Abstract
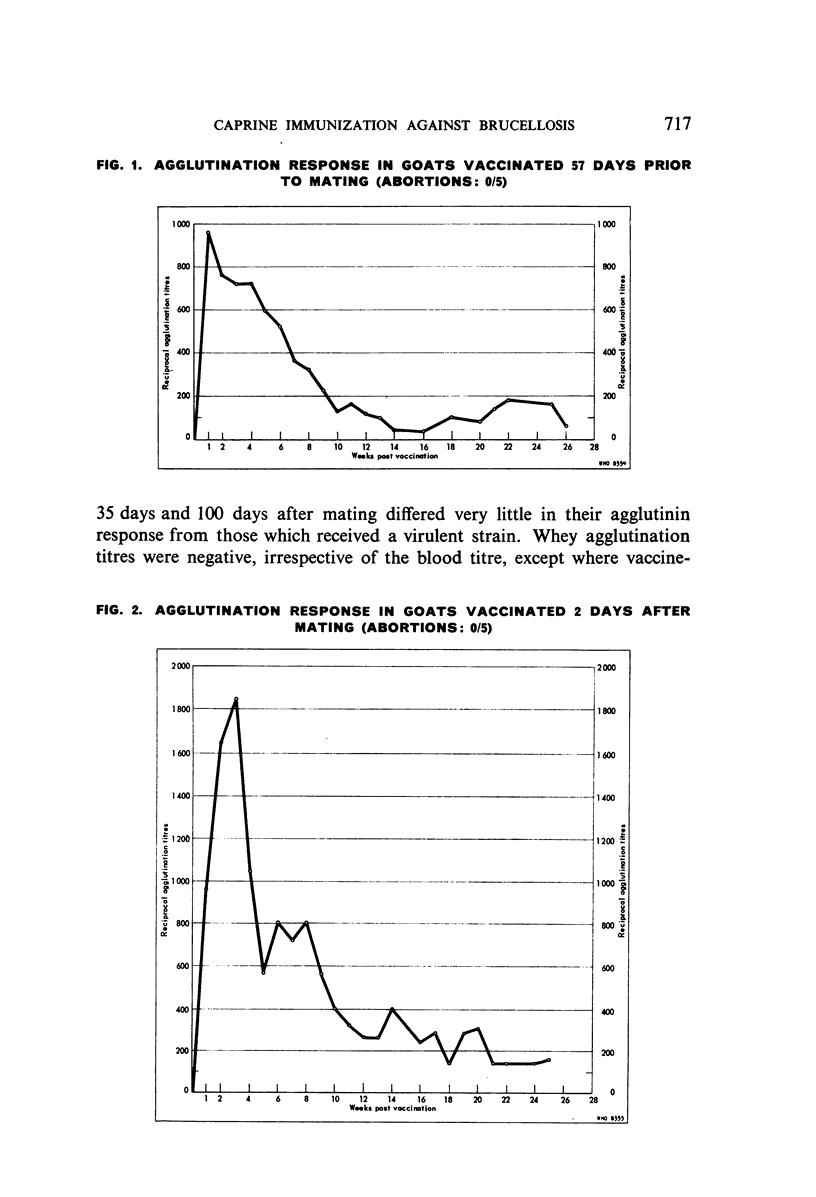
The ability of a streptomycin-non-dependent strain of Brucella melitensis to immunize goats against brucella infection and to protect against the abortion phenomenon was determined in a series of studies using both heat-killed and living cells of the strain. The data presented contrast the efficacy of both types of vaccine and demonstrate the importance of the relationship between mating date and date of vaccination in the prevention of abortion. Also included is an account of experiments on cross-immunity between infections induced by tubercle bacilli and brucellae, using monocytes from vaccinated and unvaccinated rabbits.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CARRERE L., QUATREFAGES H. Vaccination du cobaye par l'association: anacultures et souche vivante B. 112, contre l'infection à Brucella melitensis. Rev Immunol Ther Antimicrob. 1951;15(4):196–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELBERG S. S., FAUNCE K., Jr Immunization against Brucella infection. VI. Immunity conferred on goats by a nondependent mutant from a streptomycin-dependent mutant strain of Brucella melitensis. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):211–217. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.211-217.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELBERG S. S., HENDERSON D. W., HERZBERG M., PEACOCK S. Immunization against Brucella infection. IV. Response of monkeys to injection of a streptomycin-dependent strain of Brucella melitensis. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jun;69(6):643–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.6.643-648.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
