Abstract
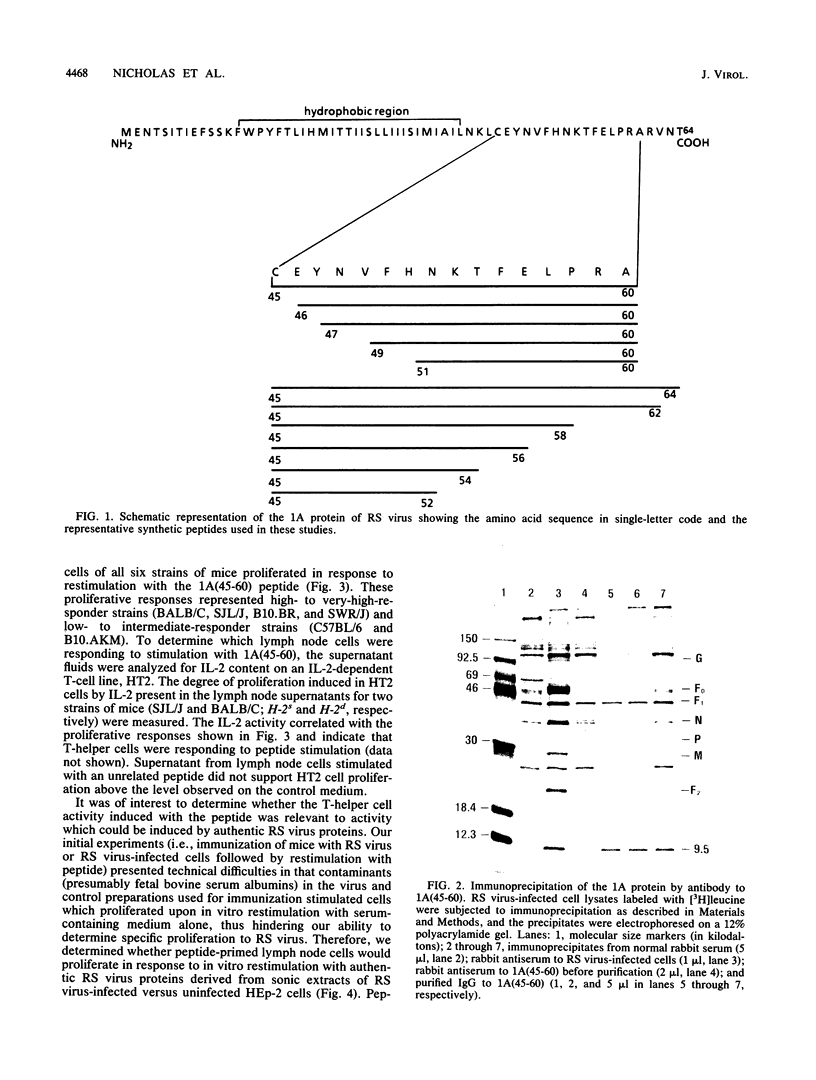
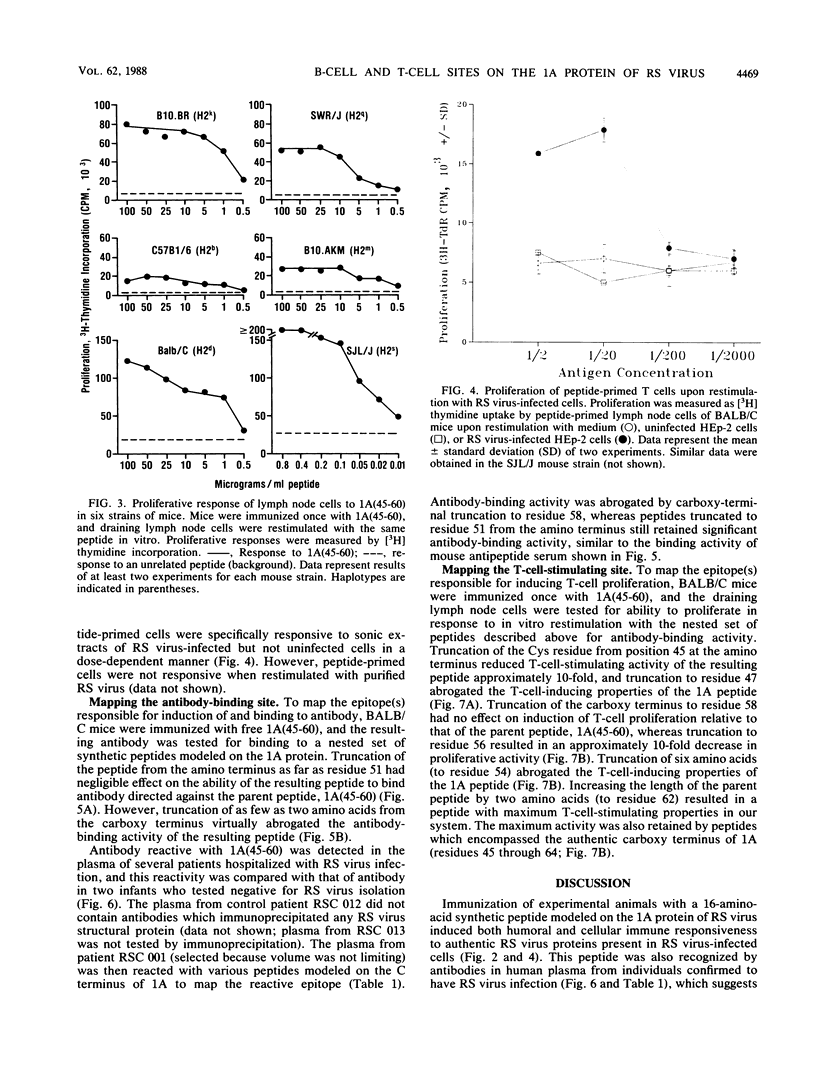
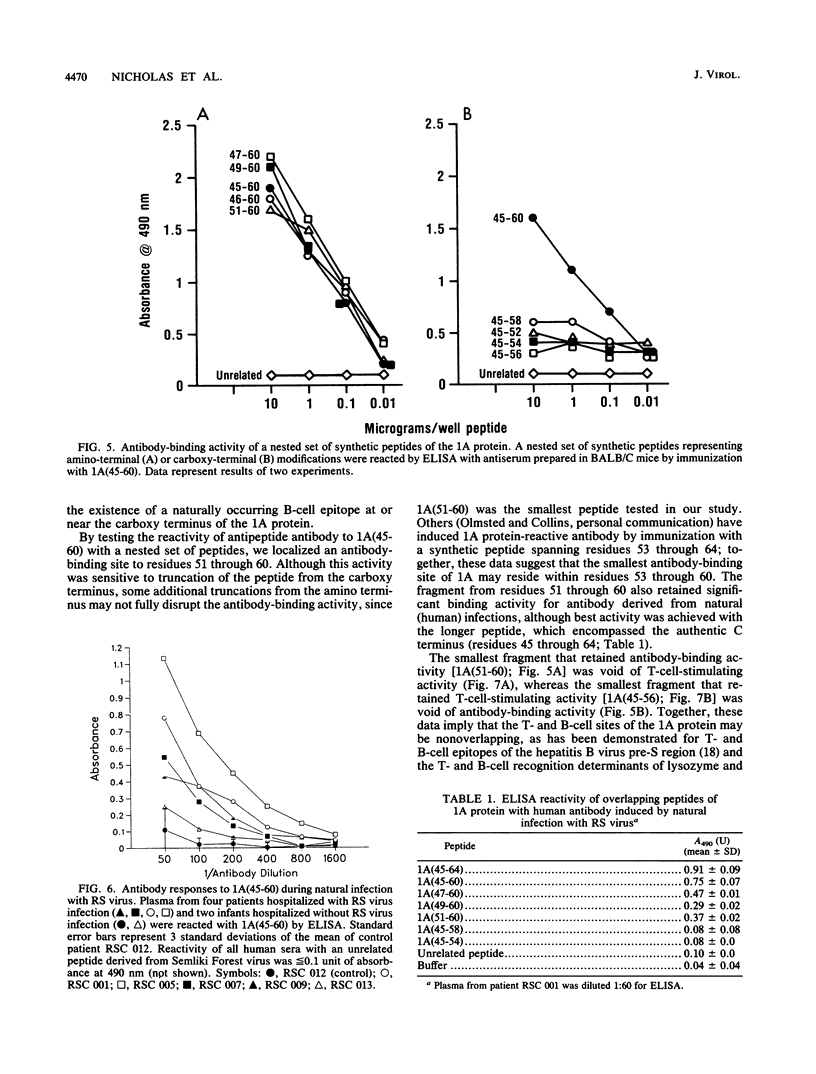
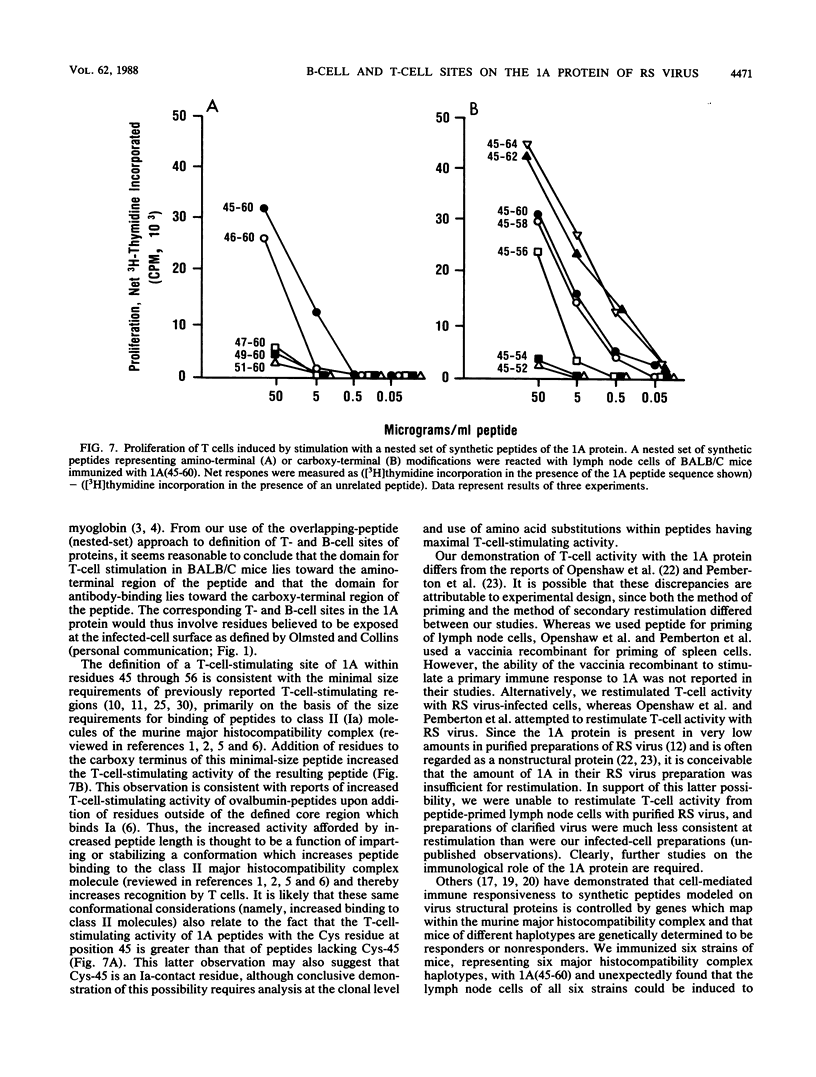
A synthetic peptide modeled on residues 45 to 60 of the 1A protein of respiratory syncytial (RS) virus [1A(45-60)] was constructed and used for immunization of mice and rabbits. The immunoglobulin G fraction of the resulting rabbit antibody, purified on protein A-Sepharose, immunoprecipitated from RS-infected HEp-2 cells a protein with a molecular size of approximately 9.5 kilodaltons, which corresponds to the previously published molecular size of the 1A protein (Y. T. Huang, P. L. Collins, and G. W. Wertz, Virus Res. 2:157-173, 1985). To investigate the T-cell-inducing properties of 1A(45-60), six strains of mice were immunized and their popliteal lymph node cells were tested for proliferation upon restimulation with peptide in vitro. The lymph node cells of all six strains of mice were responsive to restimulation with 1A(45-60) and showed high- and low-responder strain variation. These peptide-primed lymph node cells also proliferated upon in vitro restimulation with RS virus-infected cells. Correlation of proliferation with interleukin 2 production suggested that the responding lymphocytes were T-helper cells. The antibody-binding and T-cell-stimulating sites of 1A were mapped by constructing a series of overlapping synthetic peptides and testing each for ability to react with antiserum prepared by immunization of BALB/C mice with free peptide 1A(45-60) or for ability to restimulate proliferation in 1A(45-60)-primed lymph node cells of BALB/C mice. Human antibody, obtained during confirmed RS virus infection, was similarly tested with the truncated peptides. Antibody-binding activity was reduced after truncation from the carboxy terminus, and a binding site was mapped to residues 51 through 60, the smallest peptide tested. T-cell-stimulating activity in mice was relatively resistant to truncation from the carboxy terminus and sensitive to truncation from the amino terminus. The smallest region which retained significant T-cell-stimulating activity mapped to residues 46 through 