Abstract
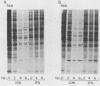
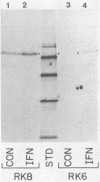
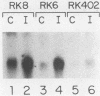
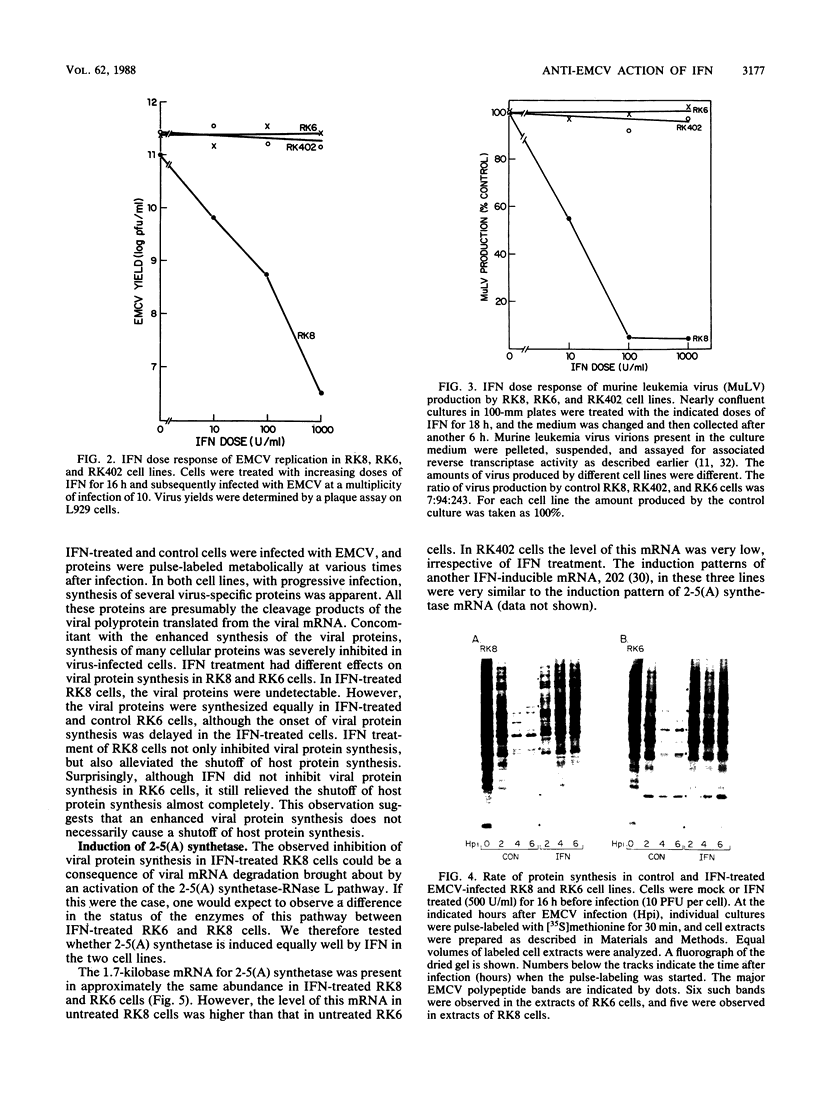
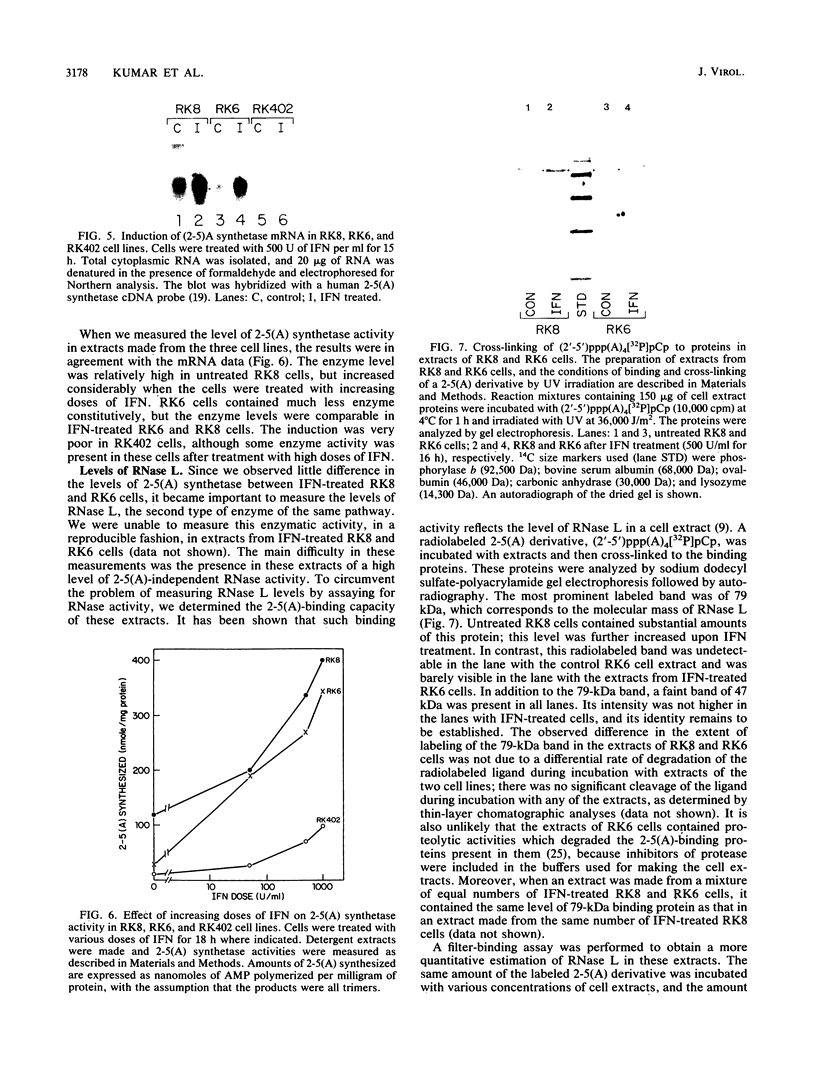
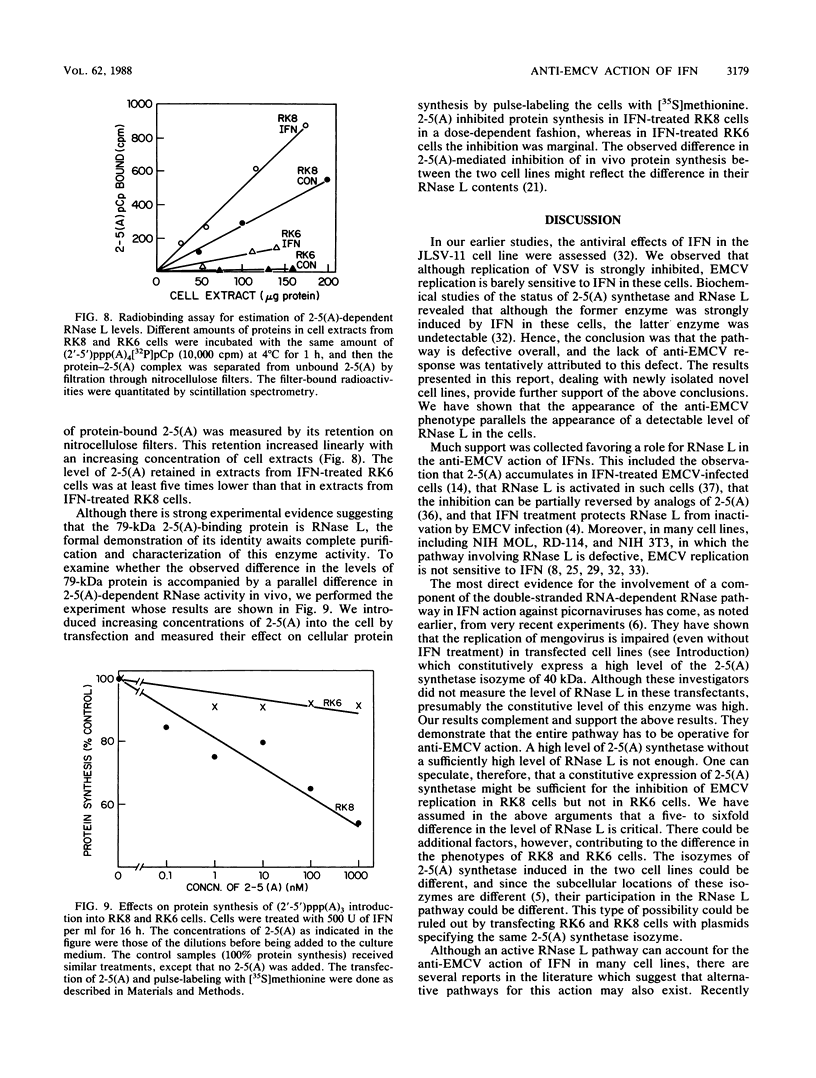
Interferons inhibit the replication of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), but not of encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV), in mouse JLSV-11 cells. We report the isolation of clonal derivatives from this cell line in which the replication of both viruses is impaired by interferons. These clones were selected from the parental line by virtue of their rescue by interferon treatment from the cytopathic effects of EMCV infection. In one such clone, RK8, the replication of VSV and EMCV and the production of resident murine leukemia virus were inhibited by interferon. On the other hand, in clone RK6, which was isolated without any selection, the replication of VSV, but not of EMCV, was impaired by interferons. The levels of 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase mRNA and enzyme activity were similarly elevated upon interferon treatment in the two clones. However, the level of RNase L, as determined by binding and cross-linking of a radiolabeled 2'-5'-oligoadenylate derivative, was much lower in RK6 cells than in RK8 cells. In accord with this observation, the introduction of 2'-5'-oligoadenylates into cells inhibited protein synthesis much less strongly in RK6 cells than in RK8 cells. These results are consistent with the notion that the 2'-5'-oligoadenylate-dependent RNase L may be a mediator of the inhibition of EMCV replication by interferons.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M., Belardelli F., Blanchard B., Marcucci F., Gresser I. High-affinity binding of 125I-labeled mouse interferon to a specific cell surface receptor. IV. Mouse gamma interferon and cholera toxin do not compete for the common receptor site of alpha / beta interferon. Virology. 1982 Mar;117(2):541–544. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90497-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C., Nilsen T. W. Mechanisms of antiviral action of interferon. Interferon. 1983;5:23–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belkowski L. S., Sen G. C. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis viral mRNA synthesis by interferons. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):653–660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.653-660.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayley P. J., Knight M., Kerr I. M. Virus-mediated inhibition of the ppp(A2'p)nA system and its prevention by interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):376–382. