Abstract
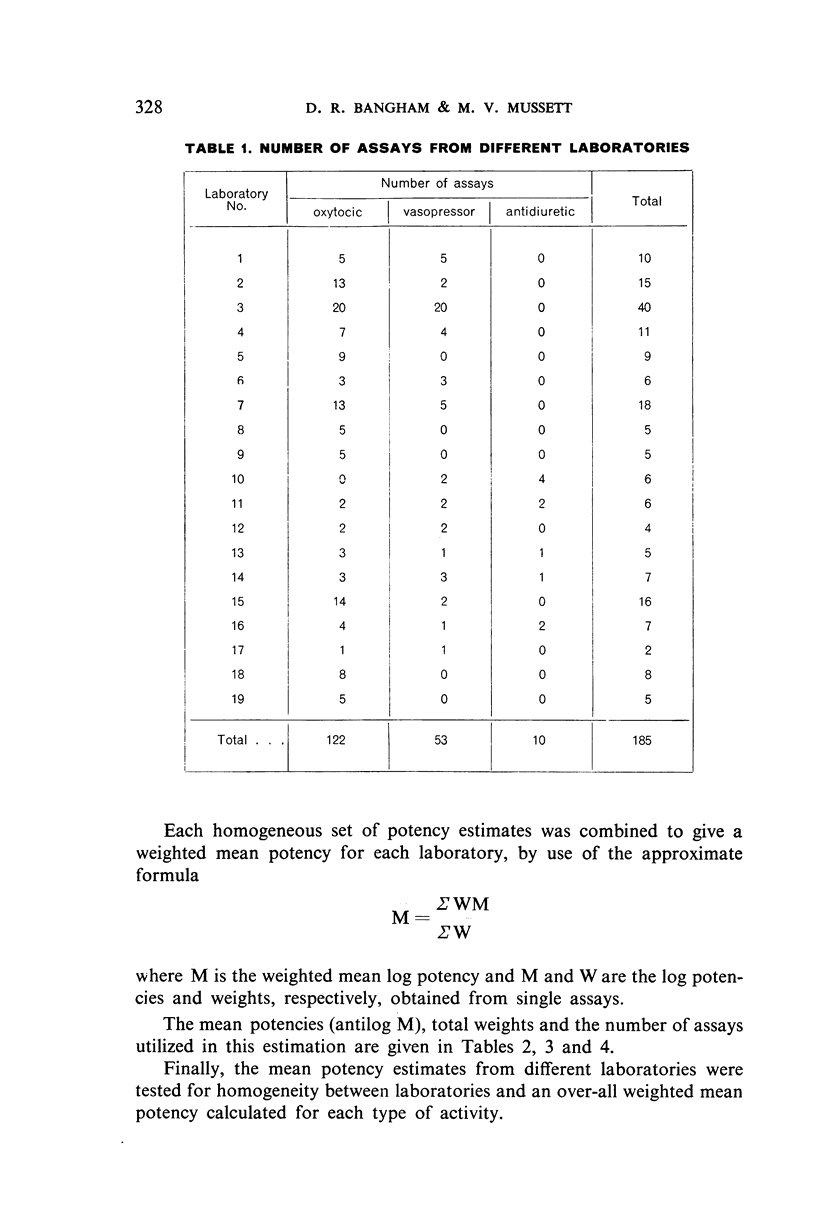
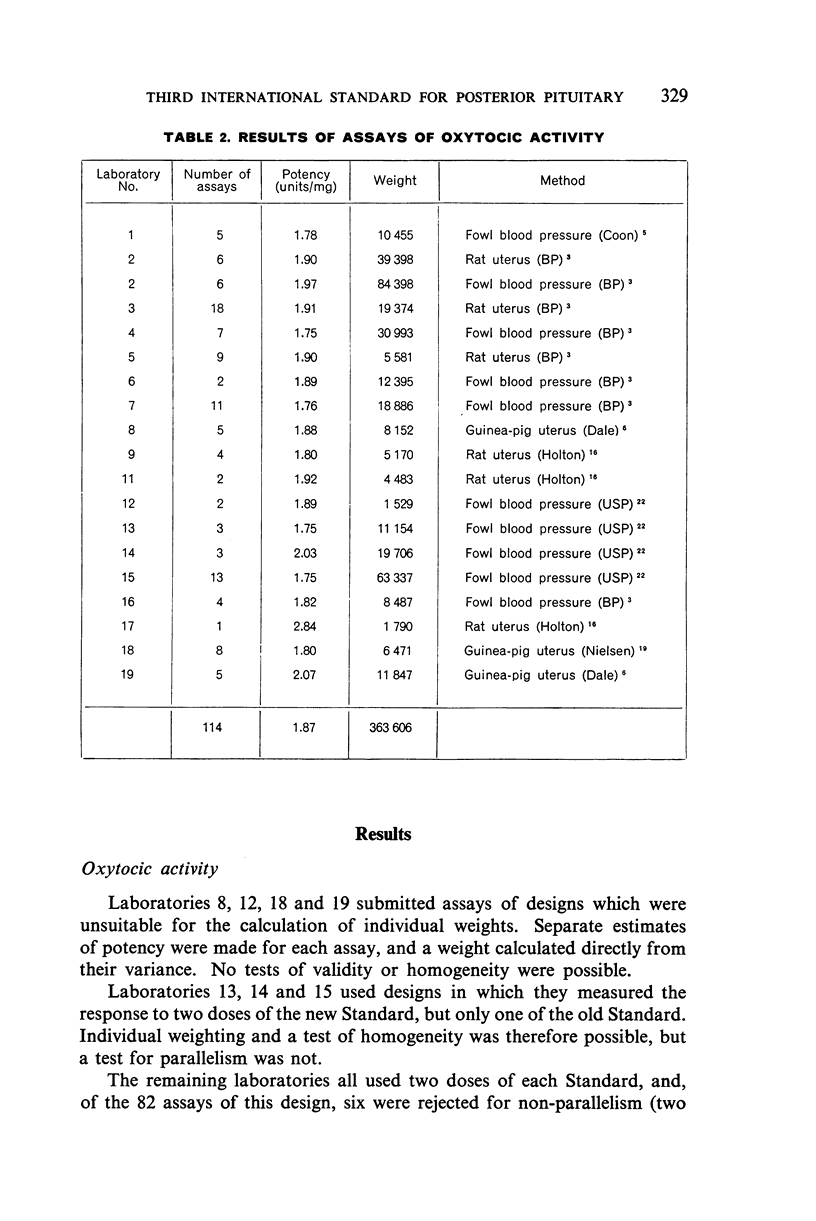
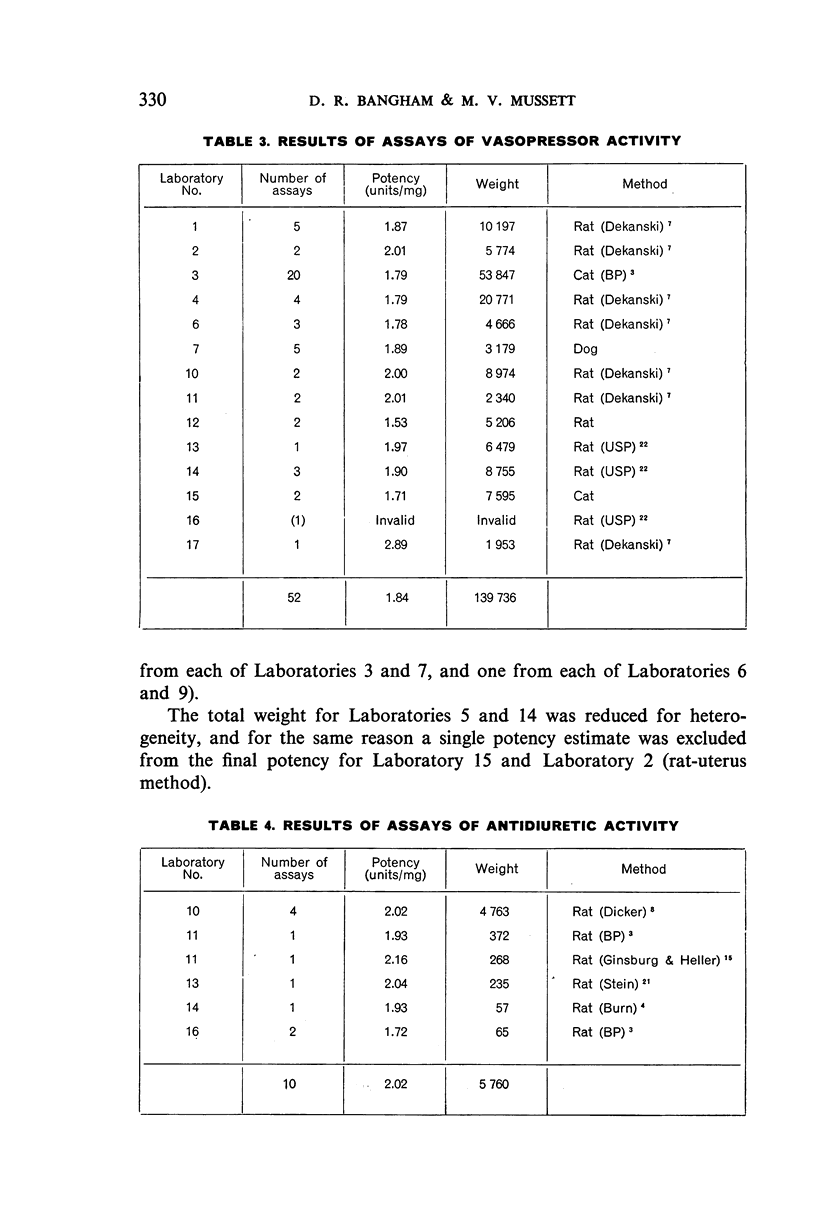
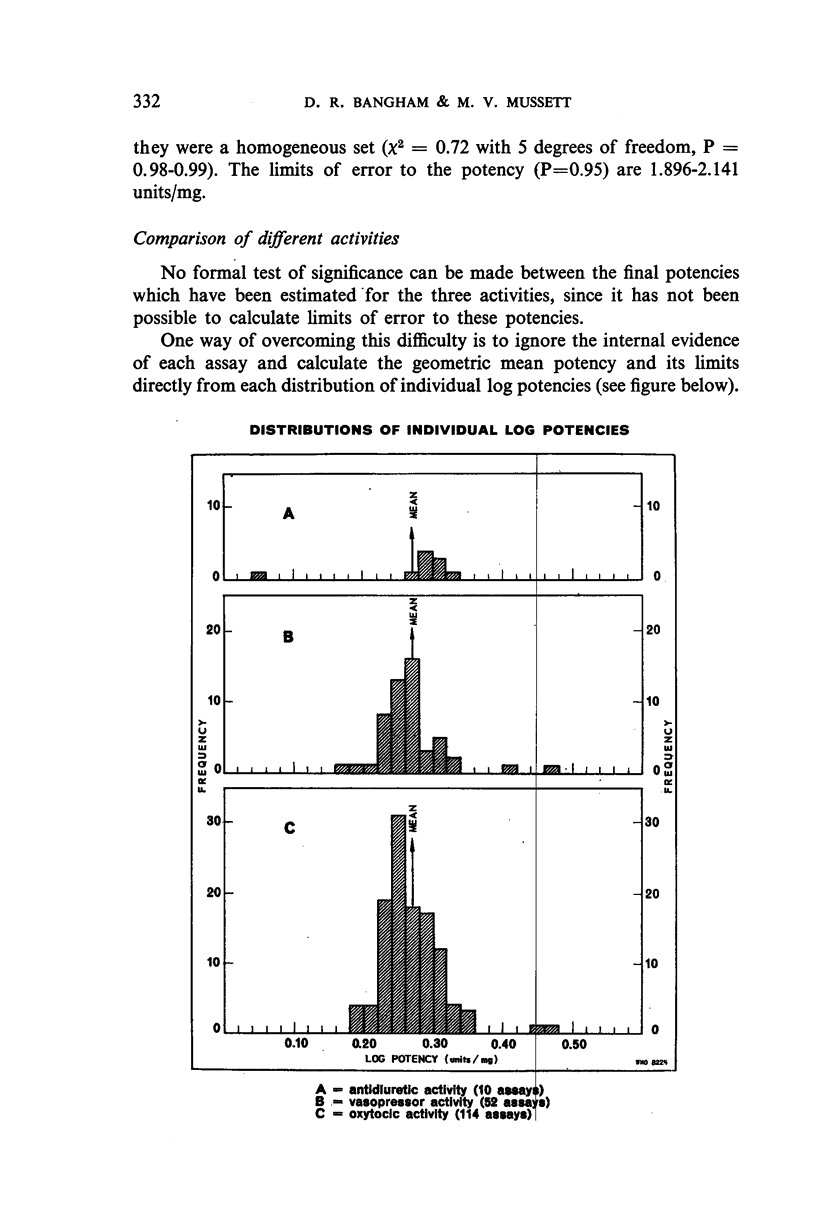
In October 1955, stocks of the Second International Standard for Posterior Pituitary were running low and the Department of Biological Standards of the National Institute for Medical Research, London, was asked to proceed with the arrangements for an international collaborative assay of material for the Third Standard. A single 142-g batch of posterior-pituitary-lobe powder was obtained and distributed in ampoules, in approximately 30-mg quantities. Samples were sent to 19 laboratories in 10 countries. In all, 185 assays were carried out, 122 for oxytocic activity, 53 for vasopressor activity and 10 for antidiuretic activity.