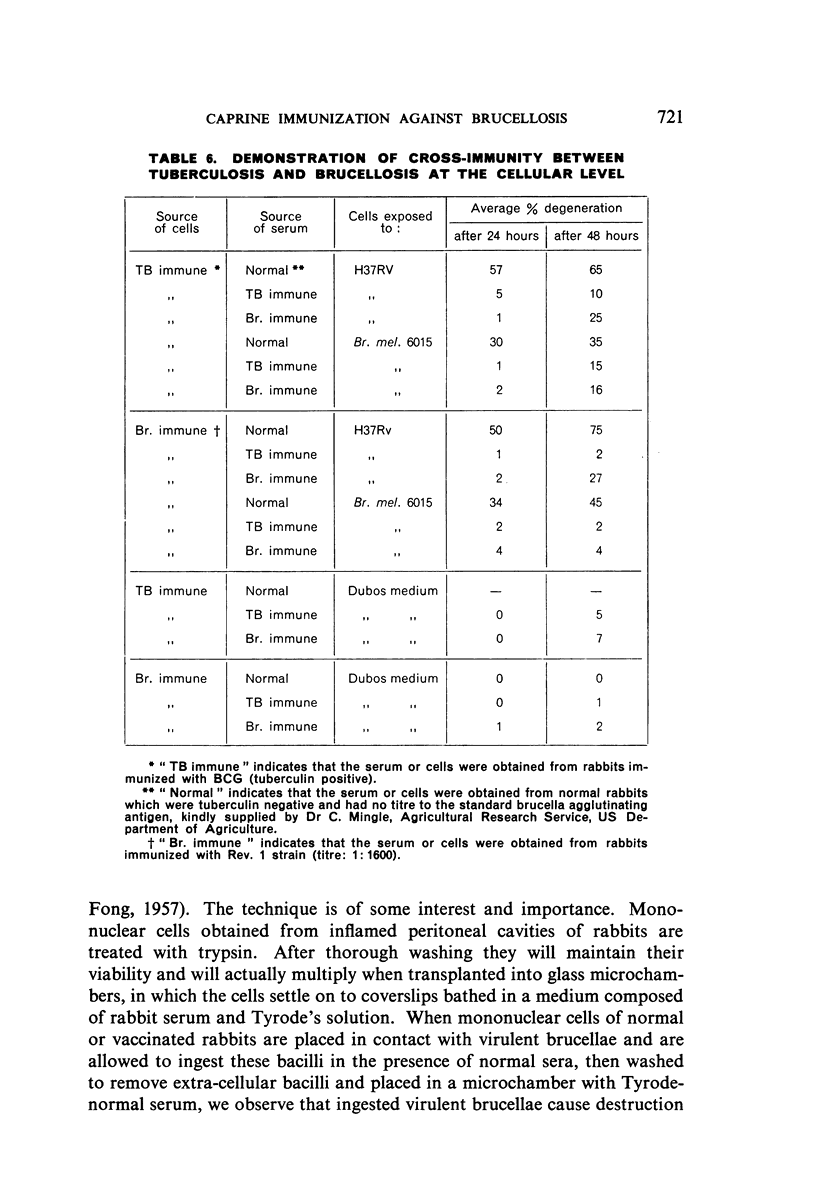
- ELBERG S. S., SCHNEIDER P., FONG J. Cross-immunity between Brucella melitensis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis; intracellular behavior of Brucella melitensis in monocytes from vaccinated animals. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):545–554. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELBERG S. S., STEINER P. E., DOLL J. P. Immunization against Brucella infection. V. Histopathologic appraisal of immunity induced in mice by a streptomycin-dependent mutant of Brucella melitensis. Am J Pathol. 1955 Nov-Dec;31(6):1065–1075. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERZBERG M., ELBERG S. S. Immunization against brucella infection. III. Response of mice and guinea pigs to injection of viable and nonviable suspensions of a streptomycin-dependent mutant of Brucella malitensis. J Bacteriol. 1955 Apr;69(4):432–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.4.432-435.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERZBERG M., ELBERG S. S., MEYER K. F. Immunization against brucella infection. II. Effectiveness of a streptomycin-dependent strain of brucella melitensis. J Bacteriol. 1953 Nov;66(5):600–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.5.600-605.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


