Abstract
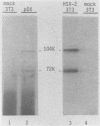
The gG-2 glycoprotein gene of herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) was cloned into the mammalian expression vector pMSG under the control of the inducible mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Transfection of this cloned gG-2 construct into NIH 3T3 cells resulted in the stable expression of gG-2 upon induction with dexamethasone. In addition, the 104,000-molecular-weight (104K) and 72K gG-2 precursors as well as the 34K secreted component were generated in the transformed cells. The synthesis of gG-2 in these transformed cells appeared to follow the same cleavage-processing pathway as gG-2 synthesis during an HSV-2 infection. These results indicate that the processing of gG-2 can occur in the absence of an HSV-2 infection.
Full text
PDF

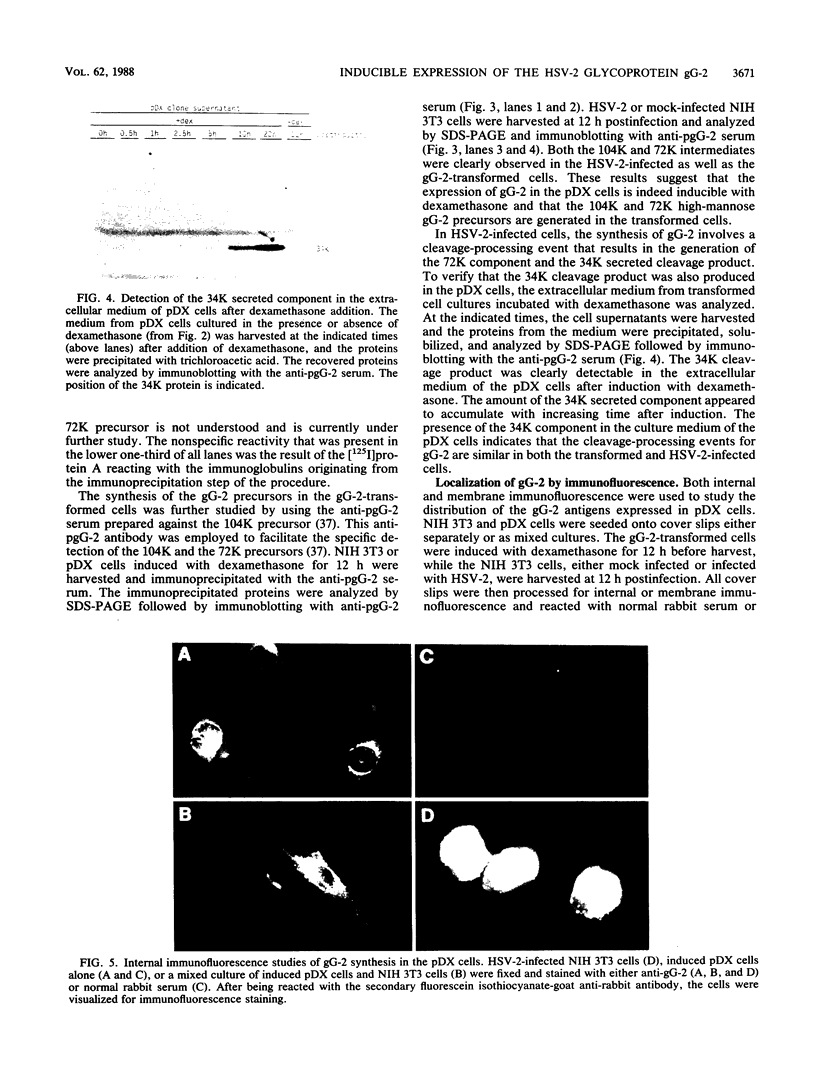



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Longnecker R., Roizman B., Pereira L. Identification, properties, and gene location of a novel glycoprotein specified by herpes simplex virus 1. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):207–220. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. Immunoprecipitation of proteins from cell-free translations. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:111–120. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Hutt-Fletcher L. M. Synthesis and processing of glycoprotein gG of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):825–832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.825-832.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett L. M., Timmins J. G., Thomsen D. R., Post L. E. The processing of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gX in infected cells and in an uninfected cell line. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):707–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone D. R., Courtney R. J. A temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1 defective in the synthesis of the major capsid polypeptide. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):17–27. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A. B., Costello M. A., Lee F., Ringold G. M. Amplification and hormone-regulated expression of a mouse mammary tumor virus-Eco gpt fusion plasmid in mouse 3T6 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1421–1429. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton T., Courtney R. J. Virus-specific glycoproteins associated with the nuclear fraction of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):594–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.594-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dall'Olio F., Malagolini N., Campadelli-Fiume G., Serafini-Cessi F. Glycosylation pattern of herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein G from precursor species to the mature form. Arch Virol. 1987;97(3-4):237–249. doi: 10.1007/BF01314424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Preparation and characterization of specific antisera to individual glycoprotein antigens comprising the major glycoprotein region of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):902–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.902-917.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flannery V. L., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. Expression of an early, nonstructural antigen of herpes simplex virus in cell transformed in vitro by herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.284-291.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., Marsden H. S., McGeoch D. J. Novel herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins identified by antiserum against a synthetic oligopeptide from the predicted product of gene US4. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):745–751. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frana M. F., Behnke J. N., Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of the E2 glycoprotein of murine coronavirus: host-dependent differences in proteolytic cleavage and cell fusion. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):912–920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.912-920.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Vapnek D. A simple method of preparing large amounts of phiX174 RF 1 supercoiled DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):516–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland J., Brown S. M. Generation of a herpes simplex virus type 2 variant devoid of XbaI sites: removal of the 0.91 map coordinate site results in impaired synthesis of glycoprotein G-2. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):113–124. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgman T. C., Minson A. C. The herpes simplex virus type 2 equivalent of the herpes simplex virus type 1 US7 gene and its flanking sequences. Virology. 