Abstract
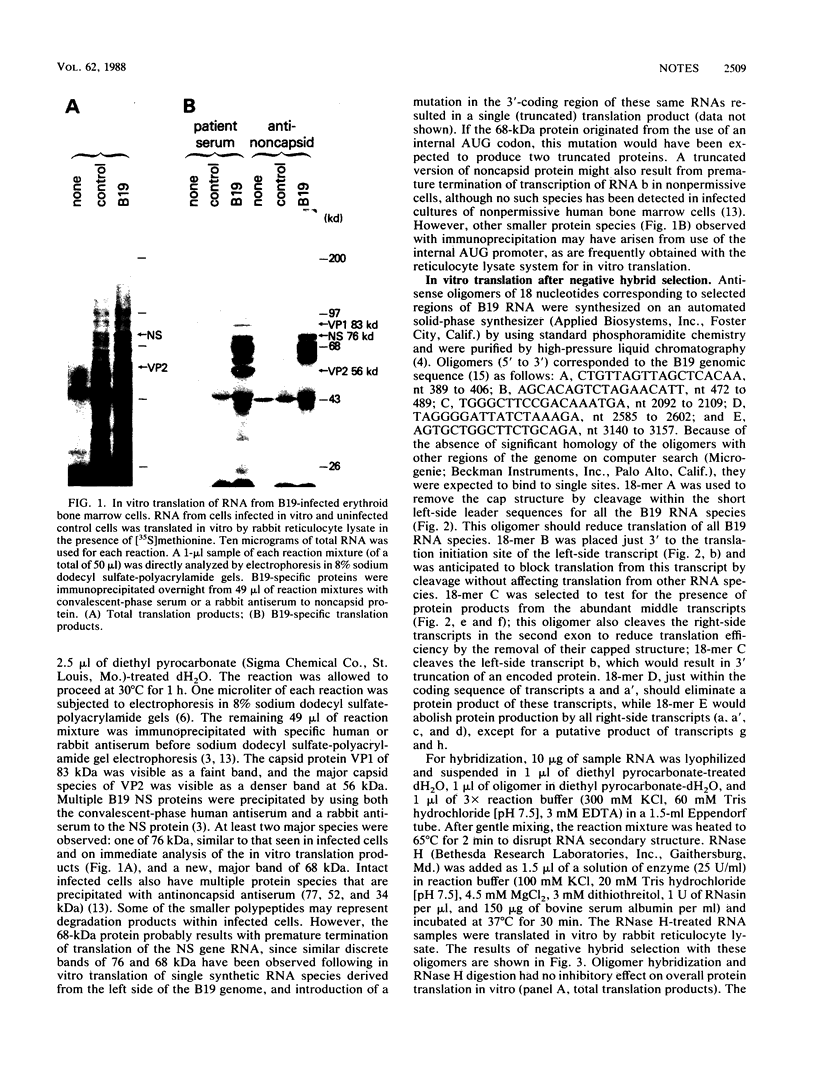
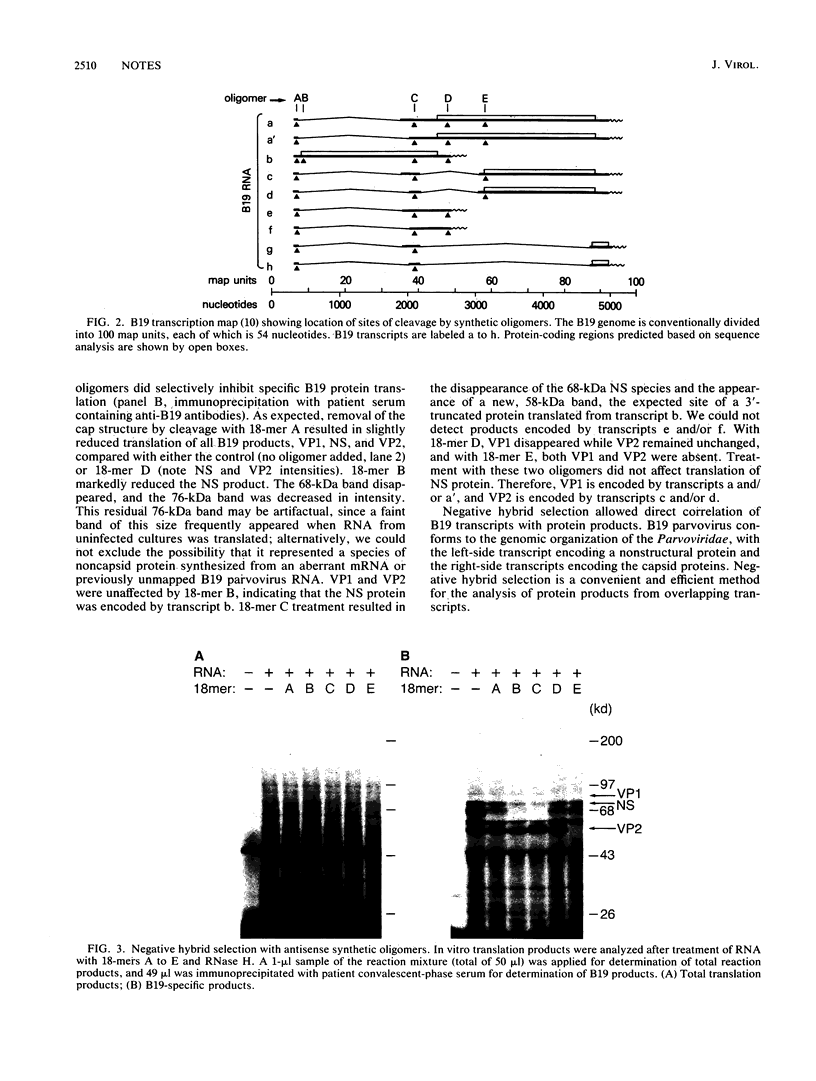
We have analyzed the coding capacity of B19 parvovirus transcripts by in vitro translation using the negative hybrid selection technique. Five different antisense oligonucleotides (18-mers) corresponding to different portions of the B19 genome were hybridized to RNA samples extracted from human erythroid bone marrow cells infected with B19 parvovirus in vitro, and RNase H was added to cleave specific B19 RNA molecules at selected sites. B19-specific translation products of these RNA samples were determined by immunoprecipitation. We localized the B19 nonstructural protein to the left-side transcript and the two capsid proteins to overlapping transcripts from the right side of the genome.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chorba T., Coccia P., Holman R. C., Tattersall P., Anderson L. J., Sudman J., Young N. S., Kurczynski E., Saarinen U. M., Moir R. The role of parvovirus B19 in aplastic crisis and erythema infectiosum (fifth disease). J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):383–393. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., McKie V. C., Anderson L. J., Astell C. R., Tattersall P. Identification of the major structural and nonstructural proteins encoded by human parvovirus B19 and mapping of their genes by procaryotic expression of isolated genomic fragments. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):548–557. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.548-557.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman G. J., Ozawa K., Cohen B., Hanson G., Oseas R., Young N. S. Chronic bone marrow failure due to persistent B19 parvovirus infection. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 30;317(5):287–294. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707303170506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. S., Paterson B. M., Ricciardi R. P., Cohen L., Roberts B. E. Methods utilizing cell-free protein-synthesizing systems for the identification of recombinant DNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:650–674. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Hunt T. The use of single-stranded DNA and RNase H to promote quantitative 'hybrid arrest of translation' of mRNA/DNA hybrids in reticulocyte lysate cell-free translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6433–6451. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. P., Humphries R. K., Moore J. G., Purcell R. H., Young N. S. A human parvovirus-like virus inhibits haematopoietic colony formation in vitro. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):426–429. doi: 10.1038/302426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Ayub J., Hao Y. S., Kurtzman G., Shimada T., Young N. Novel transcription map for the B19 (human) pathogenic parvovirus. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2395–2406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2395-2406.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Kurtzman G., Young N. Productive infection by B19 parvovirus of human erythroid bone marrow cells in vitro. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):384–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Kurtzman G., Young N. Replication of the B19 parvovirus in human bone marrow cell cultures. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):883–886. doi: 10.1126/science.3738514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Young N. Characterization of capsid and noncapsid proteins of B19 parvovirus propagated in human erythroid bone marrow cell cultures. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2627–2630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2627-2630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison J. R., Jones S. E., Hodgson J., Davis L. R., White J. M., Stroud C. E., Murtaza L. Parvovirus infections and hypoplastic crisis in sickle-cell anaemia. Lancet. 1981 Mar 21;1(8221):664–665. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91579-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shade R. O., Blundell M. C., Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P., Astell C. R. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of human parvovirus B19 isolated from the serum of a child during aplastic crisis. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):921–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.921-936.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. S., Mortimer P. P., Moore J. G., Humphries R. K. Characterization of a virus that causes transient aplastic crisis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):224–230. doi: 10.1172/JCI111195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]