Abstract
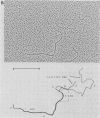
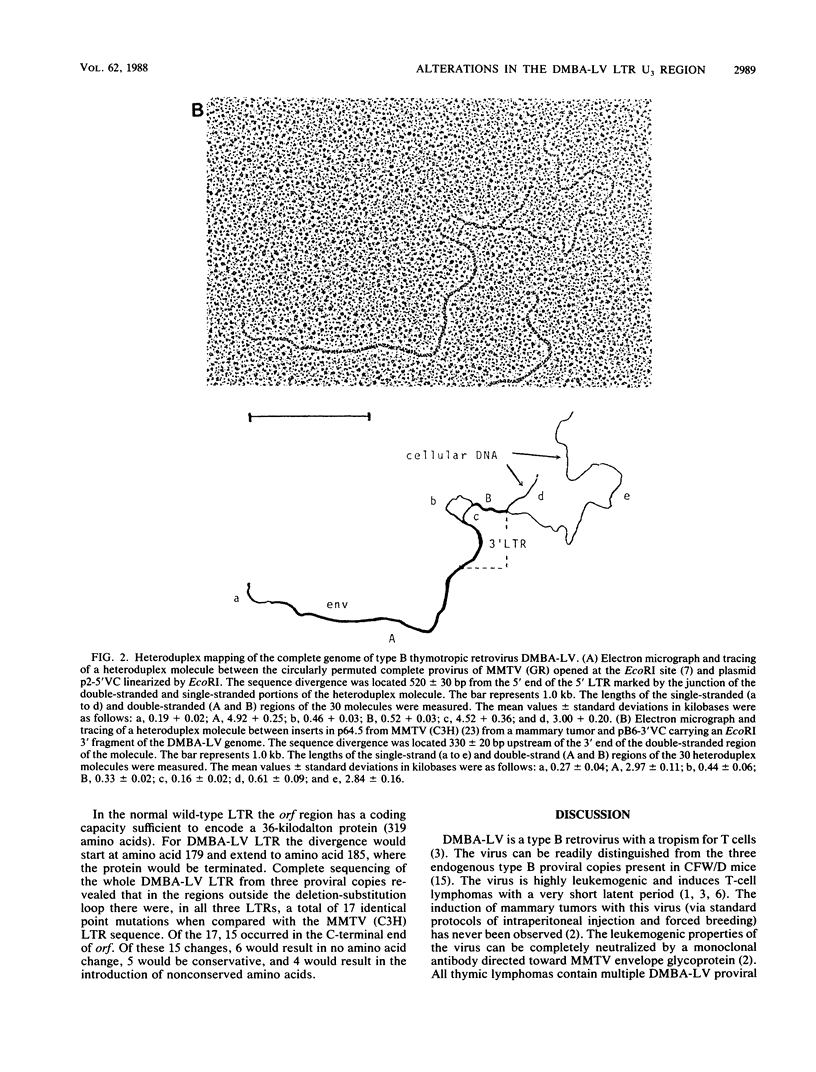
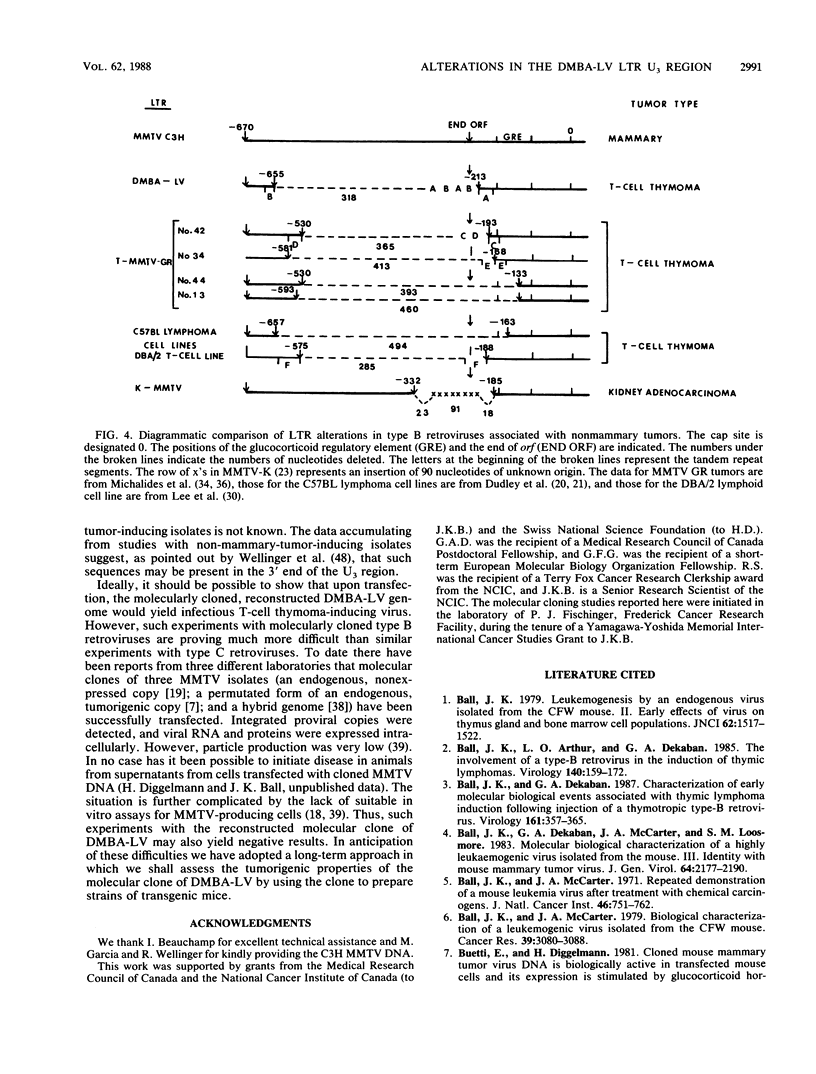
We isolated and characterized a type B thymotropic retrovirus (DMBA-LV) which is highly related to mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) isolates and which induces T-cell thymomas with a high incidence and a very short latent period. Regions of nonhomology between the DMBA-LV genome and the MMTV genome were identified by heteroduplex mapping and nucleotide sequence studies. In the electron microscope heteroduplex mapping studies the EcoRI-generated 5' and 3' fragments of the DMBA-LV genome were compared with the corresponding fragments of the MMTV (C3H and GR) genome isolated from mammary tumors. The results indicated that DMBA-LV contained a region of nonhomologous nucleotide sequences in the 3' half of the U3 region of the long terminal repeat (LTR). Nucleotide sequence studies confirmed these results and showed that in this region 440 nucleotides of the MMTV (C3H) sequences were deleted and substituted with a segment of 122 nucleotides. This substituted segment in the form of a tandem repeat structure contained nucleotide sequences derived exclusively from sequences which flanked the substitution loop. The distal glucocorticoid regulatory element was unaltered, and two additional copies of the distal glucocorticoid regulatory element-binding site were present in the substituted region. The restriction endonuclease map of the reconstructed molecular clone of DMBA-LV was identical to that corresponding to unintegrated linear DMBA-LV DNA present in DMBA-LV-induced tumor cell lines. Since the nucleotide sequences of the LTRs present in four different DMBA-LV proviral copies isolated from a single thymoma were identical, we concluded that they were derived from the same parental virus and that this type B retrovirus containing an alteration in the U3 region of its LTR could induce thymic lymphomas. Thus, DMBA-LV represents the first example of a productively replicating type B retrovirus that contains an LTR modified in the U3 region and that has target cell and disease specificity for T cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball J. K., Arthur L. O., Dekaban G. A. The involvement of a type-B retrovirus in the induction of thymic lymphomas. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):159–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90455-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J. K., Dekaban G. A. Characterization of early molecular biological events associated with thymic lymphoma induction following infection with a thymotropic type-B retrovirus. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J. K., Dekaban G. A., McCarter J. A., Loosmore S. M. Molecular biological characterization of a highly leukaemogenic virus isolated from the mouse. III. Identity with mouse mammary tumour virus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2177–2190. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J. K. Leukemogenesis by an endogenous virus isolated from the CFW mouse. II. Early effects of virus on thymus gland and bone marrow cell populations. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Jun;62(6):1517–1522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J. K., McCarter J. A. Biological characterization of a leukemogenic virus isolated from the CFW mouse. Cancer Res. 1979 Aug;39(8):3080–3088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J. K., McCarter J. A. Repeated demonstration of a mouse leukemia virus after treatment with chemical carcinogens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Apr;46(4):751–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Kühnel B. Distinct sequence elements involved in the glucocorticoid regulation of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D., Haseltine W. A. Tissue-specific transcription preference as a determinant of cell tropism and leukaemogenic potential of murine retroviruses. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):159–162. doi: 10.1038/312159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Silver J. E., Frederickson T. N., Hopkins N., Hartley J. W. A 3' end fragment encompassing the transcriptional enhancers of nondefective Friend virus confers erythroleukemogenicity on Moloney leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. C., Shank P. R., Morris V. L., Cardiff R., Varmus H. E. Integration of the DNA of mouse mammary tumor virus in virus-infected normal and neoplastic tissue of the mouse. