Abstract
A survey of the virological and epidemiological features of acute respiratory diseases in children admitted to hospital in Naples has been carried out; the results of three years of research are reported.
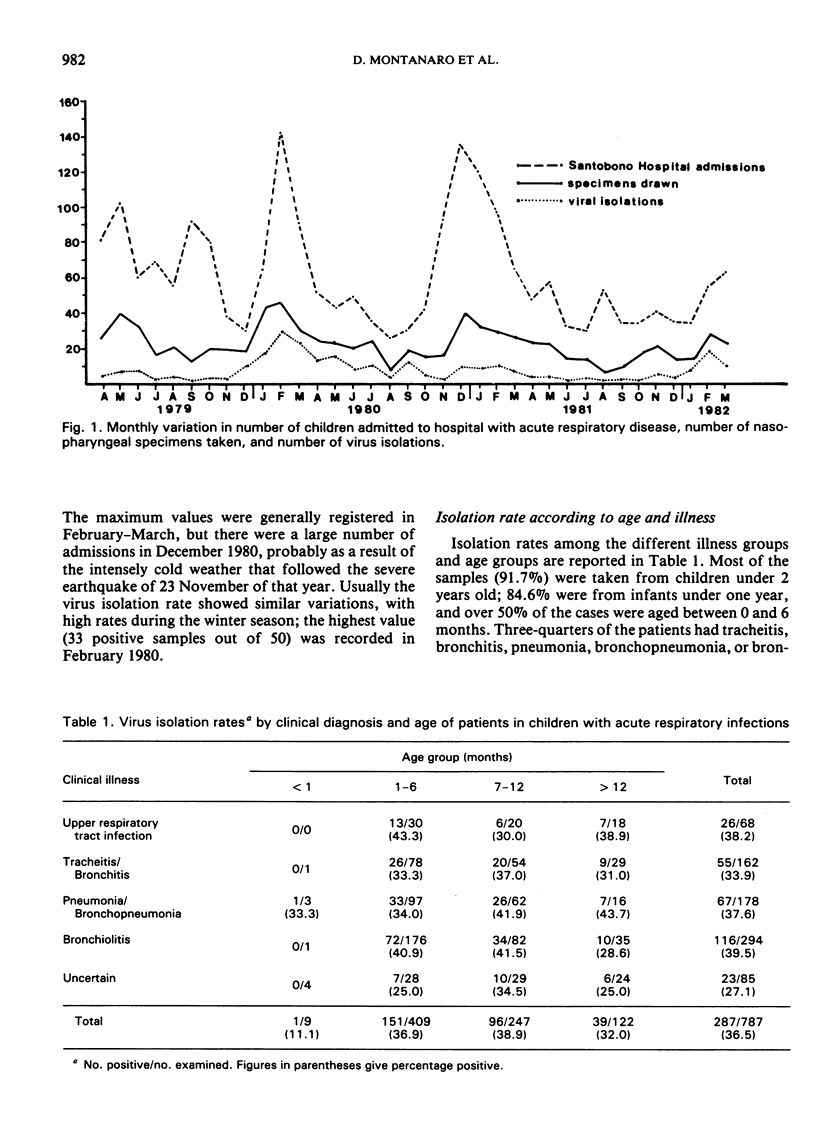
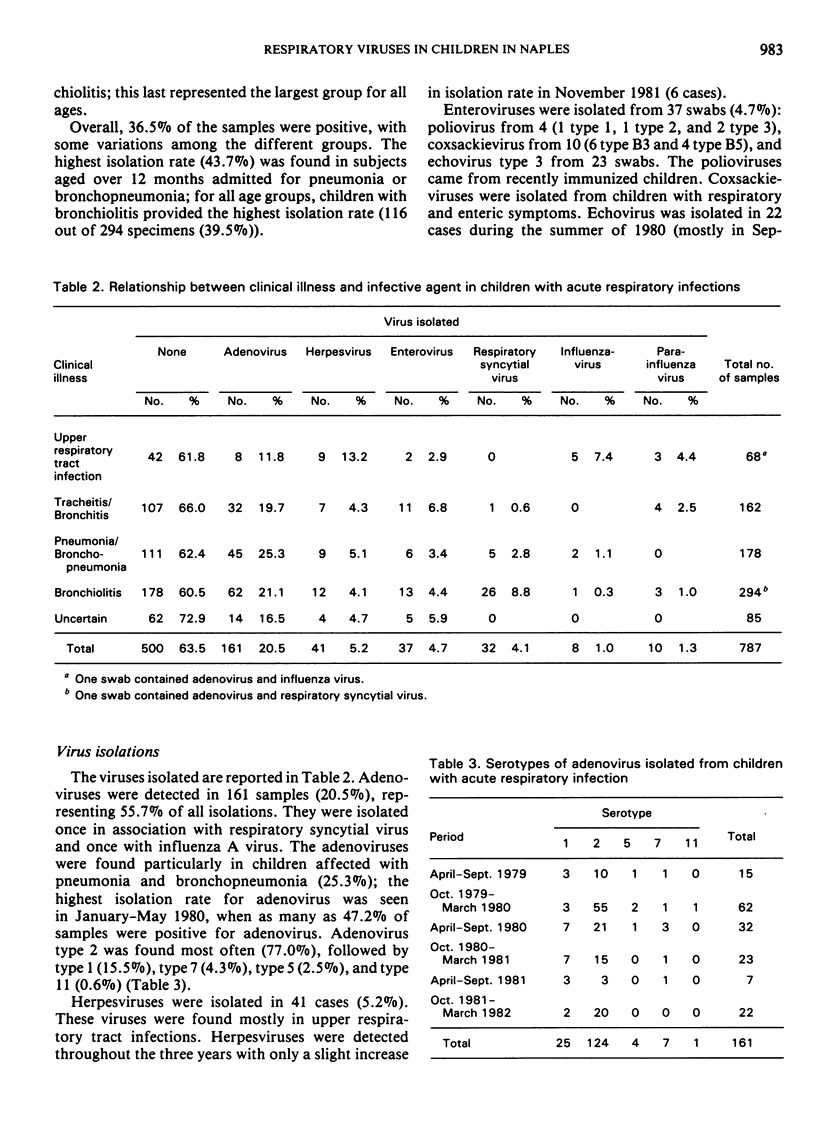
Between April 1979 and March 1982, 787 nasopharyngeal swabs were examined. There were 287 (36.5%) positive samples, with the highest isolation rate being found in children with bronchiolitis (39.5%).
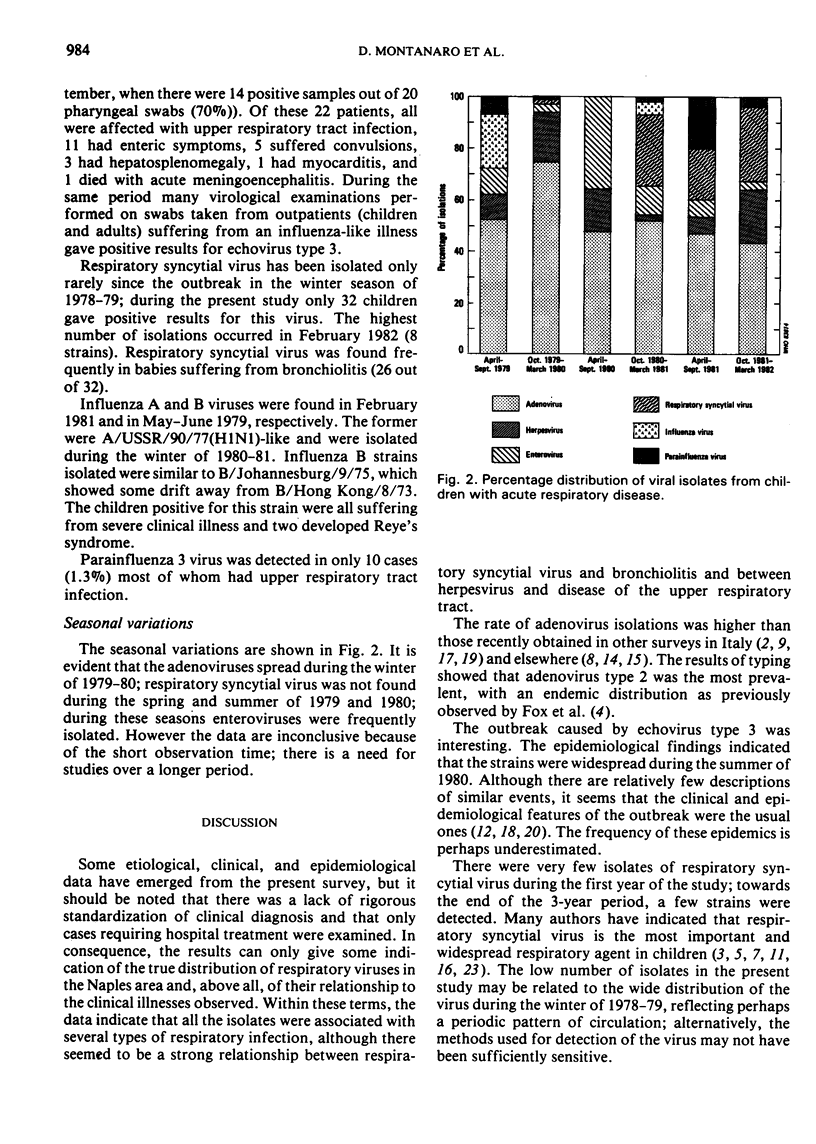
Among the different viruses isolated, adenovirus was the most common (161 positive samples, 56%); this agent appeared regularly in the different age and disease groups, with a marked increase in prevalence during the winter of 1980. Isolations of herpesvirus, respiratory syncytial virus and enterovirus were less frequent; however, echovirus 3 caused an epidemic in the summer of 1980. Influenza and parainfluenza viruses were seen fairly infrequently; two cases of Reye's syndrome yielded strains of influenza B.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Downham M. A., Gardner P. S., McQuillin J., Ferris J. A. Role of respiratory viruses in childhood mortality. Br Med J. 1975 Feb 1;1(5952):235–239. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5952.