56. However, addition of the naturally occurring Cys at residue 45 and extension of the C terminus to residue 62 resulted in maximum T-cell-stimulating activity of the peptide. These data define both a T-cell epitope and a B-cell epitope of the 1A protein of RS virus and suggest that the carboxy terminus of 1A contains a B-cell epitope, involving residues 51 through 60, which is recognized during natural human infection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. M., Babbitt B. P., Unanue E. R. T-cell recognition of lysozyme: the biochemical basis of presentation. Immunol Rev. 1987 Aug;98:171–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzofsky J. A., Cease K. B., Cornette J. L., Spouge J. L., Margalit H., Berkower I. J., Good M. F., Miller L. H., DeLisi C. Protein antigenic structures recognized by T cells: potential applications to vaccine design. Immunol Rev. 1987 Aug;98:9–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzofsky J. A., Richman L. K., Killion D. J. Distinct H-2-linked Ir genes control both antibody and T cell responses to different determinants on the same antigen, myoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4046–4050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixler G. S., Jr, Atassi M. Z. Molecular localization of the full profile of the continuous regions recognized by myoglobin-primed T-cells using synthetic overlapping peptides encompassing the entire molecule. Immunol Commun. 1983;12(6):593–603. doi: 10.3109/08820138309025440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braciale T. J., Morrison L. A., Sweetser M. T., Sambrook J., Gething M. J., Braciale V. L. Antigen presentation pathways to class I and class II MHC-restricted T lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1987 Aug;98:95–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Grey H. M. The interaction between protein-derived immunogenic peptides and Ia. Immunol Rev. 1987 Aug;98:115–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. The 1A protein gene of human respiratory syncytial virus: nucleotide sequence of the mRNA and a related polycistronic transcript. