Abstract
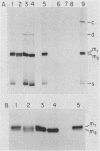
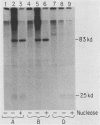
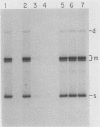
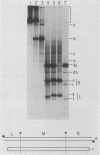
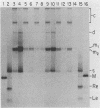
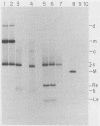
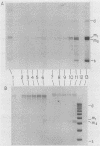
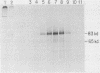
When A9 cells are infected with minute virus of mice, a small proportion of the virally coded NS-1 polypeptide becomes covalently attached to newly synthesized viral DNA. Antisera directed against NS-1 will specifically precipitate two forms of monomer duplex replicative-form DNA, multimeric duplex intermediates and progeny single strands, and restriction analysis of the duplex forms in these precipitates reveals that NS-1 is exclusively associated with extended-form conformers of the genomic termini. Pulse-labeled viral DNA, harvested at various times in a highly synchronized infection, can be almost quantitatively precipitated with any one of a series of antisera directed against different protein domains distributed throughout the NS-1 molecule but not with antibodies directed against other viral proteins. In each case the interaction with NS-1 can be shown to involve both termini of duplex DNA and single-strand forms, suggesting that in each case a full-length (83-kilodalton) copy of NS-1 is present. Precipitation of the replicating viral DNA with an antibody directed against a synthetic 16-amino-acid peptide containing the sequence at the extreme carboxy terminus of NS-1 can be quantitatively and specifically inhibited with the immunizing peptide in its unconjugated form, showing that the antibodies responsible for precipitating viral DNA are directed against the NS-1 sequence itself and not against a trace contaminant. Exonuclease digestion studies show that the association effectively blocks the 5' ends of the DNA molecules. Very little (less than 0.1%) of the newly synthesized [35S]methionine-labeled NS-1 made in highly synchronized cells during a 15-min pulse early in infection (6.25 to 6.5 h into the S phase) becomes associated with viral DNA immediately. However, pulse-chase experiments show that later in infection (10 to 13 h into the S phase), when viral DNA replication is reaching its peak, a few percent of the molecules in these preexisting pools of NS-1 do become covalently attached to the newly replicated DNA. Isolated viral DNA-protein complexes labeled with [35S]methionine in this way can be obtained by fractionation of the immunoprecipitated complexes on Sepharose CL4B in sodium dodecyl sulfate. Digestion of the purified complexes with nuclease releases an 83-kilodalton molecule which exactly comigrates with authentic NS-1 in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astell C. R., Chow M. B., Ward D. C. Sequence analysis of the termini of virion and replicative forms of minute virus of mice DNA suggests a modified rolling hairpin model for autonomous parvovirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):171–177. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.171-177.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Thomson M., Chow M. B., Ward D. C. Structure and replication of minute virus of mice DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):751–762. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Thomson M., Merchlinsky M., Ward D. C. The complete DNA sequence of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):999–1018. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon G. J., Tattersall P. J., Ward D. C. DNA of minute virus of mice: self-priming, nonpermuted, single-stranded genome with a 5'-terminal hairpin duplex. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):290–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.290-306.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Desiderio S. V., Kelly T. J., Jr Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: characterization of a protein covalently linked to nascent DNA strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5105–5109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Bodnar J. W., Polvino-Bodnar M., Ward D. C. Identification and characterization of a protein covalently bound to DNA of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1094–1104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1094-1104.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Sturzenbecker L. J., Tattersall P. The autonomous parvovirus MVM encodes two nonstructural proteins in addition to its capsid polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. Organization of nonstructural genes of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):724–732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.724-732.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The autonomously replicating parvoviruses of vertebrates. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:91–174. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Griffith J., Kornberg A. phiX174 cistron A protein is a multifunctional enzyme in DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Kornberg A. Purification and characterization of phiX174 gene A protein. A multifunctional enzyme of duplex DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5328–5332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust E. A., Ward D. C. Incomplete genomes of the parvovirus minute virus of mice: selective conservation of genome termini, including the origin for DNA replication. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):276–292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.276-292.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Labow M. A., Wright R., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Genetics of adeno-associated virus: isolation and preliminary characterization of adeno-associated virus type 2 mutants. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):329–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.329-339.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Peñalva M. A., Inciarte M. R., Salas M. The protein covalently linked to the 5' termini of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29 is involved in the initiation of DNA replication. Virology. 1980 Jul 15;104(1):84–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnar-Kimber K. L., Summers J., Taylor J. M., Mason W. S. Protein covalently bound to minus-strand DNA intermediates of duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):165–172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.165-172.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto I., Lázaro J. M., García J. A., Hermoso J. M., Salas M. Purification in a functional form of the terminal protein of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1639–1643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekosh D. M., Russell W. C., Bellet A. J., Robinson A. J. Identification of a protein linked to the ends of adenovirus DNA. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revie D., Tseng B. Y., Grafstrom R. H., Goulian M. Covalent association of protein with replicative form DNA of parvovirus H-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5539–5543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shade R. O., Blundell M. C., Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P., Astell C. R. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of human parvovirus B19 isolated from the serum of a child during aplastic crisis. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):921–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.921-936.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih M., Watabe K., Ito J. In vitro complex formation between bacteriophage phi 29 terminal protein and deoxynucleotide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):1031–1036. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Sebring E. D., Rose J. A. Concatemers of alternating plus and minus strands are intermediates in adenovirus-associated virus DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamanoi F., Stillman B. W. Function of adenovirus terminal protein in the initiation of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2221–2225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Bratton J. Reciprocal productive and restrictive virus-cell interactions of immunosuppressive and prototype strains of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):944–955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.944-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Ward D. C. Rolling hairpin model for replication of parvovirus and linear chromosomal DNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):106–109. doi: 10.1038/263106a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., Miller I. L., Carter B. J. Genetic analysis of adeno-associated virus: properties of deletion mutants constructed in vitro and evidence for an adeno-associated virus replication function. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.611-619.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Mitra S. Proteins tightly associated with the termini of replicative form DNA of Kilham rat virus, an autonomous parvovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8335–8339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]