doi: 10.1007/BF01311696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benech P., Mory Y., Revel M., Chebath J. Structure of two forms of the interferon-induced (2'-5') oligo A synthetase of human cells based on cDNAs and gene sequences. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2249–2256. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Merlin G., Metz R., Benech P., Revel M. Interferon-induced 56,000 Mr protein and its mRNA in human cells: molecular cloning and partial sequence of the cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1213–1226. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkema R., Pouwels P., de Reus A., Schellekens H. Structure and expression in Escherichia coli of a cloned rat interferon-alpha gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1227–1242. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkema R., van der Meide P. H., Pouwels P. H., Caspers M., Dubbeld M., Schellekens H. Cloning and expression of the chromosomal immune interferon gene of the rat. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):761–767. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreiding P., Staeheli P., Haller O. Interferon-induced protein Mx accumulates in nuclei of mouse cells expressing resistance to influenza viruses. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):192–196. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90460-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Acklin M., Staeheli P. Influenza virus resistance of wild mice: wild-type and mutant Mx alleles occur at comparable frequencies. J Interferon Res. 1987 Oct;7(5):647–656. doi: 10.1089/jir.1987.7.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Arnheiter H., Gresser I., Lindenmann J. Virus-specific interferon action. Protection of newborn Mx carriers against lethal infection with influenza virus. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):199–203. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Arnheiter H., Lindenmann J., Gresser I. Host gene influences sensitivity to interferon action selectively for influenza virus. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):660–662. doi: 10.1038/283660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O. Inborn resistance of ice to orthomyxoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;92:25–52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68069-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. A., Haller O., Arnheiter H. Interferon-dependent genetic resistance to influenza virus in mice: virus replication in macrophages is inhibited at an early step. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):205–210. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. A. The action of recombinant bovine interferons on influenza virus replication correlates with the induction of two Mx-related proteins in bovine cells. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90407-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Pitha P. M. Differential effect of poly rI.rC and Newcastle disease virus on the expression of interferon and cellular genes in mouse cells. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):382–393. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug R. M., Shaw M., Broni B., Shapiro G., Haller O. Inhibition of influenza viral mRNA synthesis in cells expressing the interferon-induced Mx gene product. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):201–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.201-206.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Etkind P. R., Choppin P. W. Evidence for a ninth influenza viral polypeptide. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):60–78. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Jonak G., Cheng Y. S., Korant B., Knight E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction of two genes in human cells by beta interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6733–6737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Horisberger M. A. Combined action of mouse alpha and beta interferons in influenza virus-infected macrophages carrying the resistance gene Mx. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):709–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.709-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noteborn M., Arnheiter H., Richter-Mann L., Browning H., Weissmann C. Transport of the murine Mx protein into the nucleus is dependent on a basic carboxy-terminal sequence. J Interferon Res. 1987 Oct;7(5):657–669. doi: 10.1089/jir.1987.7.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransohoff R. M., Maroney P. A., Nayak D. P., Chambers T. M., Nilsen T. W. Effect of human alpha A interferon on influenza virus replication in MDBK cells. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):1049–1052. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.1049-1052.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanta H., Pravtcheva D. D., Ruddle F. H., Lengyel P. Chromosomal location of mouse gene 202 which is induced by interferons and specifies a 56.5 kD protein. J Interferon Res. 1984 Spring;4(2):295–300. doi: 10.1089/jir.1984.4.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellekens H., De Wilde G. A., Weimar W. Production and initial characterization of rat interferon. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jan;46(1):243–247. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-1-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Danielson P., Haller O., Sutcliffe J. G. Transcriptional activation of the mouse Mx gene by type I interferon. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4770–4774. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Dreiding P., Haller O., Lindenmann J. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies to the interferon-inducible protein Mx of influenza virus-resistant mice. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1821–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Haller O., Boll W., Lindenmann J., Weissmann C. Mx protein: constitutive expression in 3T3 cells transformed with cloned Mx cDNA confers selective resistance to influenza virus. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Haller O. Interferon-induced Mx protein: a mediator of cellular resistance to influenza virus. Interferon. 1987;8:1–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Haller O. Interferon-induced human protein with homology to protein Mx of influenza virus-resistant mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2150–2153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Horisberger M. A., Haller O. Mx-dependent resistance to influenza viruses is induced by mouse interferons alpha and beta but not gamma. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):456–461. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]