Abstract
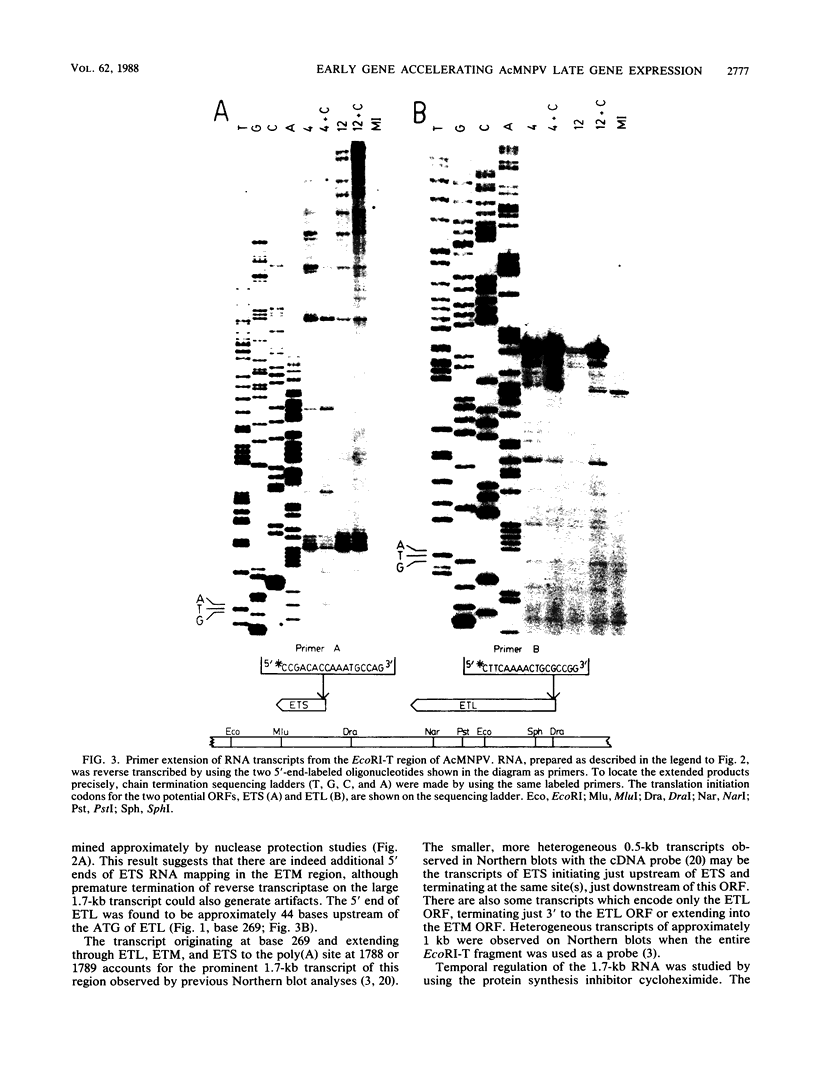
The region of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcMNPV) encompassing the EcoRI T fragment (29.0 to 30.1 map units) was characterized by DNA sequencing, transcriptional mapping, and site-directed mutagenesis. The largest transcript from this region, an early 1.7-kilobase (kb) poly(A)+ RNA, encompassed three tandem, nonoverlapping open reading frames (ORFs). The largest of these ORFs, ETL, was proximal to the 5' end of the transcript and had the capacity to encode a 28-kilodalton (kDa) polypeptide. A recombinant virus, vETL beta gal, containing the Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase (beta gal) gene fused to the N-terminal two-thirds of the ETL ORF, produced blue plaques in the presence of a chromogenic indicator of beta gal and wild-type levels of polyhedra in cell culture. This recombinant was also infectious in insect larvae by oral administration of occluded virus. Comparison of vETL beta gal and wild-type viral proteins pulse-labeled at various times postinfection (p.i.) revealed (i) absence of a virus-induced 28-kDa polypeptide, (ii) early expression of a large (approximately 130-kDa) polypeptide which may be the ETL-beta gal fusion protein, (iii) a delay in expression of early 35 and 40-kDa polypeptides, and (iv) a 4- to 6-h delay in the expression of late proteins in vETL beta gal-infected cells. Cycloheximide did not inhibit synthesis of the 1.7-kb RNA but did inhibit its shutoff, which occurs at 12 h p.i. in the absence of inhibitors. Thus, the ETL gene product is apparently an early 28-kDa protein which is necessary, directly or indirectly, for timely expression of many other AcMNPV genes. The promoter-leader regions of the 1.7-kDa transcript showed significant sequence similarities to the leader of the AcMNPV IE-1 gene. The middle ORF within the 1.7-kb transcript, ETM, would encode a hydrophobic polypeptide of 113 amino acid residues. ETS, a small ORF within and proximal to the 3' end of the 1.7-kb transcript, was also transcribed as a set of smaller (approximately 0.5-kb) RNAs initiated heterogeneously in the region between ETL and ETS and persisting throughout infection.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casadaban M. J., Martinez-Arias A., Shapira S. K., Chou J. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions for analyzing gene expression in escherichia coli and yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:293–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandson M. A., Gordon J., Carstens E. B. Size and map locations of early transcription products on the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome. Virology. 1985 Apr 15;142(1):12–23. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90418-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Divergent transcription of early 35- and 94-kilodalton protein genes encoded by the HindIII K genome fragment of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2264–2272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2264-2272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Temporal regulation of baculovirus RNA: overlapping early and late transcripts. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):392–400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.392-400.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. The regulation of baculovirus gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;131:31–49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71589-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs L. Y., Woods M. S., Weaver R. F. Viral Transcription During Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Infection: a Novel RNA Polymerase Induced in Infected Spodoptera frugiperda Cells. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):641–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.641-646.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grula M. A., Buller P. L., Weaver R. F. alpha-Amanitin-Resistant Viral RNA Synthesis in Nuclei Isolated from Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus-Infected Heliothis zea Larvae and Spodoptera frugiperda Cells. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):916–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.916-921.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of a trans-activating gene required for expression of a baculovirus delayed-early gene. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.563-571.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Interspersed Homologous DNA of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Enhances Delayed-Early Gene Expression. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):215–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.215-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Nucleotide sequence and temporal expression of a baculovirus regulatory gene. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2091–2099. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2091-2099.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hink W. F. Established insect cell line from the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni. Nature. 1970 May 2;226(5244):466–467. doi: 10.1038/226466b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Bifunctional messenger RNAs in eukaryotes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Miller L. K. Effects of serial passage of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus in cell culture. Virus Res. 1987 Jun;7(4):335–349. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. H., Miller L. K. Isolation of genotypic variants of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):754–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.754-767.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert H., Doerfler W. Mapping of Early and Late Transcripts Encoded by the Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Genome: Is Viral RNA Spliced? J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):497–506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.497-506.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert H., Doerfler W. Transcription of overlapping sets of RNAs from the genome of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus: a novel method for mapping RNAs. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):255–265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.255-265.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainprize T. H., Lee K., Miller L. K. Variation in the temporal expression of overlapping baculovirus transcripts. Virus Res. 1986 Oct;6(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. W., Miller L. K. A virus mutant with an insertion of a copia-like transposable element. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):562–564. doi: 10.1038/299562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G. Use of sodium trichloroacetate and mung bean nuclease to increase sensitivity and precision during transcript mapping. Anal Biochem. 1986 Oct;158(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90605-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oellig C., Happ B., Müller T., Doerfler W. Overlapping sets of viral RNAs reflect the array of polypeptides in the EcoRI J and N fragments (map positions 81.2 to 85.0) of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3048–3057. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3048-3057.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennock G. D., Shoemaker C., Miller L. K. Strong and regulated expression of Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase in insect cells with a baculovirus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):399–406. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A convenient and adaptable package of computer programs for DNA and protein sequence management, analysis and homology determination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):643–655. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin C., Ladin B. F., Weaver R. F. Physical mapping of temporally regulated, overlapping transcripts in the region of the 10K protein gene in Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):18–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.18-27.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. C., Miller L. K. Baculovirus transcription in the presence of inhibitors and in nonpermissive Drosophila cells. Virus Res. 1986 Nov;6(2):155–172. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohel D. Z., Faulkner P. Time Course Analysis and Mapping of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Transcripts. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):739–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.739-747.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert M., Harmison G. G., Meier E. Primary structure of the vesicular stomatitis virus polymerase (L) gene: evidence for a high frequency of mutations. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):505–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.505-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. L., Goodwin R. H., Tompkins G. J., McCawley P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro. 1977 Apr;13(4):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02615077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlak J. M., Smith G. E. Orientation of the Genome of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus: a Proposal. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1118–1121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1118-1121.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]