Abstract
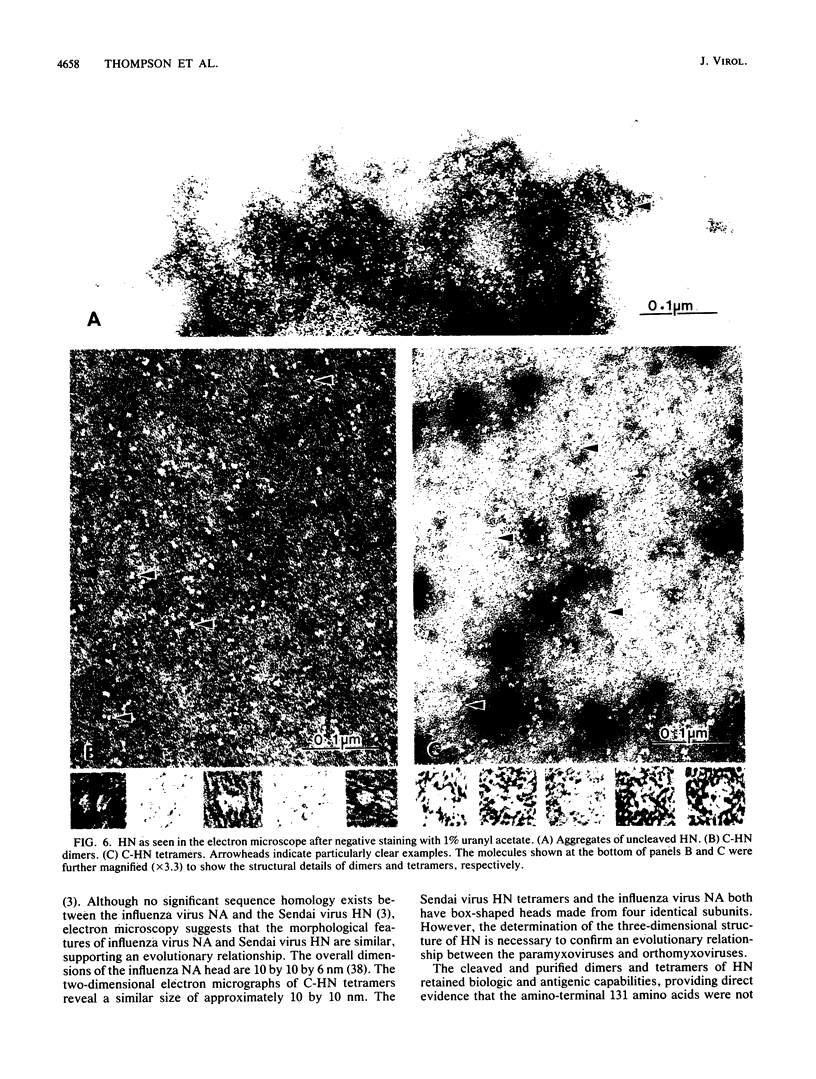
As a first step in establishing the three-dimensional structure of the Sendai virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN), we have isolated and characterized a potentially crystallizable form of the molecule. The sequence of HN, a surface glycoprotein, predicts a protein with an uncharged hydrophobic region near the amino terminus which is responsible for anchorage in the viral envelope. To avoid rosette formation (aggregation), which would preclude crystallization, this hydrophobic tail was removed from a membrane-free form of HN by proteolytic digestion. This digestion resulted in a single product with a molecular weight of about 10,000 less than native HN. N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis of cleaved HN (C-HN) indicated a single cleavage site at amino acid residue 131, resulting in a product consisting of the carboxyl-terminal 444 amino acids of HN. Functional analyses revealed that C-HN retained full neuraminidase activity and was able to bind erythrocytes, indicating that the N-terminal 131 residues were not necessary for these biological activities. Furthermore, this cleavage product retained the antigenic structure of intact HN, since monoclonal antibodies still bound to C-HN in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western (immuno-) blot analysis. Viewed by electron microscopy, the dimeric and tetrameric forms of intact HN form rosettes while C-HN maintains the oligomeric structure but no longer aggregates. Furthermore, the electron micrographs revealed a C-HN tetramer strikingly similar to the influenza virus neuraminidase in both size and gross structural features.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aymard-Henry M., Coleman M. T., Dowdle W. R., Laver W. G., Schild G. C., Webster R. G. Influenzavirus neuraminidase and neuraminidase-inhibition test procedures. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;48(2):199–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok J., Air G. M., Laver W. G., Ward C. W., Lilley G. G., Woods E. F., Roxburgh C. M., Inglis A. S. Studies on the size, chemical composition, and partial sequence of the neuraminidase (NA) from type A influenza viruses show that the N-terminal region of the NA is not processed and serves to anchor the NA in the viral membrane. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Giorgi C., Rose K., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the Sendai virus fusion protein gene. J Gen Virol. 1985 Feb;66(Pt 2):317–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-2-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B., Giorgi C., Roux L., Raju R., Dowling P., Chollet A., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the Sendai virus HN gene and its comparison to the influenza virus glycoproteins. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand C. M., Skehel J. J. Crystalline antigen from the influenza virus envelope. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 2;238(83):145–147. doi: 10.1038/newbio238145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M., Laver W. G., Varghese J. N., Baker A. T., Tulloch P. A., Air G. M., Webster R. G. Three-dimensional structure of a complex of antibody with influenza virus neuraminidase. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):358–363. doi: 10.1038/326358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., White J. M., Waterfield M. D. Purification of the fusion protein of Sendai virus: analysis of the NH2-terminal sequence generated during precursor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2737–2740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Ouchi M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. 3. Structural difference of Sendai viruses grown in eggs and tissue culture cells. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1457–1465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1457-1465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iorio R. M., Bratt M. A. Monoclonal antibodies as functional probes of the HN glycoprotein of Newcastle disease virus: antigenic separation of the hemagglutinating and neuraminidase sites. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2215–2219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen E. D., Collins P. L., Lomedico P. T. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of Newcastle disease virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase mRNA: identification of a putative sialic acid binding site. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):12–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90431-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Protein-protein interactions within paramyxoviruses identified by native disulfide bonding or reversible chemical cross-linking. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):152–166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.152-166.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura N., Nakatani Y., Ishiura M., Uchida T., Okada Y. Molecular cloning of a full-length cDNA encoding the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein of Sendai virus. FEBS Lett. 1985 Aug 19;188(1):112–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80885-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura N., Uchida T., Okada Y. HVJ (Sendai virus)-induced envelope fusion and cell fusion are blocked by monoclonal anti-HN protein antibody that does not inhibit hemagglutination activity of HVJ. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Oct;141(2):409–420. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Proteolytic cleavage of the viral glycoproteins and its significance for the virulence of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):494–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Isomura S., Suzuki S., Watanabe E., Hamaguchi M., Yoshida T., Nagai Y. Monoclonal antibodies to the HN glycoprotein of Newcastle disease virus. Biological characterization and use for strain comparisons. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):318–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvell C., Grandien M. The effects of monoclonal antibodies on biologic activities of structural proteins of Sendai virus. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2779–2787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Regulatory events in the synthesis of Sendai virus polypeptides and their assembly into virions. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A., Marx P. A., Kingsbury D. W. Isolation and characterization of Sendai virus temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):298–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.298-304.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A., Scroggs R. A., Marx P. S., Kingsbury D. W. A temperature-sensitive mutant of Sendai virus with an altered hemagglutinin-neuraminidase polypeptide: consequences for virus assembly and cytopathology. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90415-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A., Scroggs R. A., Metzger D. W. Distinct functions of antigenic sites of the HN glycoprotein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A., Webster R. G., Bean W. J. Similar frequencies of antigenic variants in Sendai, vesicular stomatitis, and influenza A viruses. Virology. 1980 Jul 15;104(1):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray R., Compans R. W. Monoclonal antibodies reveal extensive antigenic differences between the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoproteins of human and bovine parainfluenza 3 viruses. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90420-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Caliguiri L. A., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Isolation of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Association of both hemagglutinating and neuraminidase activities with the larger SV5 glycoprotein. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):640–652. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Isolation and purification of the envelope proteins of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):263–271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.263-271.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Two disulfide-linked polypeptide chains constitute the active F protein of paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):54–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90380-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Kremer M. J., Luo M., Vriend G., Arnold E., Kamer G., Rossmann M. G., McKinlay M. A., Diana G. D., Otto M. J. The site of attachment in human rhinovirus 14 for antiviral agents that inhibit uncoating. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1286–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.3018924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. D., Portner A. Localization of functional sites on the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein of Sendai virus by sequence analysis of antigenic and temperature-sensitive mutants. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozawa H., Watanabe M., Ishida N. Structural components of Sendai virus. Serological and physicochemical characterization of hemagglutinin subunit associated with neuraminidase activity. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):242–253. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulloch P. A., Colman P. M., Davis P. C., Laver W. G., Webster R. G., Air G. M. Electron and X-ray diffraction studies of influenza neuraminidase complexed with monoclonal antibodies. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese J. N., Laver W. G., Colman P. M. Structure of the influenza virus glycoprotein antigen neuraminidase at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):35–40. doi: 10.1038/303035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Caton A. J., Gerhard W. Selection of influenza A virus adsorptive mutants by growth in the presence of a mixture of monoclonal antihemagglutinin antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):623–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.623-628.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J., Absolom D. R. Zeta potentials, van der Waals forces and hemagglutination. Vox Sang. 1983 Mar;44(3):183–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb01883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







