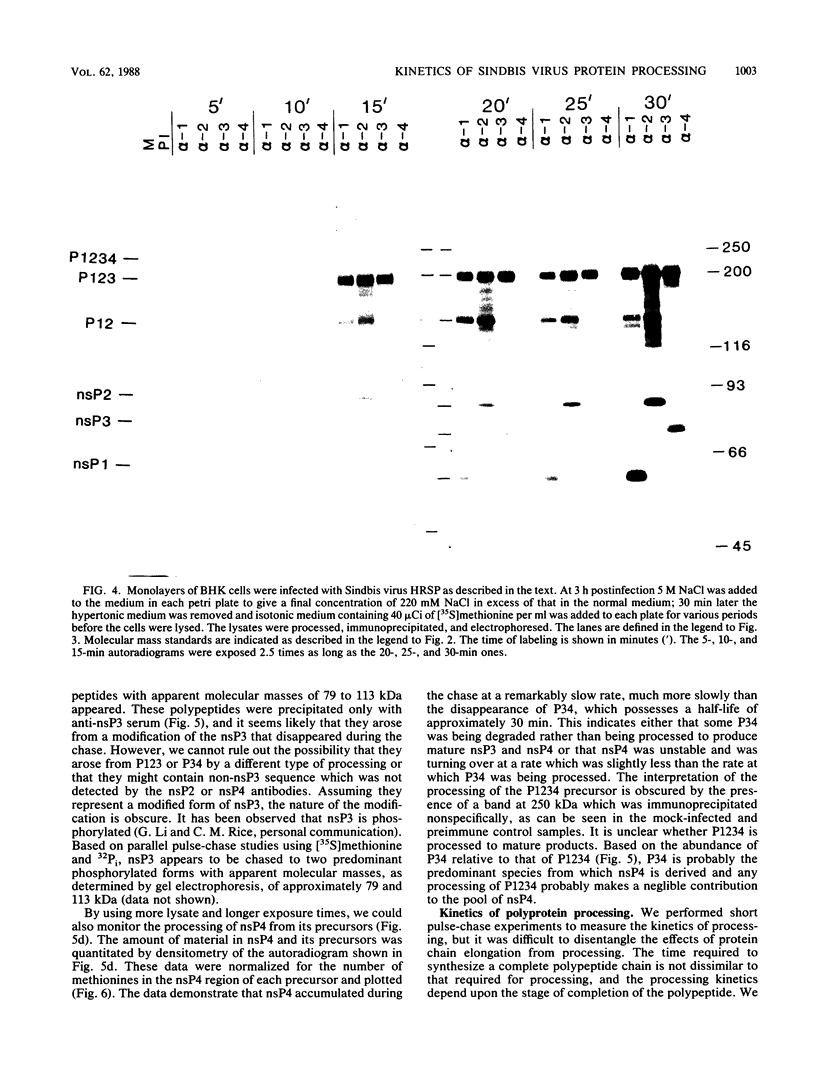
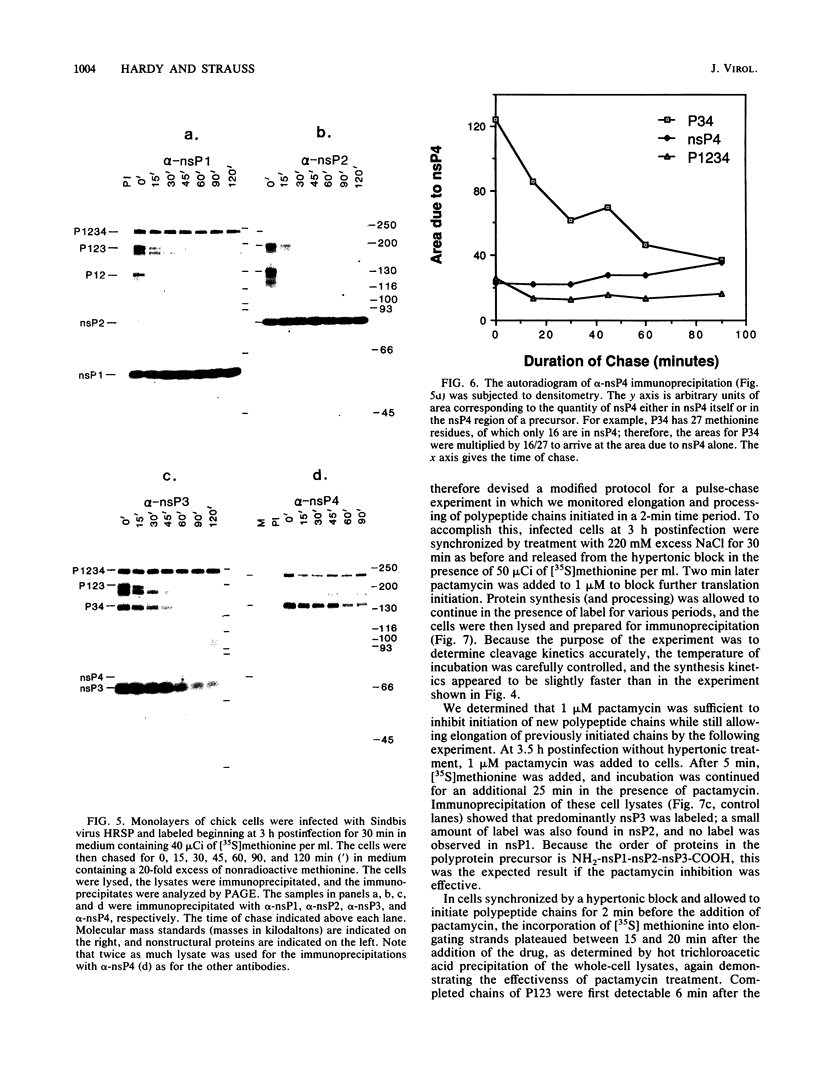
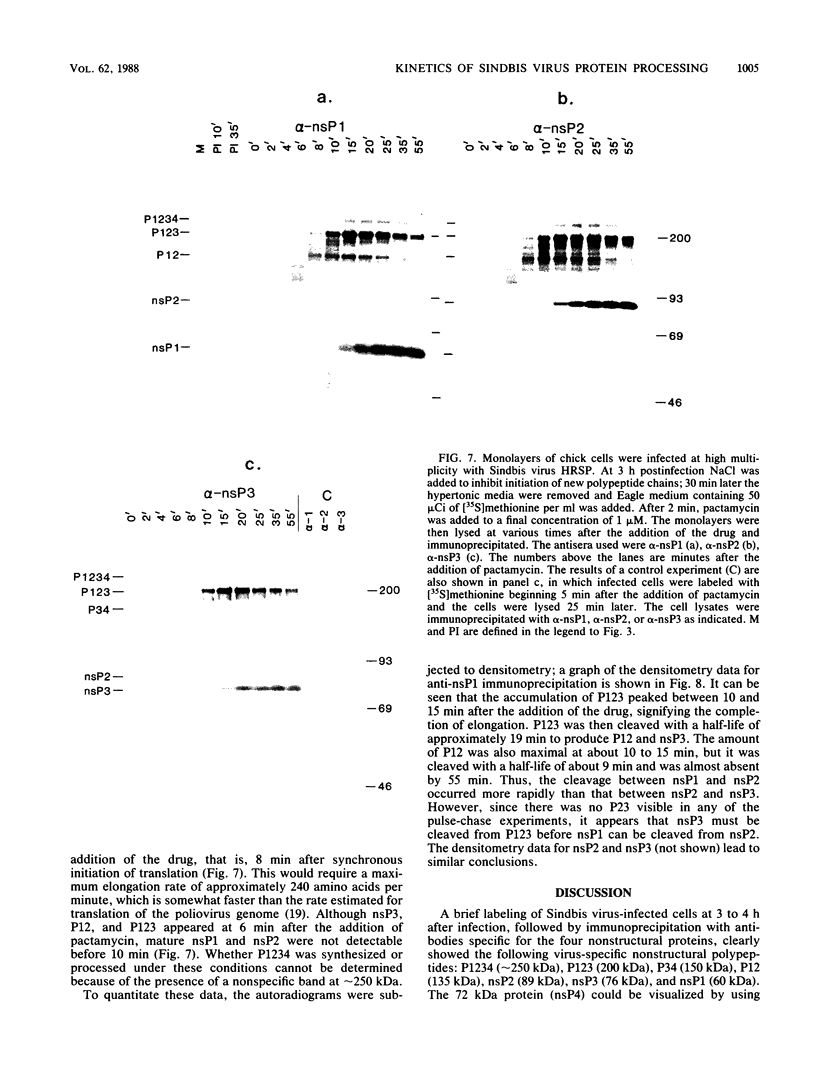
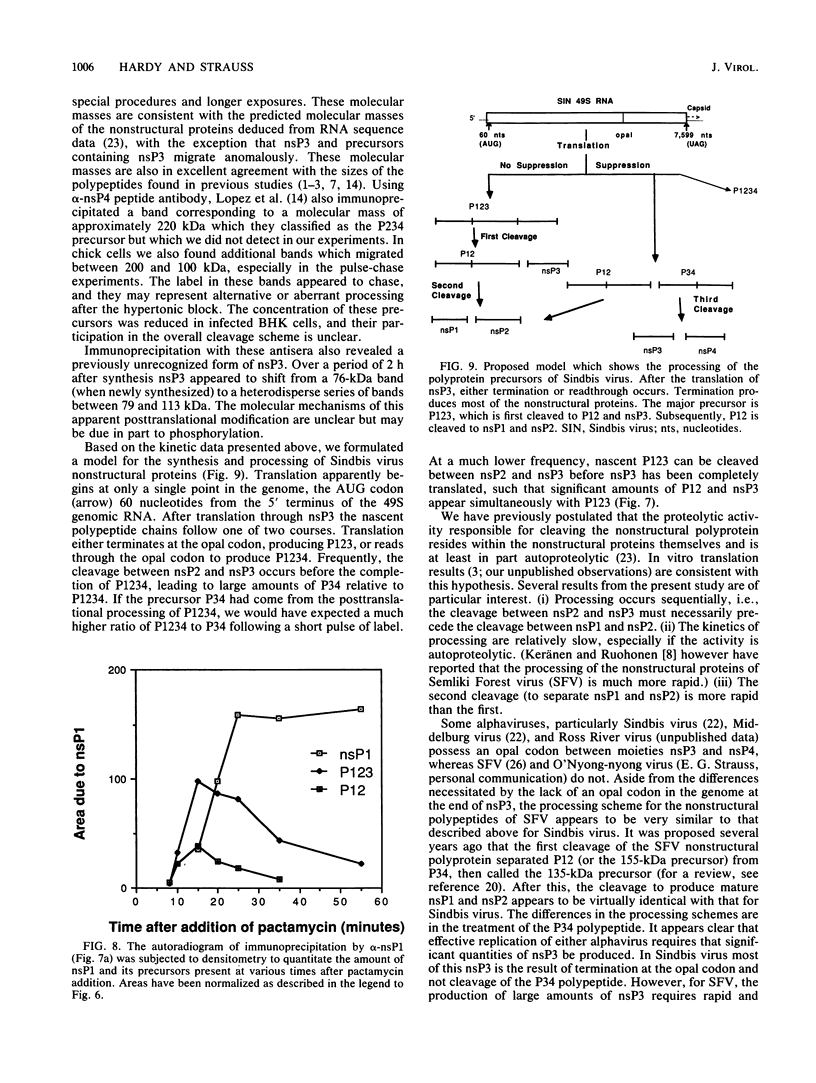
Abstract
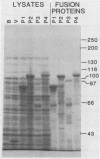
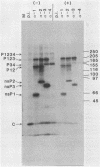
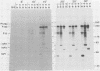
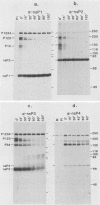
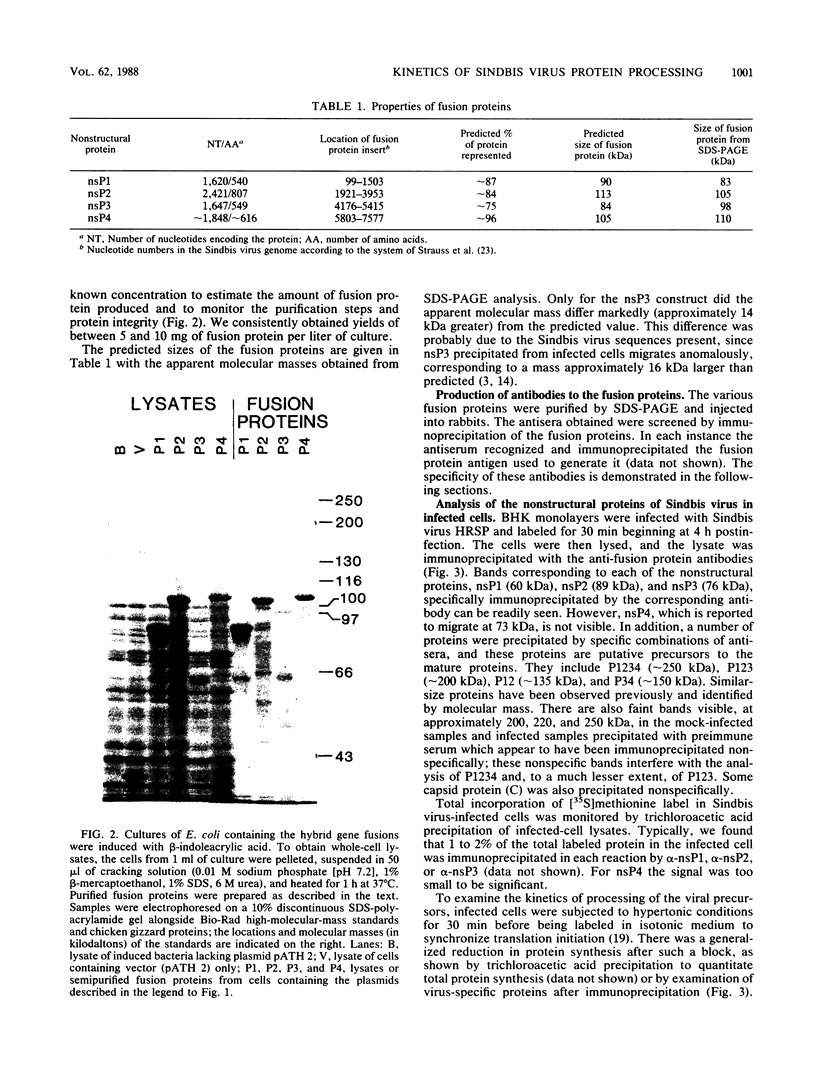
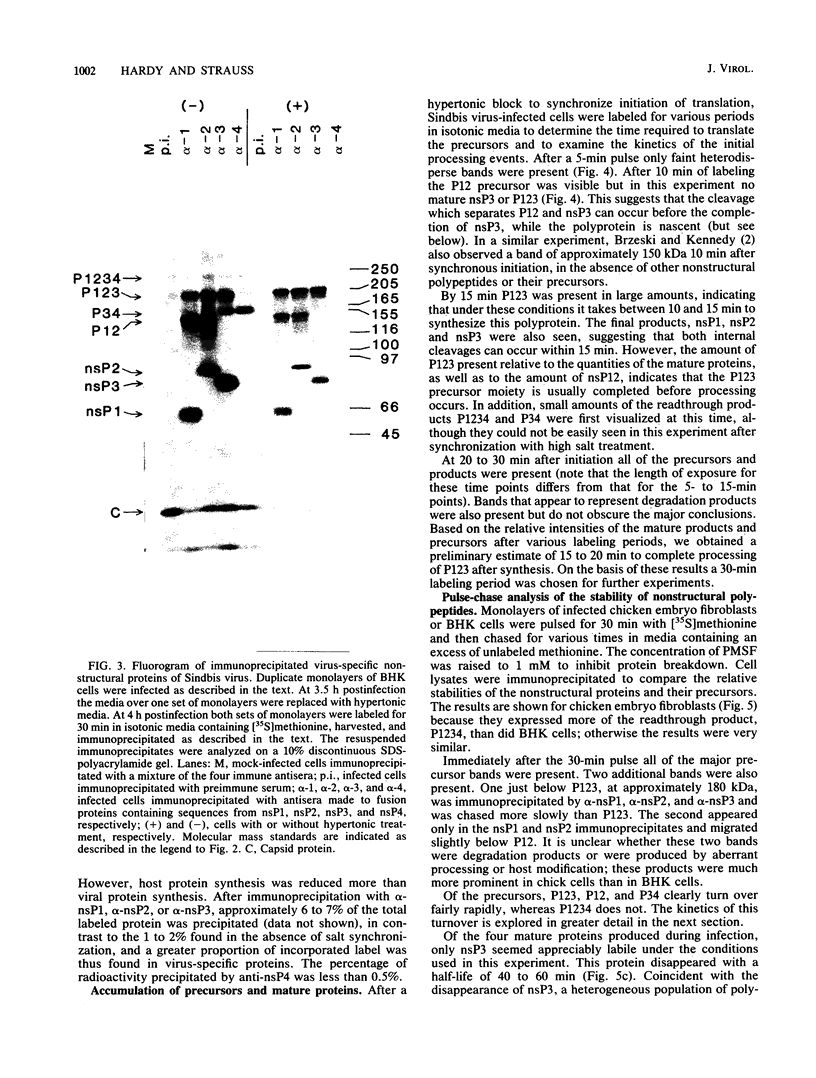
Plasmids were constructed which contained a large portion of each of the four nonstructural genes of Sindbis virus fused to the N-terminal two-thirds of the trpE gene of Escherichia coli. The large quantity of fusion protein induced from cells containing these plasmids was subsequently used as an antigen to generate polyclonal antisera in rabbits. Each antiserum was specific for the corresponding nonstructural protein and allowed ready identification of each nonstructural protein and of precursors containing the sequences of two or more nonstructural proteins. These antisera were used to determine the stability of the mature nonstructural proteins and to examine the kinetics of processing of the nonstructural proteins from their respective precursors in vivo. Pulse-chase experiments showed that the precursor P123 is cleaved with a half-life of approximately 19 min to produce P12 and nsP3; P12 is then cleaved with