Abstract
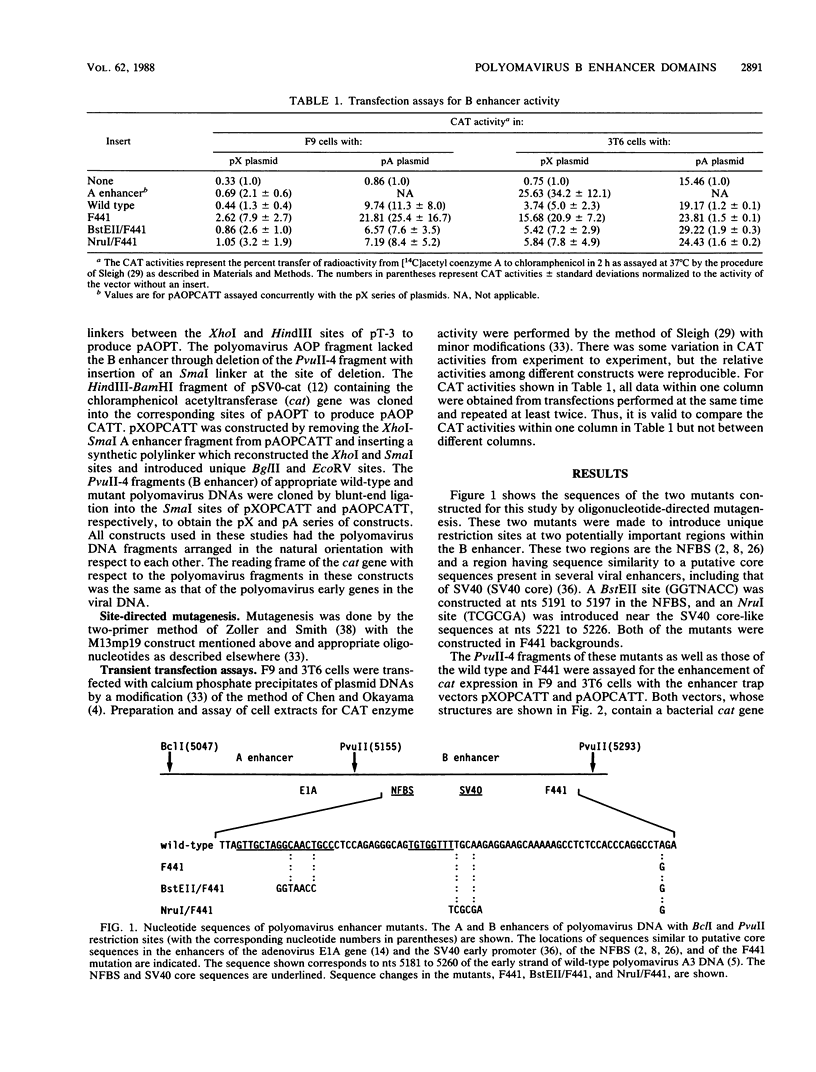
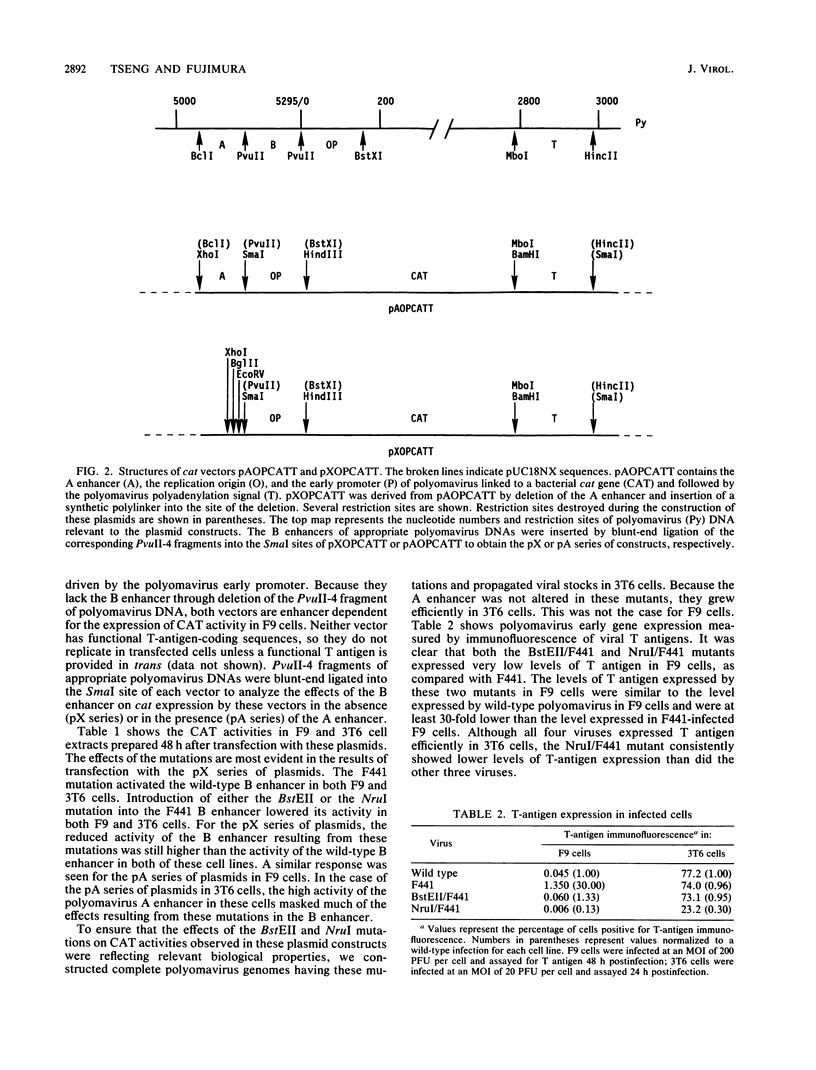
A point mutation at nucleotide 5258 in the B enhancer of the polyomavirus host range mutant F441 leads to productive infection of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells, which are refractory to infection by wild-type polyomavirus. Specific oligonucleotides were used to construct mutations in two other potentially important domains within the B enhancer of F441 DNA. One of these domains is the binding site for a factor present in nuclear extracts of F9 cells, and the other is a region that has sequence similarity to putative core sequences observed in a number of different viral enhancers. Mutation within either of these two domains, even in the presence of the F441 mutation, was detrimental to polyomavirus enhancer activity in F9 cells, as determined by both transfection and infection assays.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. Functional analysis of the regulatory region of polyoma mutant F9-1 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4789–4809. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Gruss P. Interaction of distinct nuclear proteins with sequences controlling the expression of polyomavirus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1401–1411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deninger P. L., Esty A., LaPorte P., Hsu H., Friedmann T. The nucleotide sequence and restriction enzyme sites of the polyoma genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 25;8(4):855–860. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Linney E. Mutation near the polyoma DNA replication origin permits productive infection of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):809–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90445-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K., Linney E. Polyoma mutants that productively infect F9 embryonal carcinoma cells do not rescue wild-type polyoma in F9 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1479–1483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K. Nuclear activity from F9 embryonal carcinoma cells binding specifically to the enhancers of wild-type polyoma virus and PyEC mutant DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2845–2861. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K., Silbert P. E., Eckhart W., Linney E. Polyoma virus infection of retinoic acid-induced differentiated teratocarcinoma cells. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):306–312. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.306-312.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Fromental C., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A mutated polyoma virus enhancer which is active in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells is not repressed by adenovirus-2 E1A products. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):249–251. doi: 10.1038/321249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Kao H. T., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R., Strickland S. Common control of the heat shock gene and early adenovirus genes: evidence for a cellular E1A-like activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):867–874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M., Vasseur M., Montreau N., Yaniv M., Blangy D. Polyoma DNA sequences involved in control of viral gene expression in murine embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):720–722. doi: 10.1038/290720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M., Yaniv M., Vasseur M., Blangy D. Expression of polyoma early functions in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells depends on sequence rearrangements in the beginning of the late region. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90625-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Satake M., Furukawa K., Reichel R., Ito Y., Nevins J. R. A factor discriminating between the wild-type and a mutant polyomavirus enhancer. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):87–89. doi: 10.1038/328087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryszke M. H., Piette J., Yaniv M. Induction of a factor that binds to the polyoma virus A enhancer on differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):254–256. doi: 10.1038/328254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Donerly S. DNA fragments from F9 PyEC mutants increase expression of heterologous genes in transfected F9 cells. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):693–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Mueller C. R., Mes A. M., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus origin for DNA replication comprises multiple genetic elements. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):586–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.586-599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostapchuk P., Diffley J. F., Bruder J. T., Stillman B., Levine A. J., Hearing P. Interaction of a nuclear factor with the polyomavirus enhancer region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8550–8554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Fromental C., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor represses the activity of the polyoma virus enhancer in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells. Oncogene Res. 1987 Jul;1(2):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekikawa K., Levine A. J. Isolation and characterization of polyoma host range mutants that replicate in nullipotential embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1100–1104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J. A nonchromatographic assay for expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in eucaryotic cells. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzendruber D. E., Friedrich T. D., Lehman J. M. Resistance of teratocarcinoma stem cells to infection with simian virus 40: early events. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Oct;93(1):25–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040930105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzendruber D. E., Lehman J. M. Neoplastic differentiation: interaction of simian virus 40 and polyoma virus with murine teratocarcinoma cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Apr;85(2 Pt 1):179–187. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng R. W., Williams T., Fujimura F. K. Unique requirement for the PyF441 mutation for polyomavirus infection of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2896–2902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2896-2902.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Kern F. G., Basilico C., Ziff E. B. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress expression from polyomavirus early and late promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4019–4025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyomavirus enhancer contains multiple redundant sequence elements that activate both DNA replication and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Ferrandon D., Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Ruffenach F., Chambon P. One cell-specific and three ubiquitous nuclear proteins bind in vitro to overlapping motifs in the domain B1 of the SV40 enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3005–3013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W. A small segment of polyoma virus DNA enhances the expression of a cloned beta-globin gene over a distance of 1400 base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6251–6264. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W., Tyndall C., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyoma virus DNA replication requires an enhancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):242–246. doi: 10.1038/312242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]