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90647-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Benech P., Hovanessian A., Galabru J., Revel M. Four different forms of interferon-induced 2',5'-oligo(A) synthetase identified by immunoblotting in human cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3852–3857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Benech P., Revel M., Vigneron M. Constitutive expression of (2'-5') oligo A synthetase confers resistance to picornavirus infection. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):587–588. doi: 10.1038/330587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarniecki C. W., Sreevalsan T., Friedman R. M., Panet A. Dissociation of interferon effects on murine leukemia virus and encephalomyocarditis virus replication in mouse cells. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):827–831. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.827-831.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein D. A., Czarniecki C. W., Jacobsen H., Friedman R. M., Panet A. A mouse cell line, which is unprotected by interferon against lytic virus infection, lacks ribonuclease F activity. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(1):9–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd-Smith G., Lengyel P. RNase L, a (2'-5')-oligoadenylate-dependent endoribonuclease: assays and purification of the enzyme; cross-linking to a (2'-5')-oligoadenylate derivative. Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:489–499. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd-Smith G., Yoshie O., Lengyel P. Interferon action. Covalent linkage of (2'-5')pppApApA(32P)pCp to (2'-5')(A)n-dependent ribonucleases in cell extracts by ultraviolet irradiation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8584–8587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz R. E., Rubin B. Y., Sen G. C. Human interferon-alpha-and-gamma-mediated inhibition of retrovirus production in the absence of an inhibitory effect on vesicular stomatitis virus and encephalomyocarditis virus replication in RD-114 cells. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):246–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G., Brown R. E., Martin E. M., Roberts W. K., Knight M., Kerr I. M. Enzymic synthesis, purification, and fractionation of (2'-5')-oligoadenylic acid. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):184–193. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen H., Czarniecki C. W., Krause D., Friedman R. M., Silverman R. H. Interferon-induced synthesis of 2-5A-dependent RNase in mouse JLS-V9R cells. