Abstract
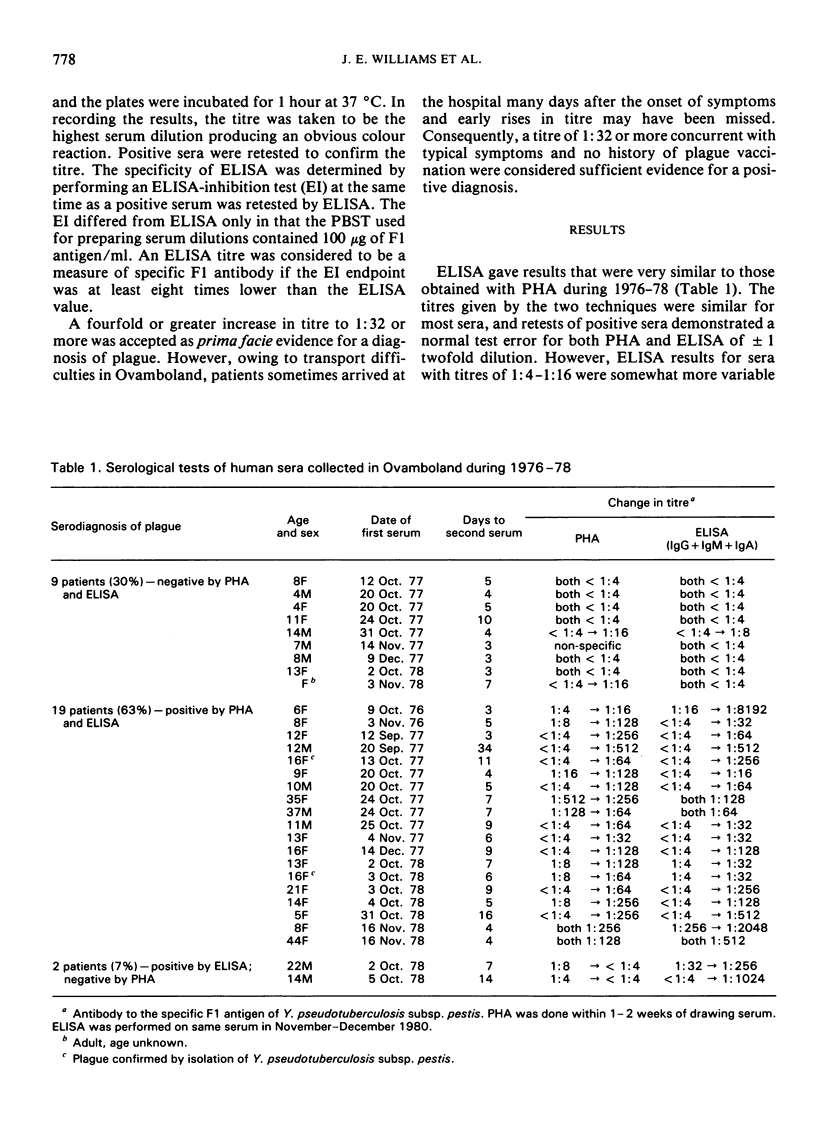
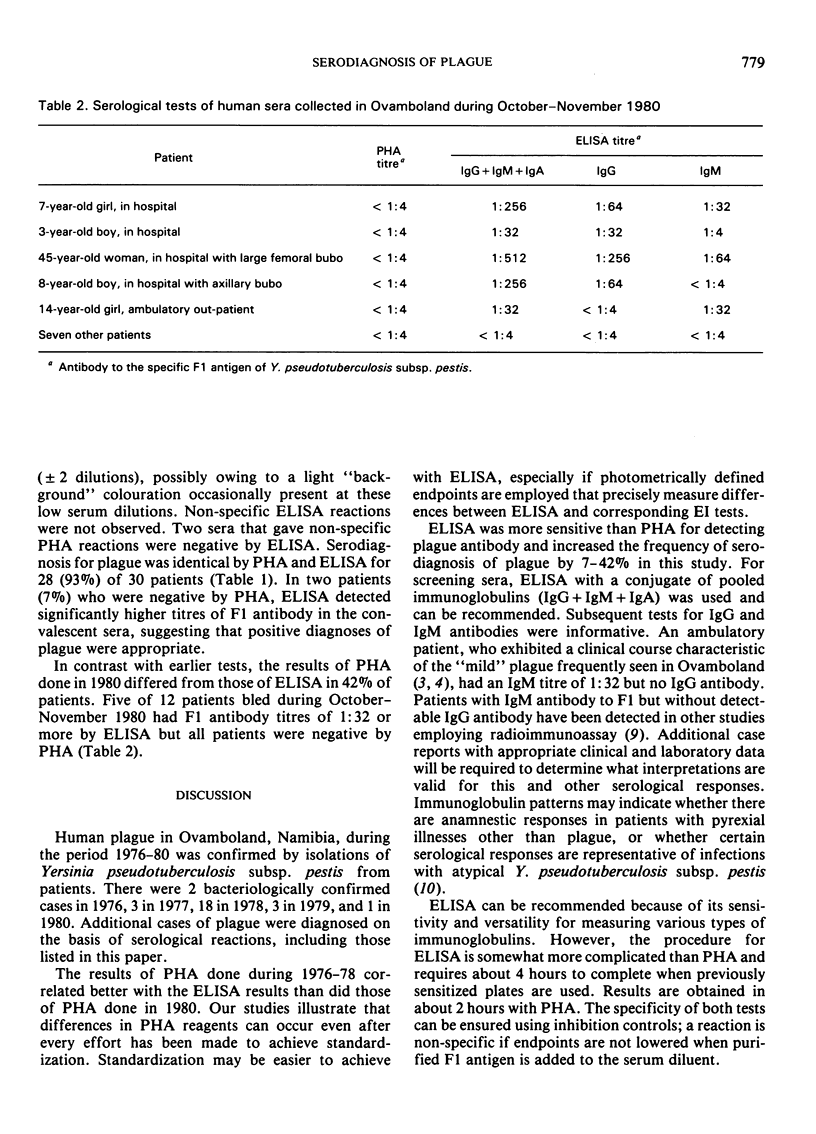
Sera of 42 suspect plague cases from Ovamboland, Namibia, were examined. ELISA proved more sensitive than passive haemagglutination for the detection of F1 antibody and increased positive serodiagnoses of plague by 7-42%.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cavanaugh D. C., Fortier M. K., Robinson D. M., Williams J. E., Rust J. H., Jr Application of the ELISA technique to problems in the serologic diagnosis of plague. Bull Pan Am Health Organ. 1979;13(4):399–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson B. W., Wolff K., Butler T. The use of solid-phase radioimmunoassay techniques for serodiagnosis of human plague infection. Bull Pan Am Health Organ. 1980;14(3):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaäcson M., Hallett A. F. Serological studies on human plague in Southern Africa. Part I. Plague antibody levels in a population during a quiescent and a subsequent active period in an endemic region. S Afr Med J. 1975 Jul 12;49(29):1165–1168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaäcson M., Levy D., Pienaar B. J., Bubb H. D., Louw J. A., Genis G. K. Unusual cases of human plague in Southern Africa. S Afr Med J. 1973 Nov 10;47(44):2109–2113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willeberg P. W., Ruppanner R., Behymer D. E., Higa H. H., Franti C. E., Thompson R. A., Bohannan B. Epidemiologic survey of sylvatic plague by serotesting coyote sentinels with enzyme immunoassay. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Sep;110(3):328–334. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



