Abstract
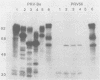
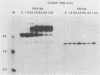
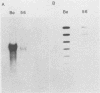
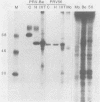
We have constructed a pseudorabies virus mutant that contains virtually a complete deletion of the predicted signal sequence coding region for a nonessential envelope glycoprotein, gIII. No signal sequence mutants have been reported previously for a herpesvirus glycoprotein. Through endoglycosidase treatments and pulse-chase analysis, we have determined that the mutant gIII protein is not posttranslationally modified like the wild-type polypeptide, but rather is present as a single, stable species within the infected cell. The mutant polypeptide cannot be detected in the virus envelope, nor is it aberrantly localized to the tissue culture medium. Immunofluorescence studies have indicated that the mutant protein also is not localized to the surfaces of infected cells. In addition, Northern (RNA) and slot blot analyses, as well as in vitro translation experiments using infected-cell cytoplasmic RNA, have indicated that the mutant gIII allele is expressed at lower levels than the wild-type gene is. This is despite the fact that no alterations have been made upstream of the gIII coding sequence. From these results, it appears that the first 22 amino acids of the wild-type gIII protein define a necessary signal peptide that is responsible for at least the correct initiation of translocation and subsequent glycosylation of the gIII envelope glycoprotein within infected cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Porat T., Demarchi J. M., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of defective interfering viral particles present in a population of pseudorabies virions. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blachly-Dyson E., Stevens T. H. Yeast carboxypeptidase Y can be translocated and glycosylated without its amino-terminal signal sequence. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1183–1191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson-Welsh L., Spear P. G. Amino-terminal sequence, synthesis, and membrane insertion of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.1-7.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Long D., Hogue-Angeletti R., Cohen G. H. Amino-terminal sequence of glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):265–268. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.265-268.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Alexander S. endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F: endoglycosidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that cleaves both high-mannose and complex glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4540–4544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Construction of influenza haemagglutinin genes that code for intracellular and secreted forms of the protein. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):598–603. doi: 10.1038/300598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Walter P., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. II. Isolation and characterization of the signal recognition particle receptor. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):470–477. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampl H., Ben-Porat T., Ehrlicher L., Habermehl K. O., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of the envelope proteins of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.583-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Holland L. E., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Physical mapping of the mutation in an antigenic variant of herpes simplex virus type 1 by use of an immunoreactive plaque assay. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):649–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.649-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. A specific 15-bp TATA box promoter element is required for expression of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):40–53. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeler C. L., Jr, Whealy M. E., Enquist L. W. Construction of an infectious pseudorabies virus recombinant expressing a glycoprotein gIII-beta-galactosidase fusion protein. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. J., Timmins J. G., Long G. W., Post L. E. Mapping and sequence of the gene for the pseudorabies virus glycoprotein which accumulates in the medium of infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):21–29. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.21-29.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Dorney D. J., Wathen M. W., Whealy M. E., Gold C., Watson R. J., Holland L. E., Weed S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. The pseudorabies virus gII gene is closely related to the gB glycoprotein gene of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2691–2701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2691-2701.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Watson R. J., Whealy M. E., Hays W. W., Enquist L. W. Characterization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene with homology to herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):339–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.339-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
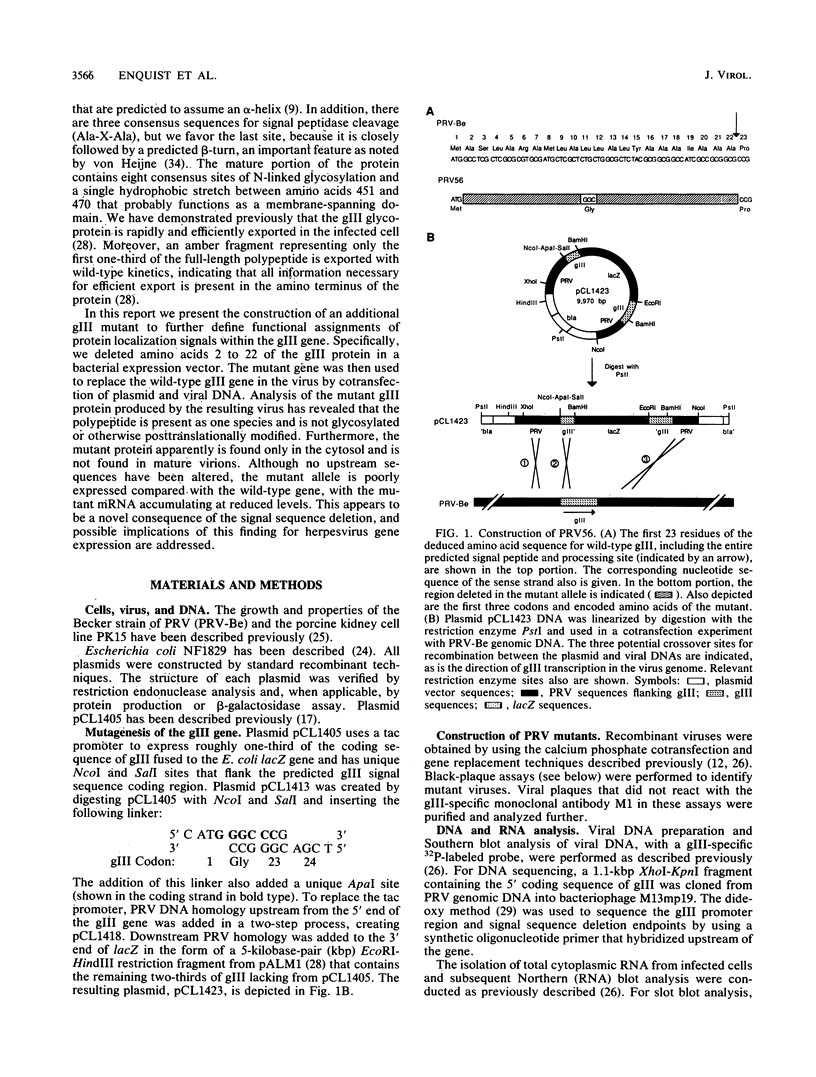
- Robbins A. K., Weis J. H., Enquist L. W., Watson R. J. Construction of E. coli expression plasmid libraries: localization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(5):485–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Whealy M. E., Watson R. J., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus gene encoding glycoprotein gIII is not essential for growth in tissue culture. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):635–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.635-645.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. P., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Analysis of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII localization and modification by using novel infectious viral mutants carrying unique EcoRI sites. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2962–2972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2962-2972.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silve S., Monod M., Hinnen A., Haguenauer-Tsapis R. The yeast acid phosphatase can enter the secretory pathway without its N-terminal signal sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3306–3314. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Kennell W. L., Lamm D. L. Visualization of minute centers of viral infection in unfixed cell cultures by an enzyme-linked antibody assay. J Immunol Methods. 1981;40(3):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90361-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptomyces griseus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann M., Kurzchalia T. V., Bielka H., Rapoport T. A. Direct probing of the interaction between the signal sequence of nascent preprolactin and the signal recognition particle by specific cross-linking. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):201–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann M., Kurzchalia T. V., Hartmann E., Rapoport T. A. A signal sequence receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):830–833. doi: 10.1038/328830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Hardwick J. M., Shaw K., Hunter E. Alterations in the transport and processing of Rous sarcoma virus envelope glycoproteins mutated in the signal and anchor regions. J Cell Biochem. 1983;23(1-4):81–94. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240230109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]