a half-life of approximately 9 min to produce nsP1 and nsP2. Thus, although the rate of cleavage between nsP1 and nsP2 is faster than that between nsP2 and nsP3, the latter cleavage must occur first and is therefore the rate-limiting step. The rate at which P34 is chased suggests that the cleavage between nsP3 and nsP4 is the last to occur; however the regulation of nsP4 function in Sindbis virus-infected cells may be even more complex than was previously thought. The products nsP1 and nsP2 (and nsP4) are relatively stable; nsP3, however, is unstable, with a half-life of about 1 h, and appears to be modified to produce heterodisperse, higher-molecular-mass forms. In general, the processing schemes used by Sindbis virus and Semliki Forest virus appear very similar, the major difference being that most nsP3 in Sindbis virus results from termination at an opal condon, whereas in Semliki Forest virus cleavage of the P34 precursor is required.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bracha M., Leone A., Schlesinger M. J. Formation of a Sindbis virus nonstructural protein and its relation of 42S mRNA function. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):612–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.612-620.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzeski H., Kennedy S. I. Synthesis of Sindbis virus nonstructural polypeptides in chicken embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):420–429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.420-429.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Fuller F. J., Marcus P. I., Hightower L. E., Ball L. A. Synthesis and processing of Sindbis virus nonstructural proteins in vitro. Virology. 1982 Apr 30;118(2):363–379. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. One-step growth curve of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus on chicken embryo cells grown in vitro and analysis of virus yields from single cells. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):183–199. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keränen S., Käriäinen L. Functional defects of RNA-negative temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis and Semliki Forest viruses. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):19–29. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.19-29.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keränen S., Ruohonen L. Nonstructural proteins of Semliki Forest virus: synthesis, processing, and stability in infected cells. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):505–515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.505-515.