Abstract
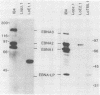
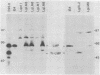
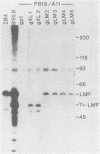
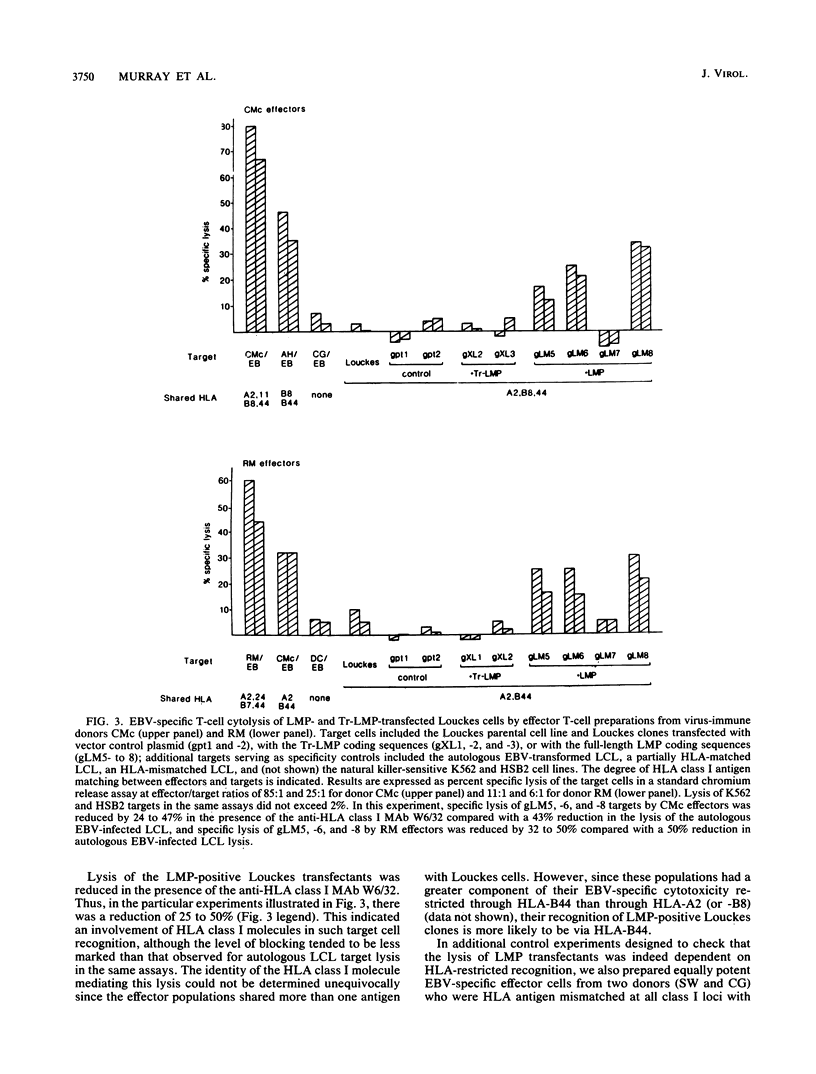
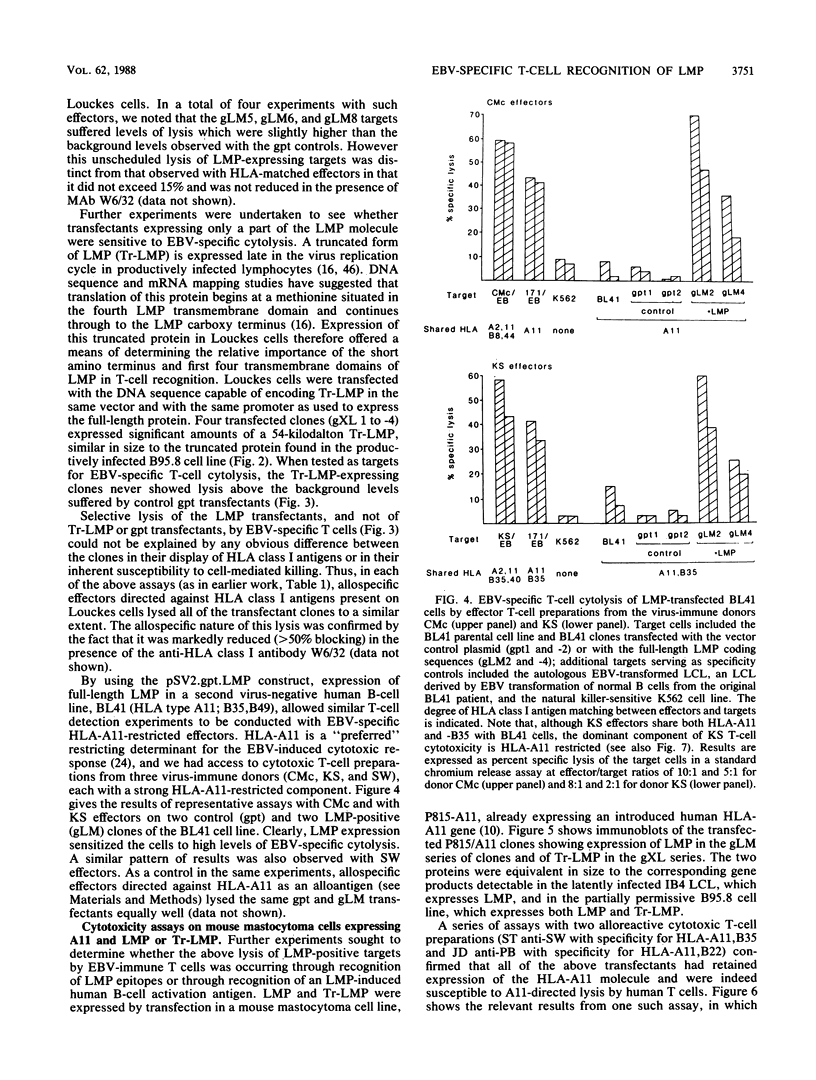
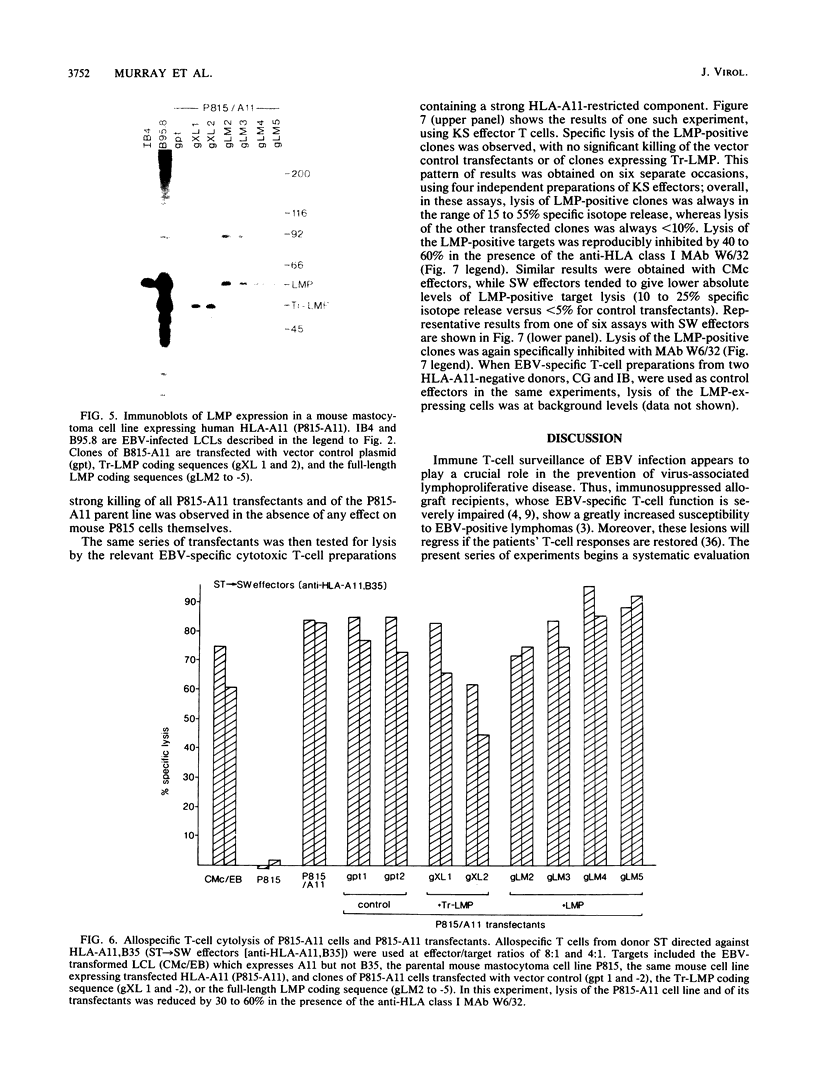
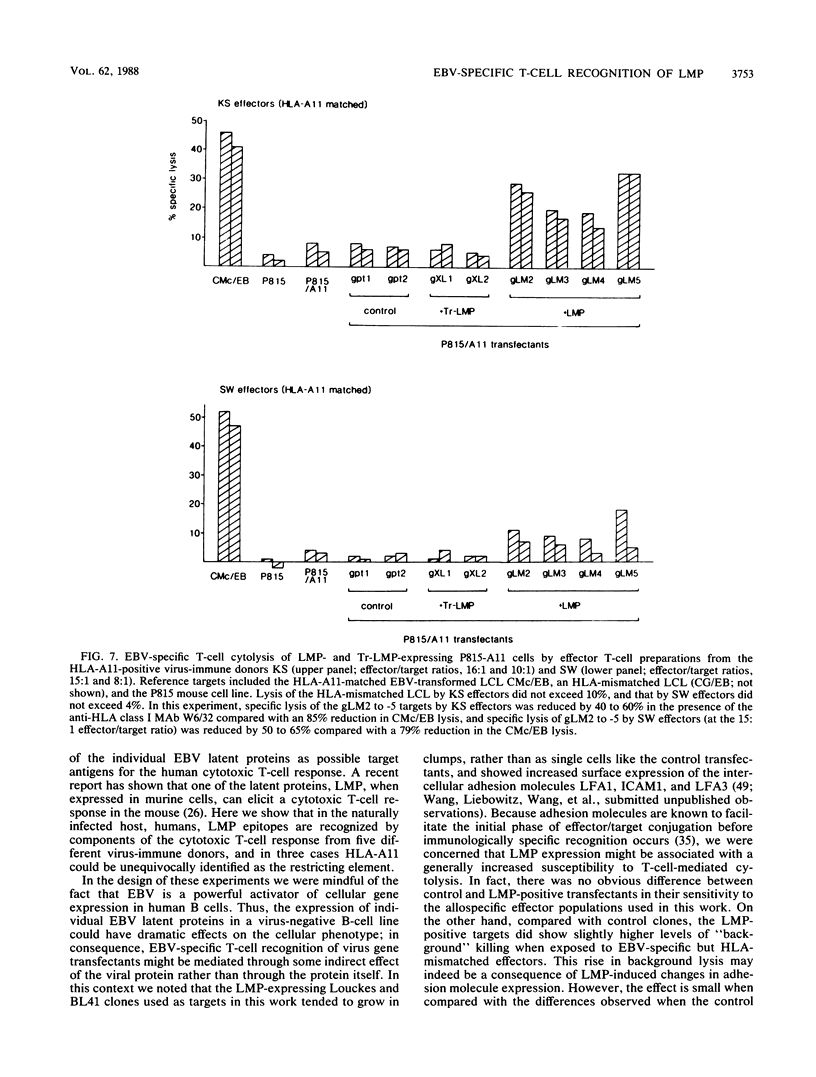
Cytotoxic T cells from Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-immune individuals specifically kill EBV-transformed B cells from HLA class I antigen-matched donors even though the latently infected cells express only a restricted set of virus genes. The virus-induced target antigens recognized by these immune T cells have not been identified. In our experiments, EBV DNA sequences encoding the virus latent gene products Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen (EBNA)1, EBNA 2, and EBNA-LP and the latent membrane protein (LMP) were individually expressed in a virus-negative human B-lymphoma cell line, Louckes. Transfected clones expressing LMP were killed by EBV-specific cytotoxic T-cell preparations from each of three virus-immune donors HLA matched with Louckes through HLA-A2, B44 antigens; control transfectants or clones expressing one of the EBNA proteins were not recognized. Expression of LMP in a second virus-negative B-cell line, BL41, sensitized these cells to EBV-specific cytolysis restricted through the HLA-A11 antigen. To distinguish between the viral protein and an induced human B-cell activation antigen as the target for T-cell recognition, LMP was then expressed in a murine mastocytoma cell line, P815-A11-restricted human T cells. The LMP-expressing P815-A11 transfectants were susceptible to lysis by EBV-specific cytotoxic T cells from three HLA-A11-positive individuals. Both Louckes and P815-A11 cells were also transfected with constructs capable of encoding a truncated form of LMP (Tr-LMP) which lacks the N-terminal 128 amino acids of the full-length protein. Tr-LMP-expressing transfectants were not recognized by the above T-cell preparations. The results suggest that LMP, and, in particular, epitopes derived from the N-terminal region of the protein, provides one of the target antigens for the EBV-induced human cytotoxic T-cell response.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. H., Edwards J. M., Sweny P., Hoffbrand A. V., Janossy G. Studies on long-term T-cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-BArr virus in immunosuppressed renal allograft recipients. Int J Cancer. 1981 Dec;28(6):705–709. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Hennessy K., Chamnankit L., Kieff E. U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA may encode Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7632–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ernberg I., Uno M., Ono Y., Klein G., Lerner R. A. An Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA5) partly encoded by the transformation-associated Bam WYH region of EBV DNA: preferential expression in lymphoblastoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6641–6645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Klein G., Jörnvall H., Alexander H., Lerner R. Antibodies against synthetic peptides react with the second Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1813–1818. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Rickinson A. B., Epstein M. A. Epstein-Barr-virus-specific T-cell memory in renal-allograft recipients under long-term immunosuppression. Lancet. 1982 Apr 24;1(8278):923–925. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91930-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomard E., Begue B., Sodoyer S., Maryanski J. L., Jordan B. R., Levy J. P. Murine cells expressing an HLA molecule are specifically lysed by HLA-restricted antiviral human T cells. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):153–154. doi: 10.1038/319153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotch F., McMichael A., Smith G., Moss B. Identification of viral molecules recognized by influenza-specific human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):408–416. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Hummel M., Cole T., Kieff E. A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7207–7211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA encodes part of the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1396–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.6304878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. A second nuclear protein is encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent infection. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.2983420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Wang F., Bushman E. W., Kieff E. Definitive identification of a member of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 3 family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5693–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson G. S., Farrell P. J., Barrell B. G. Two related but differentially expressed potential membrane proteins encoded by the EcoRI Dhet region of Epstein-Barr virus B95-8. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):528–535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.528-535.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz D., Kopan R., Fuchs E., Sample J., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein associates with vimentin in lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2299–2308. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz D., Wang D., Kieff E. Orientation and patching of the latent infection membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):233–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.233-237.