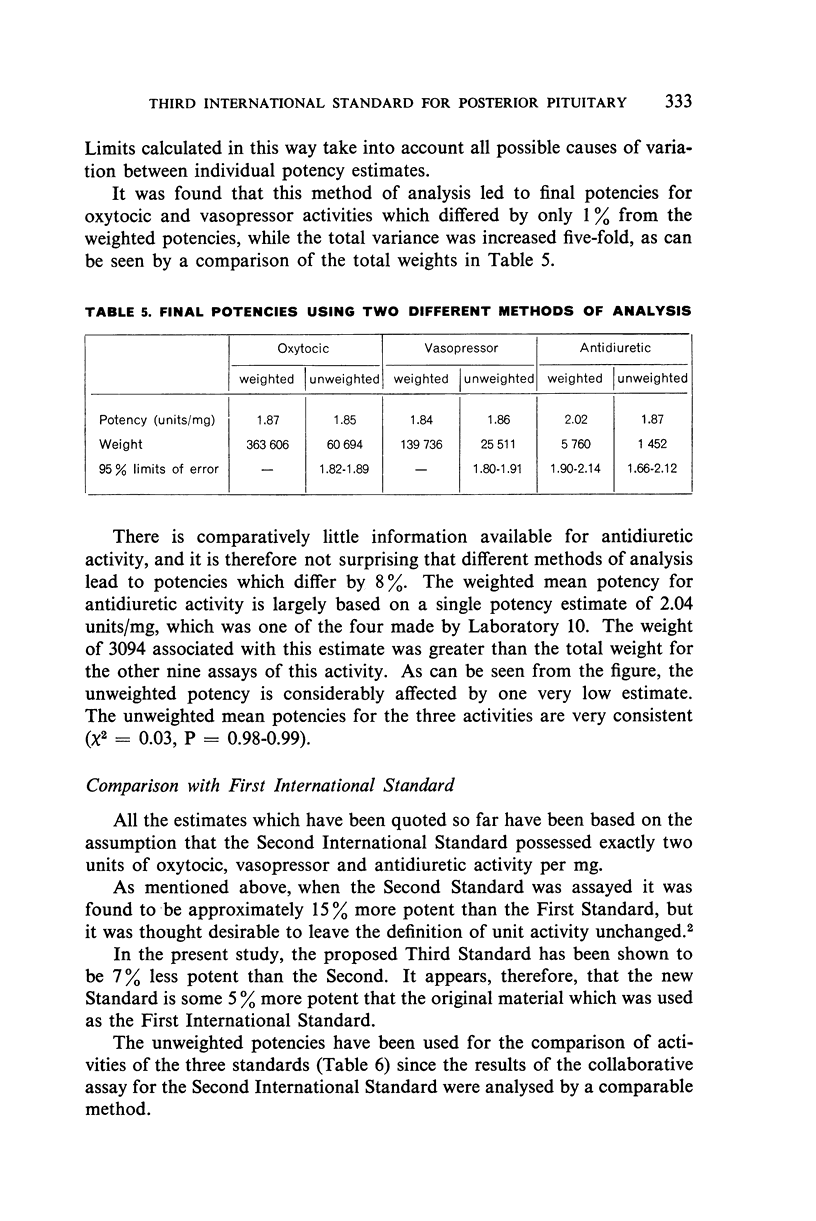
On the basis of the results, which were analysed statistically at the National Institute for Medical Research, it was agreed that the potency of the Third Standard (re-named International Standard for Oxytocic, Vasopressor and Antidiuretic Substances in 1956, in view of the recent synthesis of oxytocin and vasopressin) should be expressed as 2.0 International Units per milligram. The International Unit therefore remains unchanged as 0.5 mg of the dry powder.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DEKANSKI J. The quantitative assay of vasopressin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1952 Dec;7(4):567–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1952.tb00723.