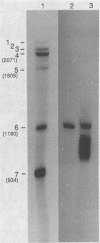
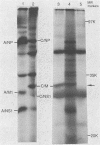
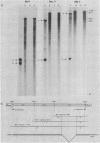
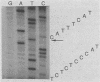
Abstract
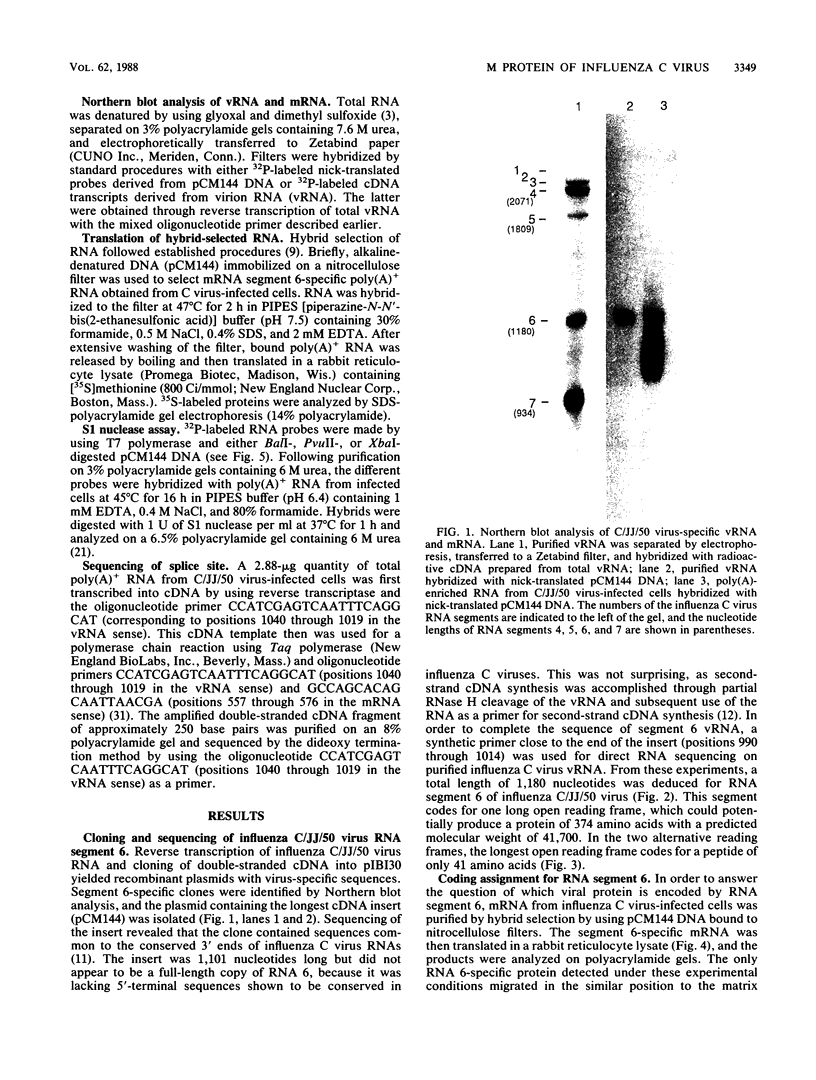
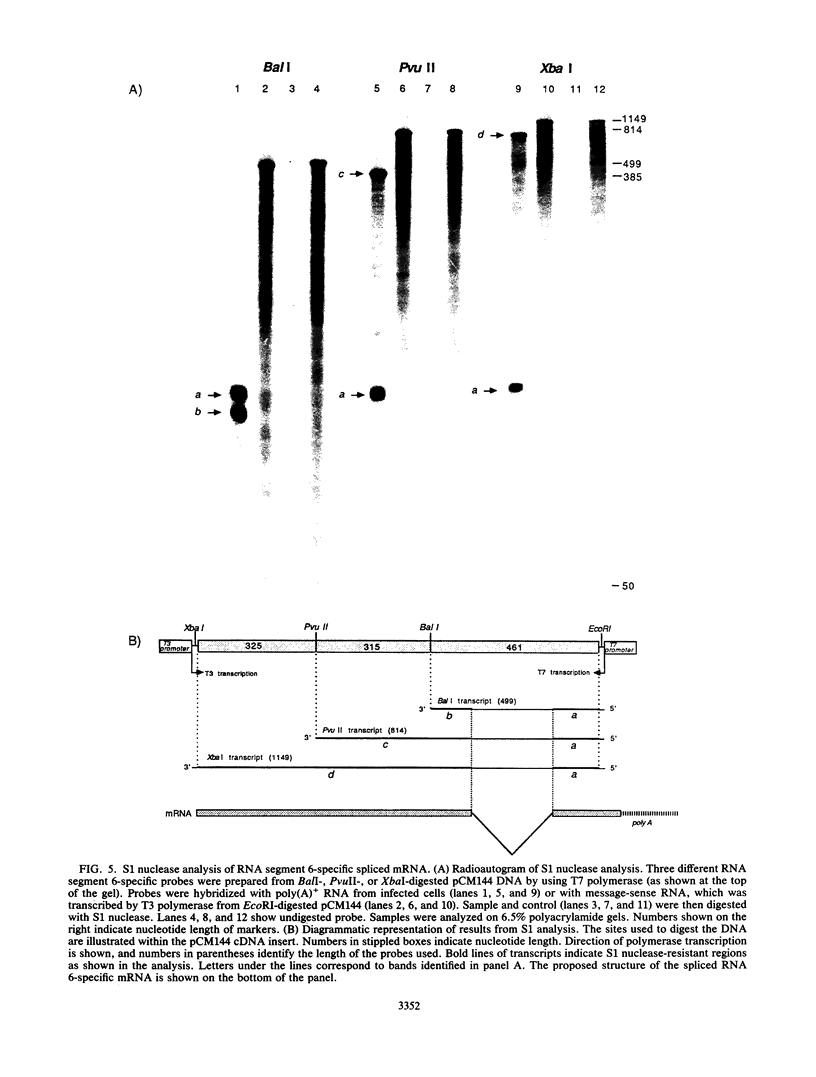
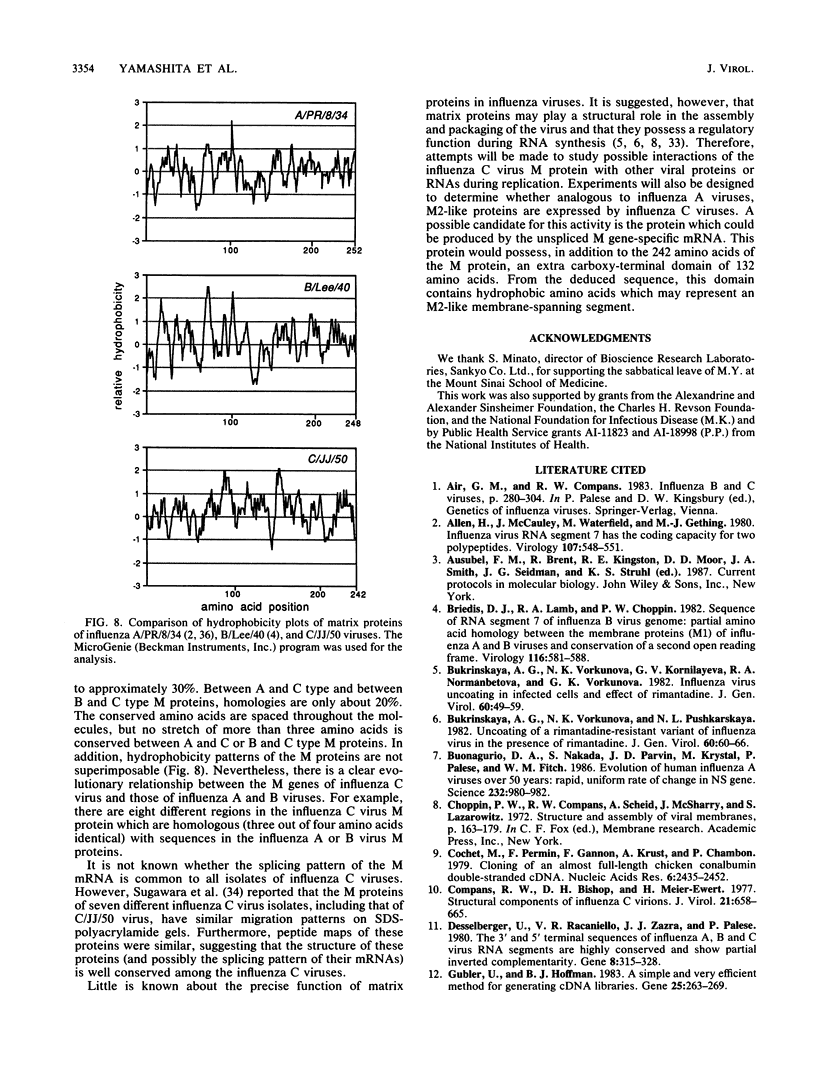
In contrast to influenza A and B viruses, which encode their matrix (M) proteins via an unspliced mRNA, the influenza C virus M protein appears to be coded for by a spliced mRNA from RNA segment 6. Although an open reading frame in RNA segment 6 of influenza C/JJ/50 virus could potentially code for a protein of 374 amino acids, a splicing event results in an mRNA coding for a 242-amino-acid M protein. The message for this protein represents the major M gene-specific mRNA species in C virus-infected cells. Despite the difference in coding strategies, there are sequence homologies among the M proteins of influenza A, B, and C viruses which confirm the evolutionary relationship of the three influenza virus types.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen H., McCauley J., Waterfield M., Gething M. J. Influenza virus RNA segment 7 has the coding capacity for two polypeptides. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):548–551. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briedis D. J., Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Sequence of RNA segment 7 of the influenza B virus genome: partial amino acid homology between the membrane proteins (M1) of influenza A and B viruses and conservation of a second open reading frame. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinskaya A. G., Vorkunova N. K., Kornilayeva G. V., Narmanbetova R. A., Vorkunova G. K. Influenza virus uncoating in infected cells and effect of rimantadine. J Gen Virol. 1982 May;60(Pt 1):49–59. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinskaya A. G., Vorkunova N. K., Pushkarskaya N. L. Uncoating of a rimantadine-resistant variant of influenza virus in the presence of rimantadine. J Gen Virol. 1982 May;60(Pt 1):61–66. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonagurio D. A., Nakada S., Parvin J. D., Krystal M., Palese P., Fitch W. M. Evolution of human influenza A viruses over 50 years: rapid, uniform rate of change in NS gene. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):980–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2939560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet M., Perrin F., Gannon F., Krust A., Chambon P., McKnight G. S., Lee D. C., Mayo K. E., Palmiter R. Cloning of an almost full-length chicken conalbumin double-stranded cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2435–2452. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compans R. W., Bishop D. H., Meier-Ewert H. Structural components of influenza C virions. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):658–665. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.658-665.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desselberger U., Racaniello V. R., Zazra J. J., Palese P. The 3' and 5'-terminal sequences of influenza A, B and C virus RNA segments are highly conserved and show partial inverted complementarity. Gene. 1980 Feb;8(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrler G., Compans R. W., Meier-Ewert H. A precursor glycoprotein in influenza C virus. Virology. 1979 Nov;99(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrler G., Rott R., Klenk H. D., Müller H. P., Shukla A. K., Schauer R. The receptor-destroying enzyme of influenza C virus is neuraminate-O-acetylesterase. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1503–1506. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendal A. P. A comparison of "influenza C" with prototype myxoviruses: receptor-destroycing activity (neuraminidase) and structural polypeptides. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Identification of a second protein (M2) encoded by RNA segment 7 of influenza virus. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90317-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Lai C. J. Conservation of the influenza virus membrane protein (M1) amino acid sequence and an open reading frame of RNA segment 7 encoding a second protein (M2) in H1N1 and H3N2 strains. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):746–751. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Zebedee S. L., Richardson C. D. Influenza virus M2 protein is an integral membrane protein expressed on the infected-cell surface. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):627–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakada S., Creager R. S., Krystal M., Aaronson R. P., Palese P. Influenza C virus hemagglutinin: comparison with influenza A and B virus hemagglutinins. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):118–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.118-124.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakada S., Creager R. S., Krystal M., Palese P. Complete nucleotide sequence of the influenza C/California/78 virus nucleoprotein gene. Virus Res. 1984 Sep;1(6):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakada S., Graves P. N., Desselberger U., Creager R. S., Krystal M., Palese P. Influenza C virus RNA 7 codes for a nonstructural protein. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):221–226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.221-226.