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. P., Staunton D., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded protein found in plasma membranes of transformed cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):710–720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.710-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misko I. S., Moss D. J., Pope J. H. HLA antigen-related restriction of T lymphocyte cytotoxicity to Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4247–4250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Misko I. S., Burrows S. R., Burman K., McCarthy R., Sculley T. B. Cytotoxic T-cell clones discriminate between A- and B-type Epstein-Barr virus transformants. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):719–721. doi: 10.1038/331719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Rickinson A. B., Pope J. H. Long-term T-cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr virus in man. I. Complete regression of virus-induced transformation in cultures of seropositive donor leukocytes. Int J Cancer. 1978 Dec;22(6):662–668. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Rickinson A. B., Pope J. H. Long-term T-cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr virus in man. III. Activation of cytotoxic T cells in virus-infected leukocyte cultures. Int J Cancer. 1979 May 15;23(5):618–625. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Rickinson A. B., Wallace L. E., Epstein M. A. Sequential appearance of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear and lymphocyte-detected membrane antigens in B cell transformation. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):664–666. doi: 10.1038/291664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Wallace L. E., Rickinson A. B., Epstein M. A. Cytotoxic T cell recognition of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells. I. Specificity and HLA restriction of effector cells reactivated in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Sep;11(9):686–693. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. J., Young L. S., Calender A., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Lenoir G. M., Rickinson A. B. Different patterns of Epstein-Barr virus gene expression and of cytotoxic T-cell recognition in B-cell lines infected with transforming (B95.8) or nontransforming (P3HR1) virus strains. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):894–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.894-901.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss C. S., Wang D., Ghosh D., Gaposchkin C., Kieff E. Recognition of EBV plasma membrane protein expressed on murine cells after gene transfer. