Abstract
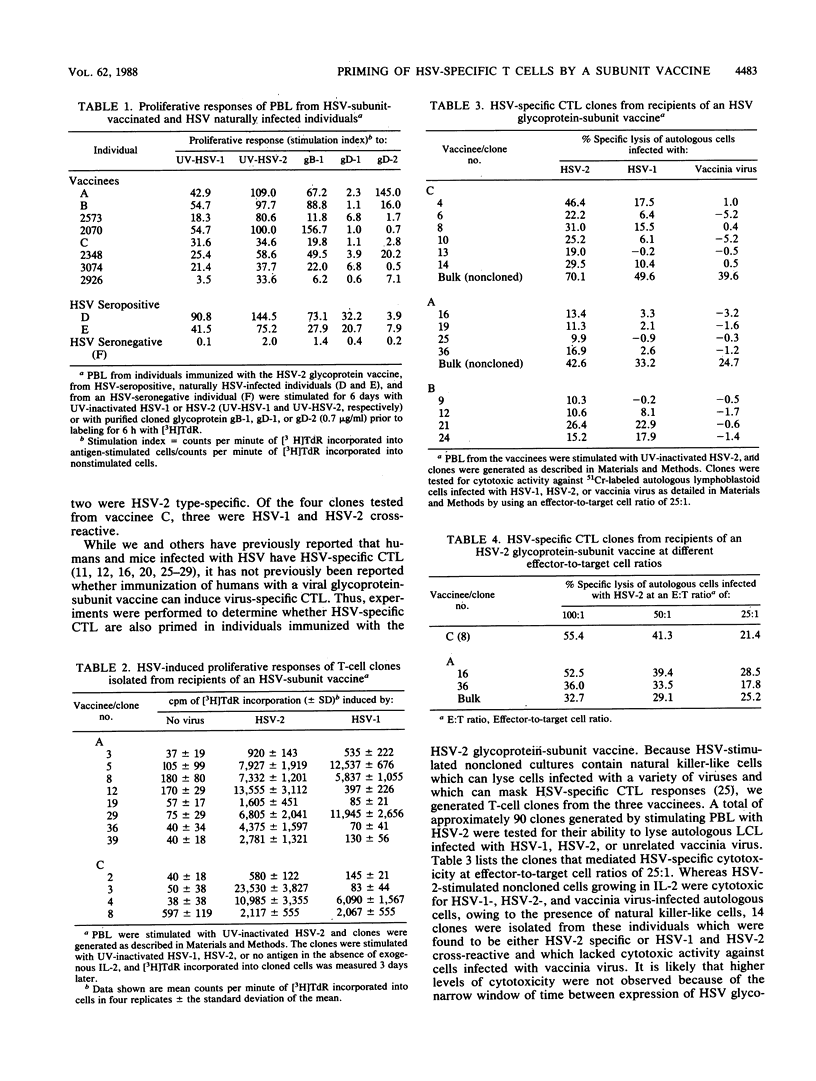
Studies were undertaken to determine whether immunization of humans with a herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) glycoprotein-subunit vaccine would result in the priming of both HSV-specific proliferating cells and cytotoxic T cells. Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) from all eight vaccines studied responded by proliferating after stimulation with HSV-2, HSV-1, and glycoprotein gB-1. The PBL of five of these eight vaccines proliferated following stimulation with gD-2, whereas stimulation with gD-1 resulted in relatively low or no proliferative responses. T-cell clones were generated from HSV-2-stimulated PBL of three vaccinees who demonstrated strong proliferative responses to HSV-1 and HSV-2. Of 12 clones studied in lymphoproliferative assays, 9 were found to be cross-reactive for HSV-1 and HSV-2. Of the approximately 90 T-cell clones isolated, 14 demonstrated HSV-specific cytotoxic activity. Radioimmunoprecipitation-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analyses confirmed that the vaccinees had antibodies only to HSV glycoproteins, not to proteins which are absent in the subunit vaccine, indicating that these vaccinees had not become infected with HSV. Immunization of humans with an HSV-2 glycoprotein-subunit vaccine thus results in the priming of T cells that proliferate in response to stimulation with HSV and its glycoproteins and T cells that have cytotoxic activity against HSV-infected cells. Such HSV-specific memory T cells were detected as late as 2 years following the last boost with the subunit vaccine.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ada G. L., Leung K. N., Ertl H. An analysis of effector T cell generation and function in mice exposed to influenza A or Sendai viruses. Immunol Rev. 1981;58:5–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley R., Benedetti J., Corey L. Humoral immune response to HSV-1 and HSV-2 viral proteins in patients with primary genital herpes. J Med Virol. 1985 Oct;17(2):153–166. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley R., Mertz G. J., Corey L. Detection of asymptomatic herpes simplex virus infections after vaccination. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):264–268. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.264-268.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley R., Mertz G., Clark H., Schick M., Salter D., Corey L. Humoral immune response to herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoproteins in patients receiving a glycoprotein subunit vaccine. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):475–481. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.475-481.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. W., Gregory T., Crase D., Lasky L. A. Protection from genital herpes simplex virus type 2 infection by vaccination with cloned type 1 glycoprotein D. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1490–1492. doi: 10.1126/science.2983428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braciale T. J., Yap K. L. Role of viral infectivity in the induction of influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1236–1252. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Holmes K. K. Genital herpes simplex virus infections: current concepts in diagnosis, therapy, and prevention. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jun;98(6):973–983. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-6-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer K. J., Mackett M., Wohlenberg C., Notkins A. L., Moss B. Vaccinia virus recombinant expressing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D prevents latent herpes in mice. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):737–740. doi: 10.1126/science.2986288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes E. L., Taylor W., Mitchison N. A., Simpson E. MHC matching shows that at least two T-cell subsets determine resistance to HSV. Nature. 1979 Jan 4;277(5691):66–68. doi: 10.1038/277067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen H. S., Russell R. G., Rouse B. T. Recovery from lethal herpes simplex virus type 1 infection is mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):197–204. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.197-204.