Abstract
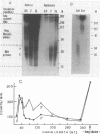
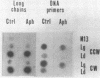
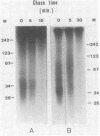
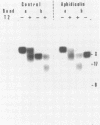
It is generally accepted that an aphidicolin-sensitive DNA polymerase elongates the eucaryotic RNA primer (iRNA) into a mature Okazaki piece reaching ca. 200 nucleotides. Yet, as shown here, nascent DNA chains below 40 nucleotides accumulated in simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA replicating in isolated nuclei in the presence of aphidicolin. These products resembled precursors of longer Okazaki pieces synthesized in the absence of aphidicolin (termed here DNA primers) in size distribution, lagging-replication-fork polarity, and content of iRNA. Within the isolated SV40 replicative intermediate, DNA primers could be extended in a reaction catalyzed by the Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I large fragment. This increased their length by an average of 21 deoxyribonucleotide residues, indicating that single-stranded gaps of corresponding length existed 3' to the DNA primers. Incubation with T4 DNA ligase converted most of the extended DNA primers into products resembling long Okazaki pieces. These data led us to propose that the synthesis of an SV40 Okazaki piece could be itself discontinuous and could comprise the following steps: (i) iRNA synthesis by DNA primase, (ii) iRNA extension into a DNA primer by an aphidicolin-resistant activity associated with DNA primase-DNA polymerase alpha, (iii) removal of iRNA moieties between adjacent DNA primers, (iv) "gap filling" between DNA primers by the aphidicolin-sensitive DNA polymerase alpha, and (v) ligation of DNA primer units onto a growing Okazaki piece. Eventually, a mature Okazaki piece is ligated onto a longer nascent DNA chain.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., DePamphilis M. L. Metabolism of Okazaki fragments during simian virus 40 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11495–11504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., Kaufman G., DePamphilis M. L. RNA primers in SV40 DNA replication: identification of transient RNA-DNA covalent linkages in replicating DNA. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):4990–4998. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Berg P. Requirement of a Cytoplasmic Fraction for Synthesis of SV40 Deoxyribonucleic Acid in Isolated Nuclei*. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4348–4354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker R. S., Yamaguchi M., Possenti R., DePamphilis M. L. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: aphidicolin causes accumulation of early-replicating intermediates and allows determination of the initial direction of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3815–3825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinter-Gottlieb G., Kaufmann G. Aphidicolin arrest irreversibly impairs replicating simian virus 40 chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3809–3812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge P., Sogo J. M., Stahl H. Inhibition of DNA synthesis by aphidicolin induces supercoiling in simian virus 40 replicative intermediates. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3241–3246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04072.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson R., Reichard P. Replication of polyoma DNA in isolated nuclei. Synthesis and distribution of initiator RNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7469–7475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., DePamphilis M. L. Initiation of SV40 DNA replication in vivo: location and structure of 5' ends of DNA synthesized in the ori region. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., Hendrickson E. A., DePamphilis M. L. Sequence specificity for the initiation of RNA-primed simian virus 40 DNA synthesis in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 15;175(2):131–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. Z., Wang T. S., Korn D. DNA primase from KB cells. Evidence for a novel model of primase catalysis by a highly purified primase/polymerase-alpha complex. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2602–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann G., Anderson S., DePamphilis M. L. RNA primers in Simian virus 40 DNA replication. II. Distribution of 5' terminal oligoribonucleotides in nascent DNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 5;116(3):549–567. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann G., Bar-Shavit R., DePamphilis M. L. Okazaki pieces grow opposite to the replication fork direction during simian virus 40 DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2535–2545. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann G. Characterization of initiator RNA from replicating simian virus 40 DNA synthesized in isolated nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):25–39. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6973–6977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. Role of DNA polymerase alpha and DNA primase in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2869–2873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Kostura M., Marshak D. R., Mathews M. B., Stillman B. The cell-cycle regulated proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):471–475. doi: 10.1038/326471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Tan C. K., Kostura M., Mathews M. B., So A. G., Downey K. M., Stillman B. Functional identity of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and a DNA polymerase-delta auxiliary protein. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):517–520. doi: 10.1038/326517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D. R., Margolskee R. F., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of the simian virus 40 replicon: pseudorevertants of mutants with a defective replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. T-antigen-DNA polymerase alpha complex implicated in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4077–4087. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taljanidisz J., Decker R. S., Guo Z. S., DePamphilis M. L., Sarkar N. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: identification of RNA-primed nascent DNA chains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7877–7888. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., DePamphilis M. L. Discontinuous DNA replication: accumulation of Simian virus 40 DNA at specific stages in its replication. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 15;120(3):401–422. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., DePamphilis M. L. Preferred DNA sites are involved in the arrest and initiation of DNA synthesis during replication of SV40 DNA. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Hu S. Z., Korn D. DNA primase from KB cells. Characterization of a primase activity tightly associated with immunoaffinity-purified DNA polymerase-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1854–1865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]