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. cDNA cloning and transcriptional mapping of nine polyadenylylated RNAs encoded by the genome of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3208–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFreitas E. C., Chesnut R. W., Grey H. M., Chiller J. M. Macrophage-dependent activation of antigen-specific T cells requires antigen and a soluble monokine. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):23–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFreitas E. C., Dietzschold B., Koprowski H. Human T-lymphocyte response in vitro to synthetic peptides of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3425–3429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett C. J., Dietzschold B., Gerhard W., Ghrist B., Knorr R., Gillessen D., Melchers F. Influenza virus site recognized by a murine helper T cell specific for H1 strains. Localization to a nine amino acid sequence in the hemagglutinin molecule. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):294–302. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. T., Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. Characterization of the 10 proteins of human respiratory syncytial virus: identification of a fourth envelope-associated protein. Virus Res. 1985 Mar;2(2):157–173. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90246-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. T., Wertz G. W. Respiratory syncytial virus mRNA coding assignments. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):667–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.667-672.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Jr, Olmsted R. A., Prince G. A., Murphy B. R., Alling D. W., Walsh E. E., Collins P. L. Antigenic relatedness between glycoproteins of human respiratory syncytial virus subgroups A and B: evaluation of the contributions of F and G glycoproteins to immunity. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3163–3166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3163-3166.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Louie R. E., Chisari F. V. Genetic regulation of the immune response to hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). V. T cell proliferative response and cellular interactions. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4194–4202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., McLachlan A., Chisari F. V., Thornton G. B. Nonoverlapping T and B cell determinants on an hepatitis B surface antigen pre-S(2) region synthetic peptide. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):532–547. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Peterson D. L., Leroux-Roels G. G., Lerner R. A., Chisari F. V. Genetic regulation of the immune response to hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). VI. T cell fine specificity. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4203–4211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Stark D., Sproul P. Genetic restriction of immune responsiveness to synthetic peptides corresponding to sequences in the pre-S region of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) envelope gene. J Med Virol. 1985 Oct;17(2):119–125. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J. A., Levely M. E., Brideau R. J., Berger A. E. During recovery from cytomegalovirus infection T-lymphocyte subsets become selectively responsive to activation and have depressed interleukin 2 (IL2) secretion and IL2 receptor expression. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jan;2(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted R. A., Elango N., Prince G. A., Murphy B. R., Johnson P. R., Moss B., Chanock R. M., Collins P. L. Expression of the F glycoprotein of respiratory syncytial virus by a recombinant vaccinia virus: comparison of the individual contributions of the F and G glycoproteins to host immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7462–7466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Openshaw P. J., Pemberton R. M., Ball L. A., Wertz G. W., Askonas B. A. Helper T cell recognition of respiratory syncytial virus in mice. J Gen Virol. 1988 Feb;69(Pt 2):305–312. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton R. M., Cannon M. J., Openshaw P. J., Ball L. A., Wertz G. W., Askonas B. A. Cytotoxic T cell specificity for respiratory syncytial virus proteins: fusion protein is an important target antigen. J Gen Virol. 