1986 Aug;153(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R. Cotranslational and posttranslational processing of viral glycoproteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1980;90:19–48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67717-5_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Brough D. E., Cleghon V. Introduction, stable integration, and controlled expression of a chimeric adenovirus gene whose product is toxic to the recipient human cell. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1354–1362. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Mulligan R., Berg P., Ringold G. Glucocorticoids regulate expression of dihydrofolate reductase cDNA in mouse mammary tumour virus chimaeric plasmids. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):228–232. doi: 10.1038/294228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. G., Kucera L. S., Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Detection of herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoproteins expressed in virus-transformed rat cells. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):275–282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.275-282.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Clustering of genes dispensable for growth in culture in the S component of the HSV-1 genome. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):573–576. doi: 10.1126/science.3033823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Buckmaster A., Palfreyman J. W., Hope R. G., Minson A. C. Characterization of the 92,000-dalton glycoprotein induced by herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):547–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.547-554.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Moss H. W., McNab D., Frame M. C. DNA sequence and genetic content of the HindIII l region in the short unique component of the herpes simplex virus type 2 genome: identification of the gene encoding glycoprotein G, and evolutionary comparisons. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):19–38. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson S., Lundström M., Marsden H., Jeansson S., Vahlne A. Characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 2-specified glycoprotein with affinity for N-acetylgalactosamine-specific lectins and its identification as g92K or gG. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):737–744. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Post L. E. Use of lambda gt11 to isolate genes for two pseudorabies virus glycoproteins with homology to herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):185–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.185-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Courtney R. J. Polypeptide synthesized in herpes simplex virus type 2-infected HEp-2 cells. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. J., Timmins J. G., Long G. W., Post L. E. Mapping and sequence of the gene for the pseudorabies virus glycoprotein which accumulates in the medium of infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):21–29. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.21-29.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Buckmaster A., Bell S., Hodgman C., Minson A. C. Identification of a new glycoprotein of herpes simplex virus type 1 and genetic mapping of the gene that codes for it. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):647–655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.647-655.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Norrild B., Chan C., Pereira L. Identification and preliminary mapping with monoclonal antibodies of a herpes simplex virus 2 glycoprotein lacking a known type 1 counterpart. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H. K., Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Processing of the herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein gG-2 results in secretion of a 34,000-Mr cleavage product. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1735–1737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1735-1737.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Marchioli C. C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Post L. E. Replication and virulence of pseudorabies virus mutants lacking glycoprotein gX. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):229–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.229-232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Rapid identification of nonessential genes of herpes simplex virus type 1 by Tn5 mutagenesis. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):576–579. doi: 10.1126/science.3033824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]