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuss D. L., Oppermann H., Koch G. Selective blockage of initiation of host protein synthesis in RNA-virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1258–1262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi M., Ohuchi R., Mifune K. Demonstration of hemolytic and fusion activities of influenza C virus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1076–1079. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1076-1079.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palese P., Young J. F. Variation of influenza A, B, and C viruses. Science. 1982 Mar 19;215(4539):1468–1474. doi: 10.1126/science.7038875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer J. B., Compans R. W. Structure of the influenza C glycoprotein gene as determined from cloned DNA. Virus Res. 1984;1(4):281–296. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Solowiejczyk D., Ballantine M., Schwartz E., Surrey S. "Nonrandom" DNA sequence analysis in bacteriophage M13 by the dideoxy chain-termination method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4298–4302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchey M. B., Palese P., Kilbourne E. D. RNAs of influenza A, B, and C viruses. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):738–744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.738-744.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze I. T. The structure of influenza virus. II. A model based on the morphology and composition of subviral particles. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):181–196. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara K., Nakamura K., Homma M. Analyses of structural polypeptides of seven different isolates of influenza C virus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Mar;64(Pt 3):579–587. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-3-579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasak R., Krystal M., Nacht M., Palese P. The influenza C virus glycoprotein (HE) exhibits receptor-binding (hemagglutinin) and receptor-destroying (esterase) activities. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Fields S. Cloning of influenza cDNA ino M13: the sequence of the RNA segment encoding the A/PR/8/34 matrix protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 10;8(9):1965–1974. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.9.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota M., Nakamura K., Sugawara K., Homma M. The synthesis of polypeptides in influenza C virus-infected cells. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):105–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]