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz G. J., Peterman G., Ashley R., Jourden J. L., Salter D., Morrison L., McLean A., Corey L. Herpes simplex virus type-2 glycoprotein-subunit vaccine: tolerance and humoral and cellular responses in humans. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):242–249. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz G. J., Schmidt O., Jourden J. L., Guinan M. E., Remington M. L., Fahnlander A., Winter C., Holmes K. K., Corey L. Frequency of acquisition of first-episode genital infection with herpes simplex virus from symptomatic and asymptomatic source contacts. Sex Transm Dis. 1985 Jan-Mar;12(1):33–39. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198501000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash A. A., Phelan J., Wildy P. Cell-mediated immunity in herpes simplex virus-infected mice: H-2 mapping of the delayed-type hypersensitivity response and the antiviral T cell response. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1260–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachl C., Burke R. L., Stuve L. L., Sanchez-Pescador L., Van Nest G., Masiarz F., Dina D. Expression of cell-associated and secreted forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein gB in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):315–325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.315-325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss C. S., Schulman J. L. Cellular immune responses of mice to influenza virus vaccines. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2182–2188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Norley S., Martin S. Antiviral cytotoxic T lymphocyte induction and vaccination. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):16–33. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Omata Y., Schneweis K. E. Protection of mice from fatal herpes simplex virus type 1 infection by adoptive transfer of cloned virus-specific and H-2-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):443–447. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staerz U. D., Karasuyama H., Garner A. M. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes against a soluble protein. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):449–451. doi: 10.1038/329449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanberry L. R., Bernstein D. I., Burke R. L., Pachl C., Myers M. G. Vaccination with recombinant herpes simplex virus glycoproteins: protection against initial and recurrent genital herpes. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):914–920. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., Askonas B. A. Induction of influenza A virus cross-reactive cytotoxic T cells by a nucleoprotein/haemagglutinin preparation. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jun;66(Pt 6):1327–1331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-6-1327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Zarling J. M. Human cytotoxic T cell clones directed against herpes simplex virus-infected cells. I. Lysis restricted by HLA class II MB and DR antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):422–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Zarling J. M. Human cytotoxic T cell clones directed against herpes simplex virus-infected cells. II. Bifunctional clones with cytotoxic and virus-induced proliferative activities exhibit herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 specific or type common reactivities. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2736–2742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Zarling J. M. Human cytotoxic T cell clones directed against herpes simplex virus-infected cells. III. Analysis of viral glycoproteins recognized by CTL clones by using recombinant herpes simplex viruses. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2679–2682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Moran P. A., Burke R. L., Pachl C., Berman P. W., Lasky L. A. Human cytotoxic T cell clones directed against herpes simplex virus-infected cells. IV. Recognition and activation by cloned glycoproteins gB and gD. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4669–4673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Moran P. A., Lasky L. A., Moss B. Herpes simplex virus (HSV)-specific human T-cell clones recognize HSV glycoprotein D expressed by a recombinant vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):506–509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.506-509.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]