1987 Aug;68(Pt 8):2177–2182. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-8-2177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson A. C., Willcocks M. M., Routledge E. G., Morgan L. A., Toms G. L. A neutralizing monoclonal antibody to respiratory syncytial virus which binds to both F1 and F2 components of the fusion protein. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1479–1483. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., Fox B. S., Fraga E., Chen C., Singh B. The T lymphocyte response to cytochrome c. V. Determination of the minimal peptide size required for stimulation of T cell clones and assessment of the contribution of each residue beyond this size to antigenic potency. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2598–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Stott E. J., Bew M., Fernie B. F., Cote P. J., Collins A. P., Hughes M., Jebbett J. Monoclonal antibodies protect against respiratory syncytial virus infection in mice. Immunology. 1984 May;52(1):137–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyeryar F. J. Report of a workshop on respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza viruses. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):588–598. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh E. E., Hall C. B., Briselli M., Brandriss M. W., Schlesinger J. J. Immunization with glycoprotein subunits of respiratory syncytial virus to protect cotton rats against viral infection. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1198–1204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh E. E., Schlesinger J. J., Brandriss M. W. Protection from respiratory syncytial virus infection in cotton rats by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):756–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.756-758.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts T. H., Gariépy J., Schoolnik G. K., McConnell H. M. T-cell activation by peptide antigen: effect of peptide sequence and method of antigen presentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5480–5484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]