Abstract
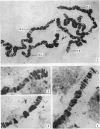
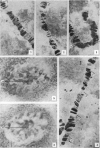
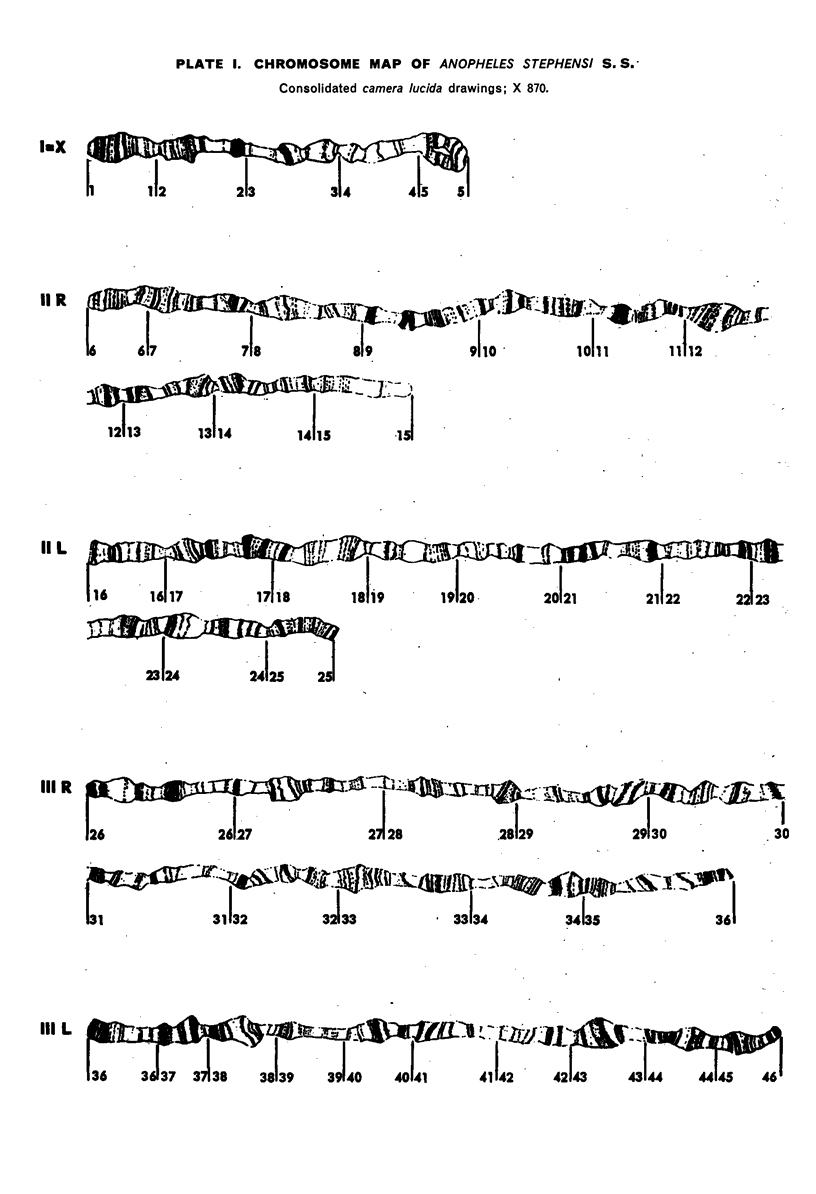
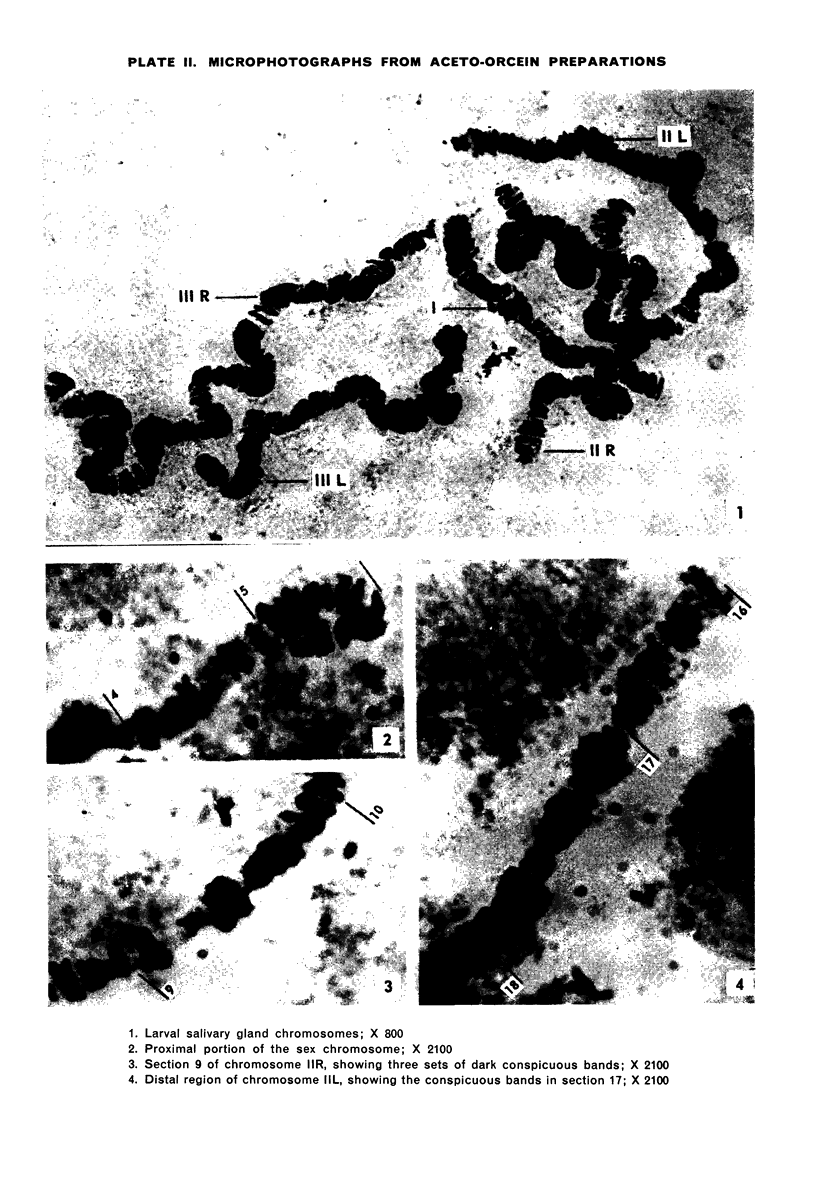
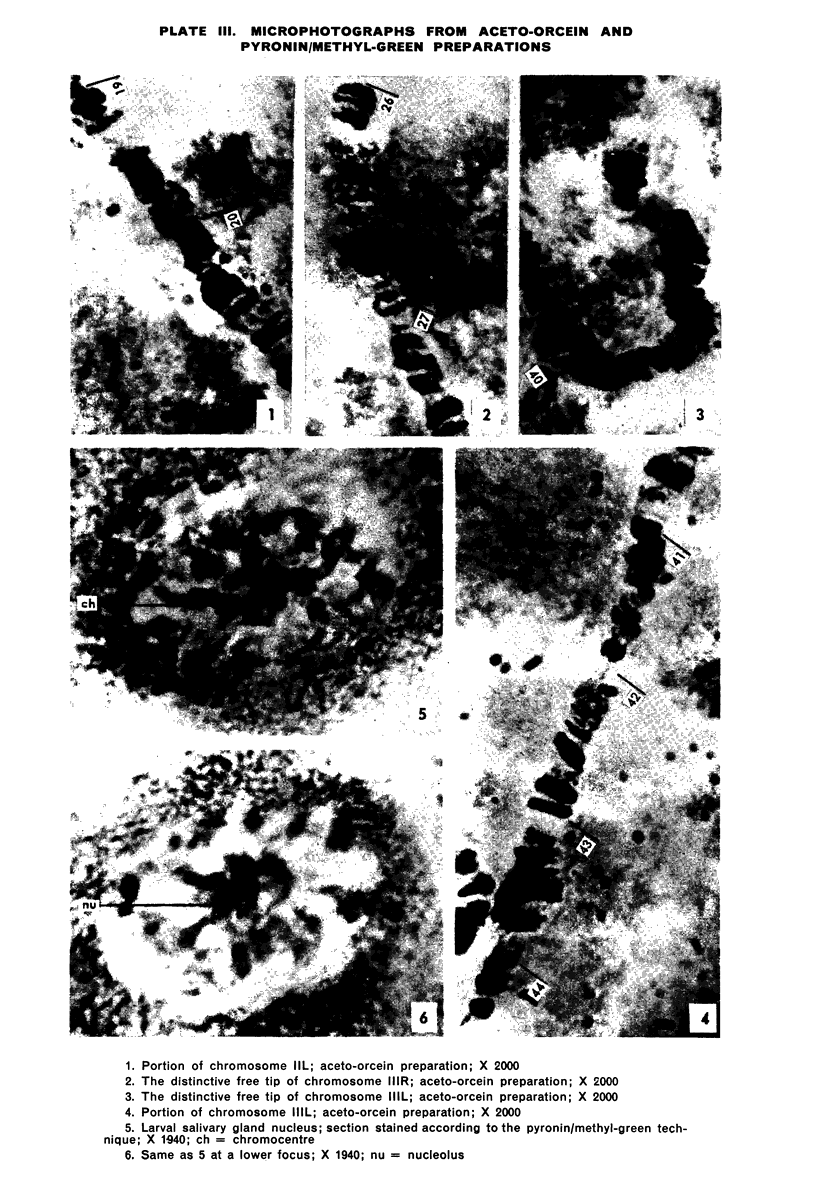
In the larvae of Anopheles stephensi s. s. five typically banded salivary chromosomes are present united proximally to a chromocentre. Maps have been constructed to illustrate their constant and characteristic banded pattern. Chromosome IIIR, however, has shown a variation in the form of a heterozygous inversion. The chromocentre is a small, fragile body, closely associated with the large nucleolus.
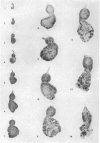
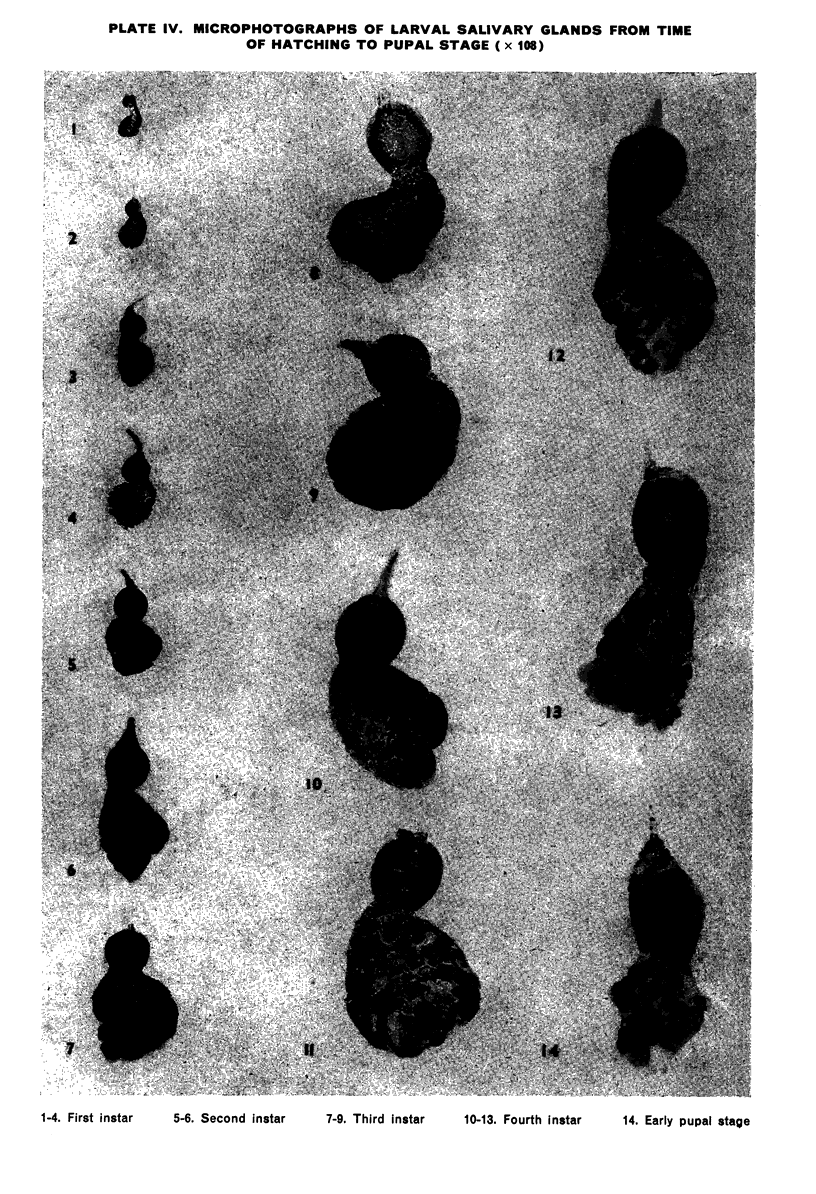
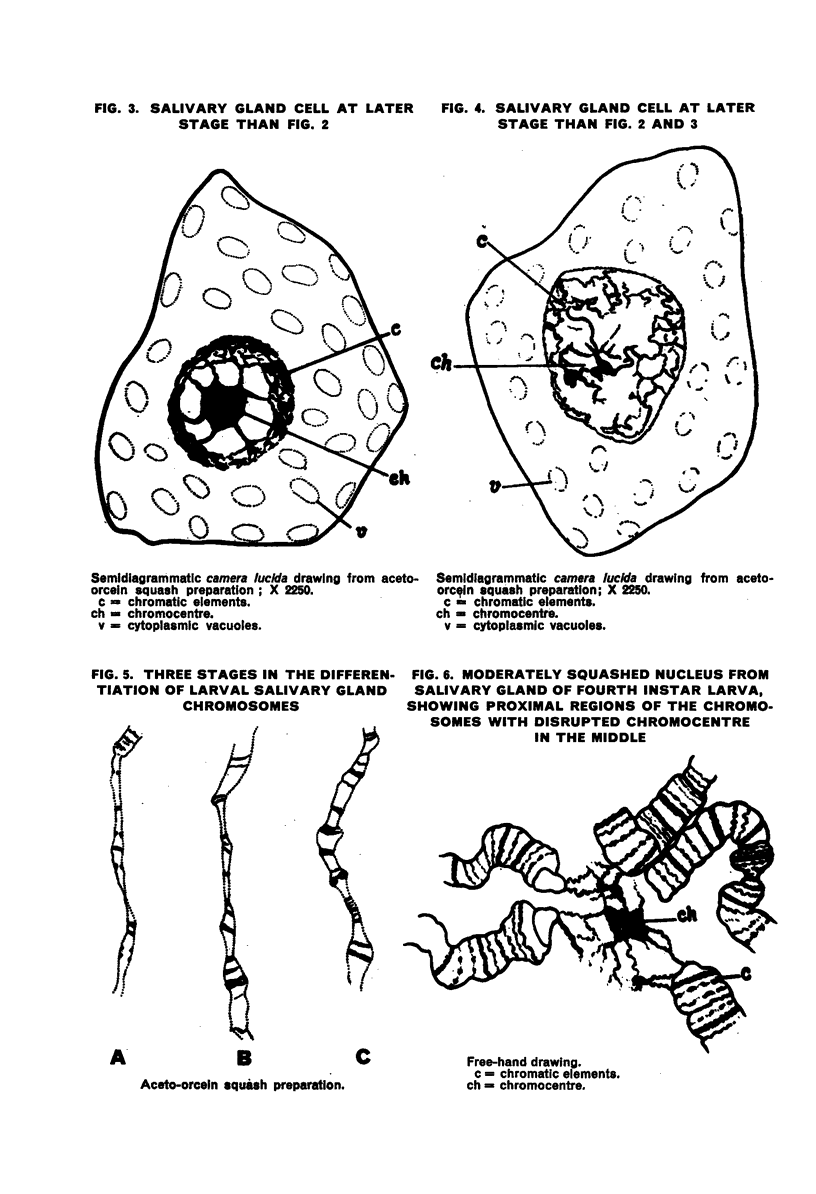
The development of the salivary glands in the larva is by cell-growth. The chromocentre appears at first as a heteropycnotic “crescent”, which soon gives place