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleid D. G., Yansura D., Small B., Dowbenko D., Moore D. M., Grubman M. J., McKercher P. D., Morgan D. O., Robertson B. H., Bachrach H. L. Cloned viral protein vaccine for foot-and-mouth disease: responses in cattle and swine. Science. 1981 Dec 4;214(4525):1125–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.6272395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A. Tapping the immunological repertoire to produce antibodies of predetermined specificity. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):593–596. doi: 10.1038/299592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez S., Bell J. R., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. The nonstructural proteins of Sindbis virus as studied with an antibody specific for the C terminus of the nonstructural readthrough polyprotein. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):235–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. The 5'-terminal sequences of the genomic RNAs of several alphaviruses. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. S., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Effect of ionic strength on the binding of Sindbis virus to chick cells. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1030–1036. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1030-1036.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saborio J. L., Pong S. S., Koch G. Selective and reversible inhibition of initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 15;85(2):195–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Rosser D. S., Berk A. J. Analysis of adenovirus transforming proteins from early regions 1A and 1B with antisera to inducible fusion antigens produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):132–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.132-141.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):92–110. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90428-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Sequence coding for the alphavirus nonstructural proteins is interrupted by an opal termination codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5271–5275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takkinen K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the nonstructural protein genes of Semliki Forest virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5667–5682. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C., Platt T., Crawford I. P., Nichols B. P., Christie G. E., Horowitz H., VanCleemput M., Wu A. M. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6647–6668. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]