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):711–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Moss D. J., Wallace L. E., Rowe M., Misko I. S., Epstein M. A., Pope J. H. Long-term T-cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4216–4221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Wallace L. E., Epstein M. A. HLA-restricted T-cell recognition of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells. Nature. 1980 Feb 28;283(5750):865–867. doi: 10.1038/283865a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Evans H. S., Young L. S., Hennessy K., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. Monoclonal antibodies to the latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus reveal heterogeneity of the protein and inducible expression in virus-transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jun;68(Pt 6):1575–1586. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-6-1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Hildreth J. E., Rickinson A. B., Epstein M. A. Monoclonal antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-induced, transformation-associated cell surface antigens: binding patterns and effect upon virus-specific T-cell cytotoxicity. Int J Cancer. 1982 Apr 15;29(4):373–381. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rooney C. M., Rickinson A. B., Lenoir G. M., Rupani H., Moss D. J., Stein H., Epstein M. A. Distinctions between endemic and sporadic forms of Epstein-Barr virus-positive Burkitt's lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 1985 Apr 15;35(4):435–441. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rowe D. T., Gregory C. D., Young L. S., Farrell P. J., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2743–2751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., de Vries J. E., Terhorst C. A permanent human cytotoxic T-cell line with high killing capacity against a lymphoblastoid B-cell line shows preference for HLA A, B target antigens and lacks spontaneous cytotoxic activity. Cell Immunol. 1981 Apr;59(2):435–447. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Dustin M. L., Kishimoto T. K., Marlin S. D. The lymphocyte function-associated LFA-1, CD2, and LFA-3 molecules: cell adhesion receptors of the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:223–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Nalesnik M. A., Porter K. A., Ho M., Iwatsuki S., Griffith B. P., Rosenthal J. T., Hakala T. R., Shaw B. W., Jr, Hardesty R. L. Reversibility of lymphomas and lymphoproliferative lesions developing under cyclosporin-steroid therapy. Lancet. 1984 Mar 17;1(8377):583–587. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90994-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Grogan E. A., Shedd D., Robert M., Liu C. R., Miller G. Stable expression in mouse cells of nuclear neoantigen after transfer of a 3.4-megadalton cloned fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Israelsohn E. S. Generation of specific cytotoxic T cells with a fragment of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded p63/latent membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5384–5388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Nadler L. M., Bhan A. K., Schooley R. T. BLAST-2 [EBVCS], an early cell surface marker of human B cell activation, is superinduced by Epstein Barr virus. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3007–3012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torsteinsdottir S., Masucci M. G., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Brautbar C., Ben Bassat H., Klein G., Klein E. Differentiation-dependent sensitivity of human B-cell-derived lines to major histocompatibility complex-restricted T-cell cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5620–5624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Gotch F. M., Davey J. Cytotoxic T cells recognize fragments of the influenza nucleoprotein. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Rothbard J., Gotch F. M., Bahadur G., Wraith D., McMichael A. J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Pel A., De Plaen E., Boon T. Selection of highly transfectable variant from mouse mastocytoma P815. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Sep;11(5):467–475. doi: 10.1007/BF01534840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. E., Rowe M., Gaston J. S., Rickinson A. B., Epstein M. A. Cytotoxic T cell recognition of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells. III. Establishment of HLA-restricted cytotoxic T cell lines using interleukin 2. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Dec;12(12):1012–1018. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. The truncated form of the Epstein-Barr virus latent-infection membrane protein expressed in virus replication does not transform rodent fibroblasts. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2337–2346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2337-2346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Petti L., Braun D., Seung S., Kieff E. A bicistronic Epstein-Barr virus mRNA encodes two nuclear proteins in latently infected, growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):945–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.945-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V., Cheung A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA VII: size and direction of transcription of virus-specified cytoplasmic RNAs in a transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1930–1934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]