Abstract
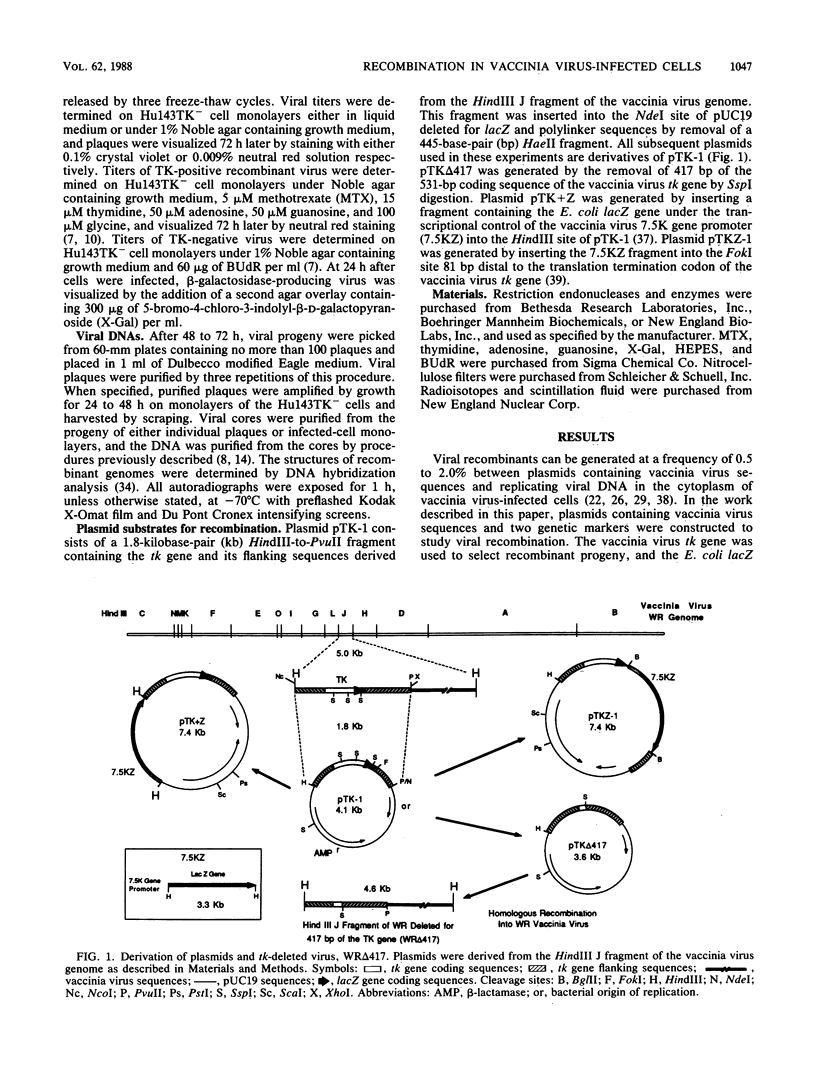
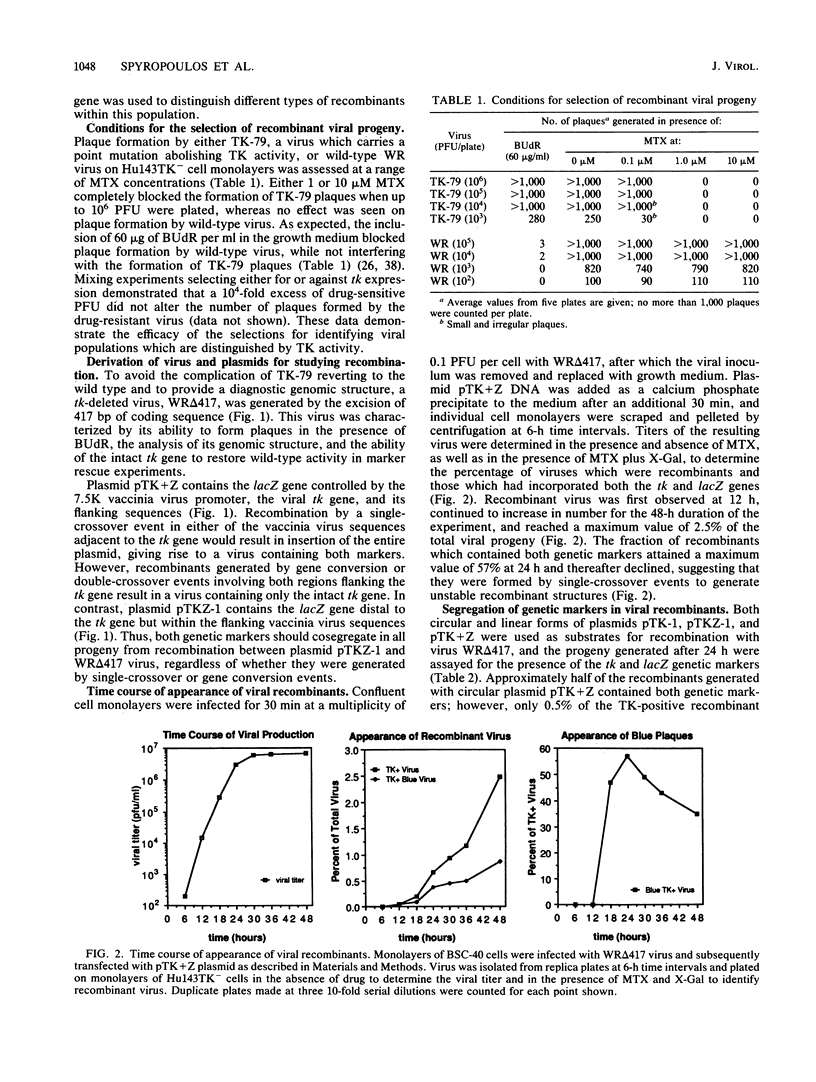
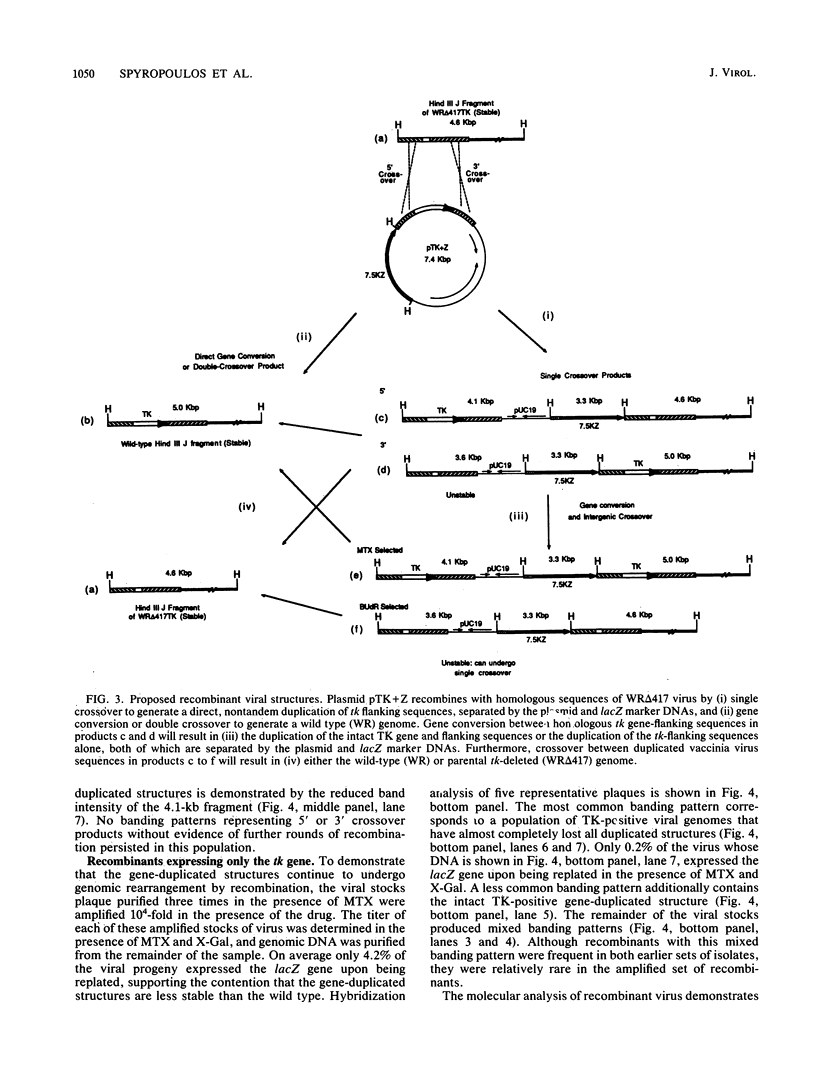
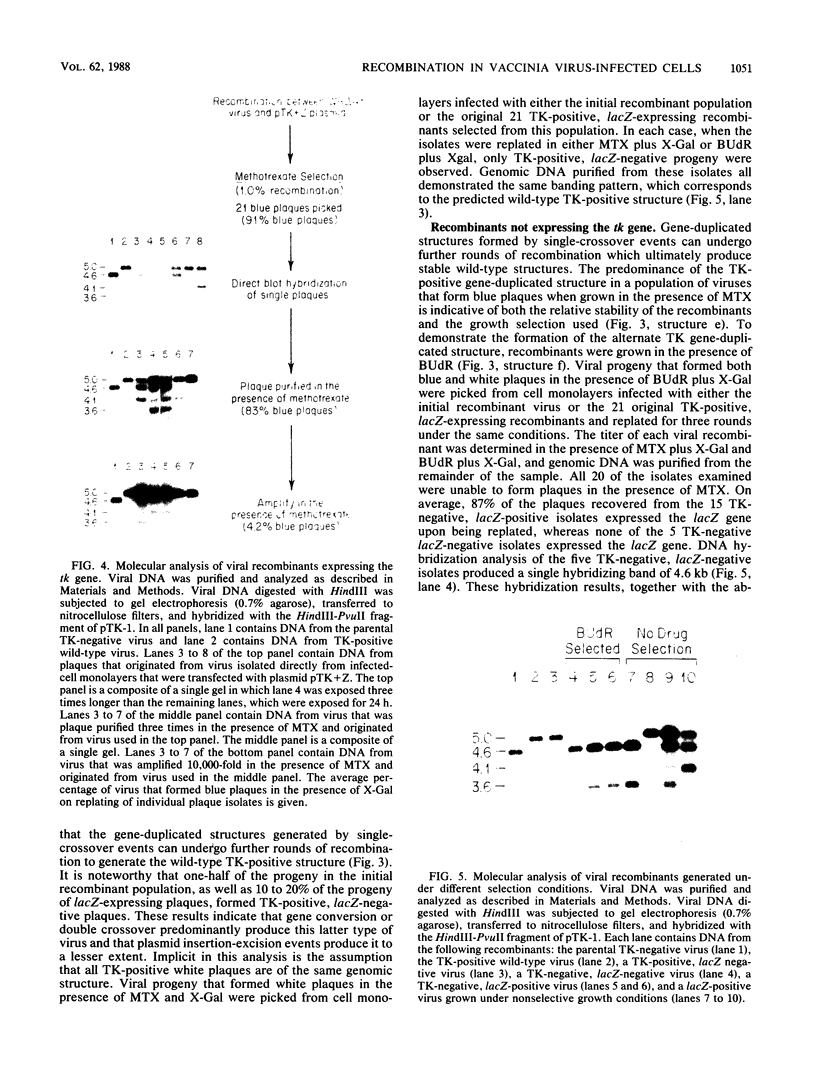
Plasmids containing the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene, its flanking DNA sequences, and the Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase gene were used in conjunction with a thymidine kinase-deficient virus to examine the viral products of recombination. Progeny derived from single-crossover events could be distinguished from those generated by gene conversion or double-crossover events when the beta-galactosidase gene was separated from the thymidine kinase gene by the flanking sequences. Using methotrexate to select for recombinant virus and a chromogenic indicator to detect beta-galactosidase, the generation of viral recombinants was measured over a 48-h period. Recombinant progeny were first observed at 12 h and increased to a maximum of 2.5% at 48 h. Single-crossover products, as determined by beta-galactosidase expression, reached a maximum of 57% of the recombinant population at 24 h and thereafter declined. DNA hybridization analysis was used to examine genomic structures of the progeny of the initial viral plaques, plaques purified three times, and those subject to a 10(4)-fold amplification. These analyses confirmed that single-crossover events within either the 5'- or 3'-homologous flanking sequences generated unstable recombinant structures. These structures were shown to contain a single copy of the intact thymidine kinase gene within the corresponding copy of the duplicated thymidine kinase flanking sequences, separated by the beta-galactosidase gene and plasmid DNA. Significantly, these duplicated structures could undergo further recombination to produce repeats of either the intact or the deleted thymidine kinase sequences. These intermediate structures ultimately degenerated to produce either the parental thymidine kinase-deleted or the wild-type genome. The wild-type genome was also shown to be generated directly by gene conversion or double-crossover events.