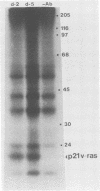
Abstract
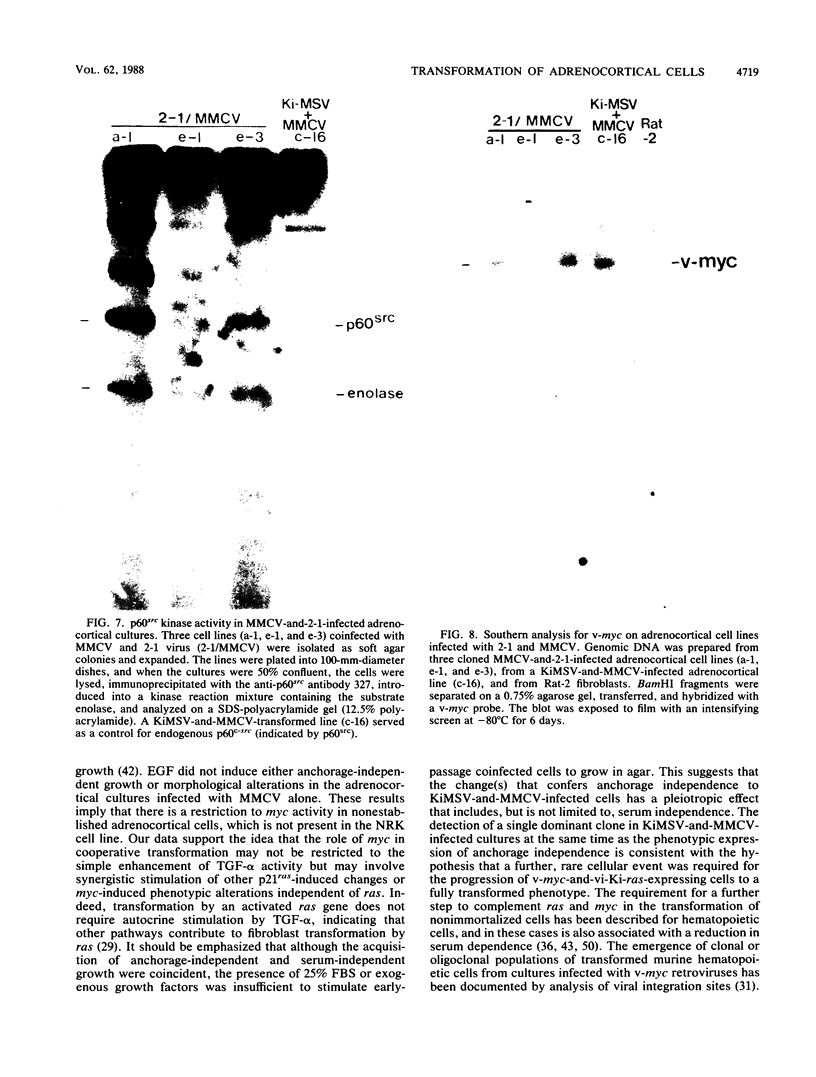
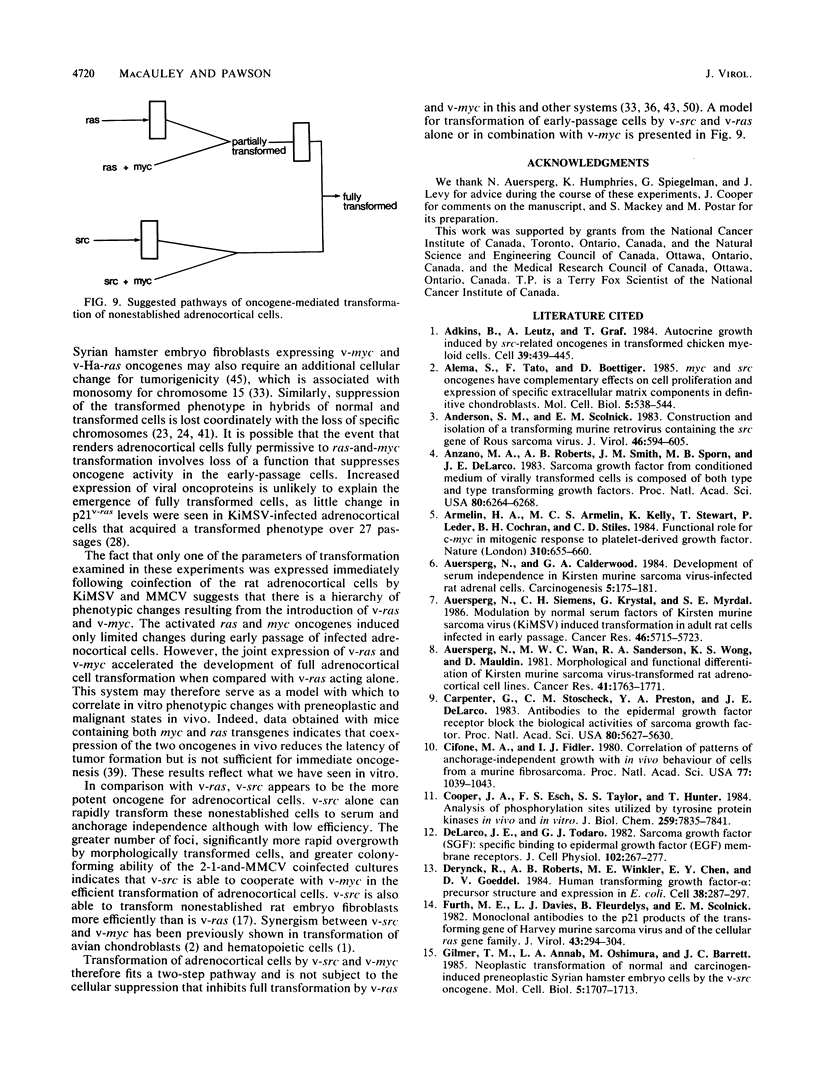
Early-passage rat adrenocortical cells were infected with Kirsten murine sarcoma virus and MMCV mouse myc virus, two retroviruses carrying the v-Ki-ras and v-myc oncogenes, respectively. Efficient morphological transformation required coinfection with the two viruses, was dependent on the presence of high serum concentrations, and was not immediately accompanied by growth in soft agar. The doubly infected cells coordinately acquired the capacity for anchorage- and serum-independent growth during passage in culture. The appearance of such highly transformed cells was correlated with the emergence of a dominant clone, as suggested by an analysis of retrovirus integration sites. These results indicate that the concerted expression of v-Ki-ras and v-myc could induce rapid morphological transformation of nonestablished adrenocortical cells but that an additional genetic or epigenetic event was required to permit full transformation by these two oncogenes. In contrast, v-src, introduced by retrovirus infection in conjunction with v-myc, rapidly induced serum- and anchorage-independent growth. Therefore, the p60v-src protein-tyrosine kinase, unlike p21v-ras, is apparently not restricted in the induction of a highly transformed phenotype in adrenocortical cells. This system provides an in vitro model for the progressive transformation of epithelial cells by dominantly acting oncogenes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adkins B., Leutz A., Graf T. Autocrine growth induced by src-related oncogenes in transformed chicken myeloid cells. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alema S., Tato F., Boettiger D. myc and src oncogenes have complementary effects on cell proliferation and expression of specific extracellular matrix components in definitive chondroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):538–544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. M., Scolnick E. M. Construction and isolation of a transforming murine retrovirus containing the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):594–605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.594-605.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anzano M. A., Roberts A. B., Smith J. M., Sporn M. B., De Larco J. E. Sarcoma growth factor from conditioned medium of virally transformed cells is composed of both type alpha and type beta transforming growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6264–6268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armelin H. A., Armelin M. C., Kelly K., Stewart T., Leder P., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D. Functional role for c-myc in mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):655–660. doi: 10.1038/310655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auersperg N., Calderwood G. A. Development of serum independence in Kirsten murine sarcoma virus-infected rat adrenal cells. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Feb;5(2):175–181. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.2.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auersperg N., Siemens C. H., Krystal G., Myrdal S. E. Modulation by normal serum factors of Kirsten murine sarcoma virus-induced transformation in adult rat cells infected in early passage. Cancer Res. 1986 Nov;46(11):5715–5723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auersperg N., Wan M. W., Sanderson R. A., Wong K. S., Mauldin D. Morphological and functional differentiation of Kirsten murine sarcoma virus-transformed rat adrenocortical cell lines. Cancer Res. 1981 May;41(5):1763–1771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Stoscheck C. M., Preston Y. A., DeLarco J. E. Antibodies to the epidermal growth factor receptor block the biological activities of sarcoma growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5627–5630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cifone M. A., Fidler I. J. Correlation of patterns of anchorage-independent growth with in vivo behavior of cells from a murine fibrosarcoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1039–1043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Esch F. S., Taylor S. S., Hunter T. Phosphorylation sites in enolase and lactate dehydrogenase utilized by tyrosine protein kinases in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7835–7841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Sarcoma growth factor (SGF): specific binding to epidermal growth factor (EGF) membrane receptors. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Feb;102(2):267–277. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041020218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Roberts A. B., Winkler M. E., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-alpha: precursor structure and expression in E. coli. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90550-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmer T. M., Annab L. A., Oshimura M., Barrett J. C. Neoplastic transformation of normal and carcinogen-induced preneoplastic Syrian hamster embryo cells by the v-src oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1707–1713. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Naturally occurring murine leukemia viruses in wild mice: characterization of a new "amphotropic" class. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):19–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.19-25.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelle B., Liu E., Bishop J. M. Oncogene v-src transforms and establishes embryonic rodent fibroblasts but not diploid human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4355–4359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn P., Shin S. I. Cellular tumorigenicity in nude mice. Test of associations among loss of cell-surface fibronectin, anchorage independence, and tumor-forming ability. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jul;82(1):1–16. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. L., Anderson M., Ozanne B. Transforming growth factor(s) production enables cells to grow in the absence of serum: an autocrine system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. L., Ozanne B. Cellular responsiveness to growth factors correlates with a cell's ability to express the transformed phenotype. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):931–938. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keath E. J., Caimi P. G., Cole M. D. Fibroblast lines expressing activated c-myc oncogenes are tumorigenic in nude mice and syngeneic animals. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger H. P. Suppression of tumorigenicity in somatic cell hybrids. I. Suppression and reexpression of tumorigenicity in diploid human X D98AH2 hybrids and independent segregation of tumorigenicity from other cell phenotypes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(4):254–266. doi: 10.1159/000131494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger H. P. Suppression of tumorigenicity. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1982;32(1-4):68–84. doi: 10.1159/000131688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Chen A. C., Morgenstern J. P., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Behavior of myc and ras oncogenes in transformation of rat embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1917–1925. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacAuley A., Auersperg N., Pawson T. Expression of viral p21ras during acquisition of a transformed phenotype by rat adrenal cortex cells infected with Kirsten murine sarcoma virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):342–346. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Todaro G. J. Rat transforming growth factor type 1: structure and relation to epidermal growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 9;223(4640):1079–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6320373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay I. A., Malone P., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Malignant transformation of murine fibroblasts by a human c-Ha-ras-1 oncogene does not require a functional epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3382–3387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Hartley J. W., Fredrickson T. N., Yetter R. A., Majumdar C., Cleveland J. L., Rapp U. R. Recombinant murine retroviruses containing avian v-myc induce a wide spectrum of neoplasms in newborn mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6868–6872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. J., Cunningham J. M., Parada L. F., Dautry F., Lebowitz P., Weinberg R. A. The HL-60 transforming sequence: a ras oncogene coexisting with altered myc genes in hematopoietic tumors. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):749–757. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshimura M., Gilmer T. M., Barrett J. C. Nonrandom loss of chromosome 15 in Syrian hamster tumours induced by v-Ha-ras plus v-myc oncogenes. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):636–639. doi: 10.1038/316636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Fulton R. J., Kaplan P. L. Kirsten murine sarcoma virus transformed cell lines and a spontaneously transformed rat cell-line produce transforming factors. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Oct;105(1):163–180. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. C., Stanton L. W., Riley S. C., Marcu K. B., Witte O. N. Synergism of v-myc and v-Ha-ras in the in vitro neoplastic progression of murine lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3221–3231. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Papageorge A. G., Stokes P. E., Weeks M. O., Scolnick E. M. Guanine nucleotide-binding and autophosphorylating activities associated with the p21src protein of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):686–691. doi: 10.1038/287686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Stokes P. E., Smythers G. W., Dhar R., Oroszlan S. Characterization of the phosphorylation sites and the surrounding amino acid sequences of the p21 transforming proteins coded for by the Harvey and Kirsten strains of murine sarcoma viruses. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11767–11773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinn E., Muller W., Pattengale P., Tepler I., Wallace R., Leder P. Coexpression of MMTV/v-Ha-ras and MMTV/c-myc genes in transgenic mice: synergistic action of oncogenes in vivo. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavinski E. A., Auersperg N., Jull J. W. Propagation in vitro of functional rat adrenal cortical cells: modifications of the differentiated state by culture conditions. In Vitro. 1974 Jan-Feb;9(4):260–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J., Der C. J., Doersen C. J., Nishimi R. Y., Peehl D. M., Weissman B. E., Wilkinson J. E. Human cell hybrids: analysis of transformation and tumorigenicity. Science. 1982 Jan 15;215(4530):252–259. doi: 10.1126/science.7053574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Roberts A. B., Roche N. S., Sporn M. B., Weinberg R. A. Differential responsiveness of myc- and ras-transfected cells to growth factors: selective stimulation of myc-transfected cells by epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):870–877. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Volsky D. J. Activated v-myc and v-ras oncogenes do not transform normal human lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3410–3417. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taya Y., Hosogai K., Hirohashi S., Shimosato Y., Tsuchiya R., Tsuchida N., Fushimi M., Sekiya T., Nishimura S. A novel combination of K-ras and myc amplification accompanied by point mutational activation of K-ras in a human lung cancer. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2943–2946. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen D. G., Gilmer T. M., Annab L. A., Barrett J. C. Evidence for multiple steps in neoplastic transformation of normal and preneoplastic Syrian hamster embryo cells following transfection with Harvey murine sarcoma virus oncogene (v-Ha-ras). Cancer Res. 1985 Feb;45(2):726–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Fryling C., De Larco J. E. Transforming growth factors produced by certain human tumor cells: polypeptides that interact with epidermal growth factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5258–5262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W. C. Normal rat cell lines deficient in nuclear thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Kahn P., Adkins B., Enrietto P., Hayman M. J., Graf T., Luciw P. Transformation of mammalian fibroblasts and macrophages in vitro by a murine retrovirus encoding an avian v-myc oncogene. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3223–3229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Moscovici C., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning of the avian myelocytomatosis virus genome and recovery of infectious virus by transfection of chicken cells. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):625–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.625-631.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt M., Lesley J., Bogenberger J., Volkman S., Haas M. Coinfection with viruses carrying the v-Ha-ras and v-myc oncogenes leads to growth factor independence by an indirect mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3545–3549. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]