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKER S. E. A method for the assay of very small amounts of antidiuretic activity with a note on the antidiuretic titre of rat's blood. J Physiol. 1953 Oct;122(1):149–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROMAGEOT P., ACHER R., CLAUSER H., MAIER-HUSER H. Purification des hormones du lobe postérieur de l'hypophyse de boeuf. II. La vasopressine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Nov;12(3):424–431. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90162-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG M., HELLER H. The antidiuretic assay of vasopressin by intravenous injection into unanaesthetized rats. J Endocrinol. 1953 Jul;9(3):267–273. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0090267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLTON P. A modification of the method of Dale and Laidlaw for standardization of posterior pituitary extract. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1948 Dec;3(4):328–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1948.tb00396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H., LIGHTBOWN J. W., MUSSETT M. V. International standard for erythromycin. Bull World Health Organ. 1957;17(4-5):527–535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIVERMORE A. H., DU VIGNEAUD V. Preparation of high potency oxytocic material by the use of counter-current distribution. J Biol Chem. 1949 Aug;180(1):365–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIELSEN A. T., HAMBURGER C. The oxytocic and pressor activities of the U.S.P. Posterior Pituitary Reference Standard. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1956;12(2):200–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1956.tb01377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPENOE E. A., PIERCE J. G., DU VIGNEAUD V., VAN DYKE H. B. Oxytocic activity of purified vasopressin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Nov;81(2):506–508. doi: 10.3181/00379727-81-19924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN M., JINKS R., MIRSKY I. A. The bioassay of pitressin and antidiuretic substances in blood and urine. Endocrinology. 1952 Dec;51(6):492–503. doi: 10.1210/endo-51-6-492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