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin N., Keeling J. W., Tomlinson A. H. Reye's syndrome associated with respiratory syncytial virus infection. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Jan;54(1):74–76. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. B., Kopelman A. E., Douglas R. G., Jr, Geiman J. M., Meagher M. P. Neonatal respiratory syncytial virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1979 Feb 22;300(8):393–396. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197902223000803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. B. Viruses associated with acute respiratory infections 1961-71. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Jun;72(3):425–432. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips C. A., Aronson M. D., Tomkow J., Phillips M. E. Enteroviruses in Vermont, 1969-1978: an important cause of illness throughout the year. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):162–164. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims D. G. A two year prospective study of hospital-acquired respiratory virus infection on paediatric wards. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Jun;86(3):335–342. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims D. G., Downham M. A., Gardner P. S., Webb J. K., Weightman D. Study of 8-year-old children with a history of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infancy. Br Med J. 1978 Jan 7;1(6104):11–14. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6104.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindoni L., Farina W., Picerno I., Loggini F. Sulla diffusione di adenovirus nell'italia meridionale in bambini dell'eta' scolare. Ann Sclavo. 1978 May-Jun;20(3):239–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagni G., Mancini G., Pauluzzi S., Archetti I. Indagine su un episodio epidemico di meningite sierosa da ECHO 30. Boll Ist Sieroter Milan. 1977 Nov 30;56(5):418–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi M. L., Sansebastiano G., Cavàlieri S., Bracchi U., Landucci Rubini L., Casa F., Benaglia G., Montanarini G. Le sindromi respiratorie acute da virus in un reparto pediatrico. Studi clinico-epidemiologici su una casistica raccolta nel periodo febbraio-maggio 1979. Ann Sclavo. 1981 Jan-Feb;23(1):64–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenner H. A., Abel D., Olson L. C., Burry V. F. A mixed epidemic associated with echovirus types 6 and 11: virologic, clinical and epidemiologic studies. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Sep;114(3):369–378. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