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn B. Y., Livingston D. M. Mitotic gene conversion lengths, coconversion patterns, and the incidence of reciprocal recombination in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae plasmid system. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3685–3693. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchetti S., Graham F. L. Transfer of the gene for thymidine kinase to thymidine kinase-deficient human cells by purified herpes simplex viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1590–1594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A. High-frequency homologous recombination in vaccinia virus DNA. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1788–1795. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1788-1795.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman W. W., Nathans D. The isolation of simian virus 40 variants with specifically altered genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):942–946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campione-Piccardo J., Rawls W. E., Bacchetti S. Selective assay for herpes simplex viruses expressing thymidine kinase. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):281–287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.281-287.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condit R. C., Motyczka A., Spizz G. Isolation, characterization, and physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):429–443. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D. B., Munyon W., Buchsbaum R., Chawda R. Virus type-specific thymidine kinase in cells biochemically transformed by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):140–145. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.140-145.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange A. M., McFadden G. Sequence-nonspecific replication of transfected plasmid DNA in poxvirus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):614–618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drillien R., Koehren F., Kirn A. Host range deletion mutant of vaccinia virus defective in human cells. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):488–499. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensinger M. J., Rovinsky M. Marker rescue of temperature-sensitive mutations of vaccinia virus WR: correlation of genetic and physical maps. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):419–428. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.419-428.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito J., Condit R., Obijeski J. The preparation of orthopoxvirus DNA. J Virol Methods. 1981 Feb;2(3):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENNER F., COMBEN B. M. [Genetic studies with mammalian poxviruses. I. Demonstration of recombination between two strains of vaccina virus]. Virology. 1958 Jun;5(3):530–548. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENNER F. Genetic studies with mammalian poxviruses. II. Recombination between two strains of vaccinia virus in single HeLa cells. Virology. 1959 Aug;8:499–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathi Z., Sridhar P., Pacha R. F., Condit R. C. Efficient targeted insertion of an unselected marker into the vaccinia virus genome. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C. A., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H., Hruby D. E. Neomycin resistance as a dominant selectable marker for selection and isolation of vaccinia virus recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1918–1924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. V., Moss B. Mapping of the vaccinia virus DNA polymerase gene by marker rescue and cell-free translation of selected RNA. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.72-77.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L., Moss B. Vaccinia virus: a selectable eukaryotic cloning and expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse M L, Lederberg E M, Lederberg J. Transductional Heterogenotes in Escherichia Coli. Genetics. 1956 Sep;41(5):758–779. doi: 10.1093/genetics/41.5.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano E., Panicali D., Paoletti E. Molecular genetics of vaccinia virus: demonstration of marker rescue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1593–1596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Yeast recombination: the association between double-strand gap repair and crossing-over. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panicali D., Paoletti E. Construction of poxviruses as cloning vectors: insertion of the thymidine kinase gene from herpes simplex virus into the DNA of infectious vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogo B. G., Berkowitz E. M., Dales S. Investigation of vaccinia virus DNA replication employing a conditional lethal mutant defective in DNA. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):436–444. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A., Martin P. The repair of double-strand breaks in the nuclear DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its genetic control. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jan 16;143(2):119–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00266917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim J. S., Cho H. Y., Huebner R. J. Non-producer human cells induced by murine sarcoma virus. Int J Cancer. 1975 Jan 15;15(1):23–29. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Davis R. W. Replacement of chromosome segments with altered DNA sequences constructed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4951–4955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Baroudy B. M., Moss B. Distinctive nucleotide sequences adjacent to multiple initiation and termination sites of an early vaccinia virus gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):805–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Bajszár G., Moss B. Mapping of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene by marker rescue and by cell-free translation of selected mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1210–1214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Moss B. Nucleotide sequence of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene and the nature of spontaneous frameshift mutations. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):530–537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.530-537.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]