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):496–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight M., Cayley P. J., Silverman R. H., Wreschner D. H., Gilbert C. S., Brown R. E., Kerr I. M. Radioimmune, radiobinding and HPLC analysis of 2-5A and related oligonucleotides from intact cells. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):189–192. doi: 10.1038/288189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D., Panet A., Arad G., Dieffenbach C. W., Silverman R. H. Independent regulation of ppp(A2'p)nA-dependent RNase in NIH 3T3, clone 1 cells by growth arrest and interferon treatment. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9501–9507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Chattopadhyay D., Banerjee A. K., Sen G. C. Ribonuclease activity is associated with subviral particles isolated from interferon-treated vesicular stomatitis virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):641–643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.641-643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Sen G. C. Clonal derivatives of the RD-114 cell line differ in their antiviral and gene-inducing responses to interferons. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2727–2732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2727-2732.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusari J., Sen G. C. Regulation of synthesis and turnover of an interferon-inducible mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2062–2067. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusari J., Tiwari R. K., Kumar R., Sen G. C. Expression of interferon-inducible genes in RD-114 cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1524–1531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1524-1531.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Content J. Mechanisms of interferon action: biochemical and genetic approaches. Interferon. 1982;4:47–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A. Induction of an antiviral state by interferon in the absence of elevated levels of 2,5-oligo(A) synthetase and eIF-2 kinase. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):118–127. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90400-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittnacht S., Jacobsen H. Selection and characterization of interferon-sensitive cells derived from an interferon-resistant NIH 3T3 line. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2945–2951. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Baglioni C. Mechanism for discrimination between viral and host mRNA in interferon-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2600–2604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., McCandless S., Baglioni C. 2', 5'-oligo(A)-activated endonuclease in NIH 3T3 mouse cells chronically infected with Moloney murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):498–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90252-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Wood D. L., Baglioni C. Virus-specific effects of interferon in embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):178–180. doi: 10.1038/286178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzberg S., Wreschner D. H., Oberman F., Panet A., Bakhanashvili M. Isolation and characterization of an interferon-resistant cell line deficient in the induction of (2'-5')oligoadenylate synthetase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1759–1765. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanta H., Engel D. A., Chao H. M., Thakur A., García-Blanco M. A., Lengyel P. Interferons as gene activators. Cloning of the 5' terminus and the control segment of an interferon activated gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11849–11858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C. Biochemical pathways in interferon-action. Pharmacol Ther. 1984;24(2):235–257. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(84)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Herz R. E. Differential antiviral effects of interferon in three murine cell lines. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1017–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1017-1027.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Herz R. E., Rubin B. Y. Antiviral, anticellular and enzyme-inducing activities of interferons in RD-114 cells. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2213–2220. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Haller O., Boll W., Lindenmann J., Weissmann C. Mx protein: constitutive expression in 3T3 cells transformed with cloned Mx cDNA confers selective resistance to influenza virus. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita Y., Nishimaki J., Takahashi F., Kuwata T. Human interferon suppression of retrovirus production and cell fusion, and failure to inhibit replication of encephalomyocarditis virus in rhabdomyosarcoma (RD114) cells. Virology. 1982 Jul 15;120(1):258–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watling D., Serafinowska H. T., Reese C. B., Kerr I. M. Analogue inhibitor of 2-5A action: effect on the interferon-mediated inhibition of encephalomyocarditis virus replication. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):431–436. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03647.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreschner D. H., James T. C., Silverman R. H., Kerr I. M. Ribosomal RNA cleavage, nuclease activation and 2-5A(ppp(A2'p)nA) in interferon-treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1571–1581. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]