to a disc-shaped body. Later on in development the chromocentre loses both its heteropycnotic nature and compactness. The nucleolus persists until the time of histolysis of the glands, which begins at the distal end of the gland and gradually involves the more anterior regions. At the earliest observable stage the homologous chromatin elements constitute a tight coil. Full synapsis is preceded by a process of uncoiling accompanied by a chromomere-to-chromomere fusion. The rate of this process varies among different pairs of homologues and along different regions of the same pair. Synapsis is completed in the late third instar larva.
RNA is localized in the cytoplasm and the nucleolus of the larval salivary gland cells. The chromosomes and the chromocentre include DNA. A faint reaction of the interband areas show that DNA is present in a diffuse state throughout the chromosomes.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer H. Structure and Arrangement of Salivary Gland Chromosomes in Drosophila Species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1936 Apr;22(4):216–222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.22.4.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. A. Observations on the Relation between Salivary Gland Chromosomes and Multiple Chromosome Complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1936 Mar;22(3):186–187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.22.3.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck J. B. Growth and Development of the Salivary Gland Chromosomes in Sciara. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1937 Aug;23(8):423–428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.23.8.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'ALESSANDRO G., LAZZARO G. F., MARIANI M. Effect of DDT selection pressure on the frequency of chromosomal structures in Anopheles atroparvus. Bull World Health Organ. 1957;16(4):859–864. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIZZI G. Extension of the salivary chromosome method to Anopheles claviger, quadrimaculatus and aquasalis. Nature. 1953 Jun 13;171(4363):1072–1072. doi: 10.1038/1711072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIZZI G., HOLSTEIN M. Etude cytogénétique d'Anopheles gambiae. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;15(3-5):425–435. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber L. F., Sprague V. G. ALFALFA YELLOWS. Science. 1933 Oct 27;78(2026):385–386. doi: 10.1126/science.78.2026.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITZMILLER J. B. Mosquito genetics and cytogenetics. Rev Bras Malariol Doencas Trop. 1953 Oct;5(4):285–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURNICK N. B. Histological staining with methyl-green-pyronin. Stain Technol. 1952 Sep;27(5):233–242. doi: 10.3109/10520295209105083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter T S. A New Method for the Study of Chromosome Aberrations and the Plotting of Chromosome Maps in Drosophila Melanogaster. Genetics. 1934 May;19(3):175–188. doi: 10.1093/genetics/19.3.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter T S, Griffen A B. The Structure and the Development of the Salivary Gland Chromosomes of Simulium. Genetics. 1937 Nov;22(6):612–633. doi: 10.1093/genetics/22.6.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton E. Salivary Gland Type Chromosomes in Mosquitoes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1942 Jul;28(7):268–272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.28.7.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]