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):333–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekaban G. A., Ball J. K. Integration of type B retroviral DNA in virus-induced primary murine thymic lymphomas. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):784–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.784-792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekaban G. A., Ball J. K., Robey W. G., Arthur L. O., McCarter J. A. Molecular biological characterization of a highly leukaemogenic virus isolated from the mouse. IV. Viral proteins. J Gen Virol. 1984 Oct;65(Pt 10):1791–1802. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-10-1791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Villemur R., Jolicoeur P. The high leukemogenic potential of Gross passage A murine leukemia virus maps in the region of the genome corresponding to the long terminal repeat and to the 3' end of env. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):24–32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.24-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Peters G. Proteins encoded by mouse mammary tumour virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;106:1–34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69357-1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diggelmann H., Vessaz A. L., Buetti E. Cloned endogenous mouse mammary tumor virus DNA is biologically active in transfected mouse cells and its expression is stimulated by glucocorticoid hormones. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):332–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90233-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley J. P., Arfsten A., Hsu C. L., Kozak C., Risser R. Molecular cloning and characterization of mouse mammary tumor proviruses from a T-cell lymphoma. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):385–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.385-388.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley J., Risser R. Amplification and novel locations of endogenous mouse mammary tumor virus genomes in mouse T-cell lymphomas. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):92–101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.92-101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etkind P. R., Szabo P., Sarkar N. H. Restriction endonuclease mapping of the proviral DNA of the exogenous RIII murine mammary tumor virus. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):855–867. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.855-867.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M., Wellinger R., Vessaz A., Diggelmann H. A new site of integration for mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA common to BALB/cf(C3H) mammary and kidney adenocarcinomas. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):127–134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. A., Chan E. C., MacInnes J. I., Morris V. L. Restriction endonuclease map of endogenous mouse mammary tumor virus loci in GR, DBA, and NFS mice. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90421-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Adachi A., Sakai K., Matsuyama M. Long terminal repeat of Friend-MCF virus contains the sequence responsible for erythroid leukemia. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):30–42. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. J., Fung Y. K., Majors J. E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Synthesis of plus strands of retroviral DNA in cells infected with avian sarcoma virus and mouse mammary tumor virus. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):127–138. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.127-138.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnel B., Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Functional analysis of the glucocorticoid regulatory elements present in the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat. A synthetic distal binding site can replace the proximal binding domain. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. T., Prakash O., Klein D., Sarkar N. H. Structural alterations in the long terminal repeat of an acquired mouse mammary tumor virus provirus in a T-cell leukemia of DBA/2 mice. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequencing of an apparent proviral copy of env mRNA defines determinants of expression of the mouse mammary tumor virus env gene. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):495–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.495-504.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalides R., Wagenaar E., Hilkens J., Hilgers J., Groner B., Hynes N. E. Acquisition of proviral DNA of mouse mammary tumor virus in thymic leukemia cells from GR mice. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):819–829. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.819-829.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalides R., Wagenaar E. Site-specific rearrangements in the long terminal repeat of extra mouse mammary tumor proviruses in murine T-cell leukemias. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):76–84. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90431-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalides R., Wagenaar E., Weijers P. Rearrangements in the long terminal repeat of extra mouse mammary tumor proviruses in T-cell leukemias of mouse strain GR result in a novel enhancer-like structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):823–830. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puma J. P., Fanning T. G., Young L. J., Cardiff R. D. Identification of a unique mouse mammary tumor virus in the BALB/cNIV mouse strain. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):158–165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.158-165.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmons B., Groner B., Calberg-Bacq C. M., Ponta H. Production of mouse mammary tumor virus upon transfection of a recombinant proviral DNA into cultured cells. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):101–114. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90309-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmons B., Günzburg W. H. Current perspectives in the biology of mouse mammary tumour virus. Virus Res. 1987 Aug;8(2):81–102. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Cohen J. C., Varmus H. E., Yamamoto K. R., Ringold G. M. Mapping of linear and circular forms of mouse mammary tumor virus DNA with restriction endonucleases: evidence for a large specific deletion occurring at high frequency during circularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. H., Young L. J., Benjamini F., Medina D., Cardiff R. D. Proteins antigenically related to peptides encoded by the mouse mammary tumour virus long terminal repeat sequence are associated with intracytoplasmic A particles. J Gen Virol. 1987 Feb;68(Pt 2):473–486. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-2-473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya A. B., Long C. A., Sheffield J. B., Tamura A., Tanaka H. Murine mammary tumor virus deficient in the major glycoprotein: biochemical and biological studies on virions produced by a lymphoma cell line. Virology. 1980 Jul 30;104(2):279–293. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt M., Haggblom C., Swift S., Haas M. Envelope gene and long terminal repeat determine the different biological properties of Rauscher, Friend, and Moloney mink cell focus-inducing viruses. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.184-192.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. The structural organization of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):193–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellinger R. J., Garcia M., Vessaz A., Diggelmann H. Exogenous mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA isolated from a kidney adenocarcinoma cell line contains alterations in the U3 region of the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.1-11.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F. K., Davison B., Chaffin K. Murine leukemia virus long terminal repeat sequences can enhance gene activity in a cell-type-specific manner. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2832–2835. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]