Abstract
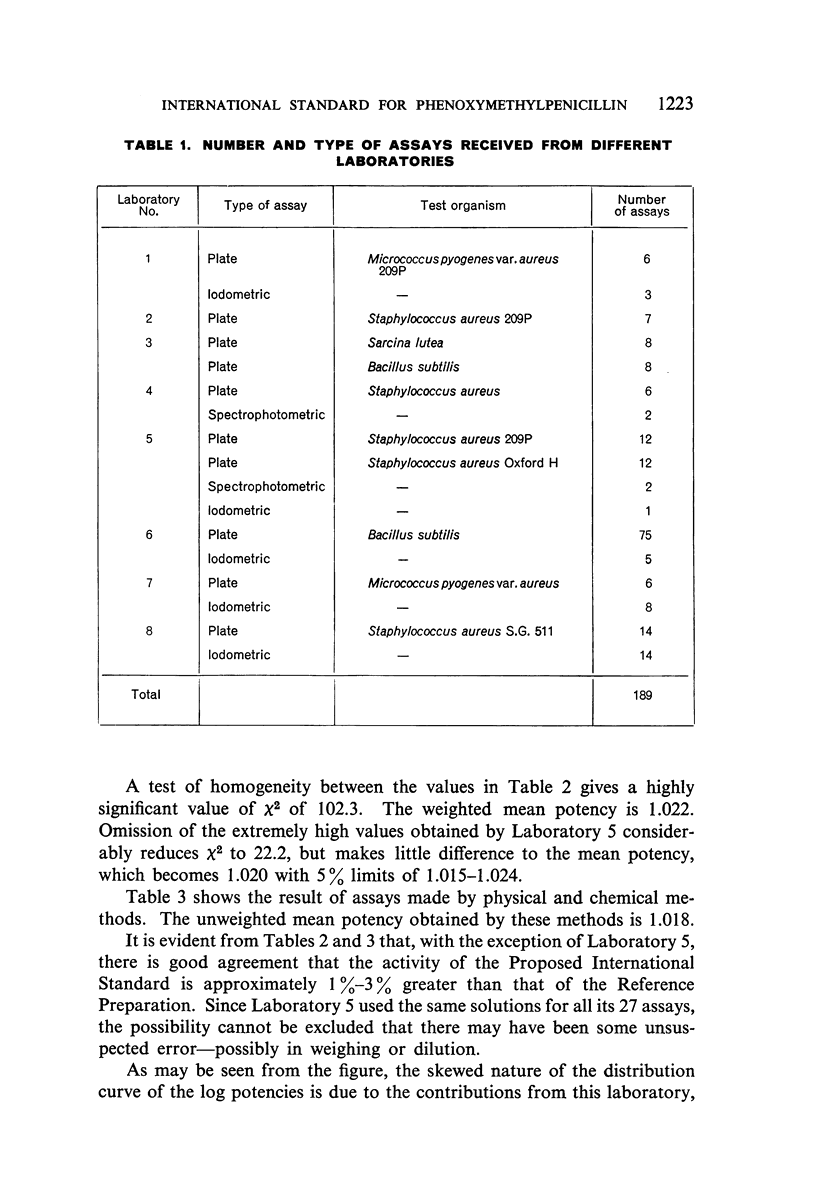
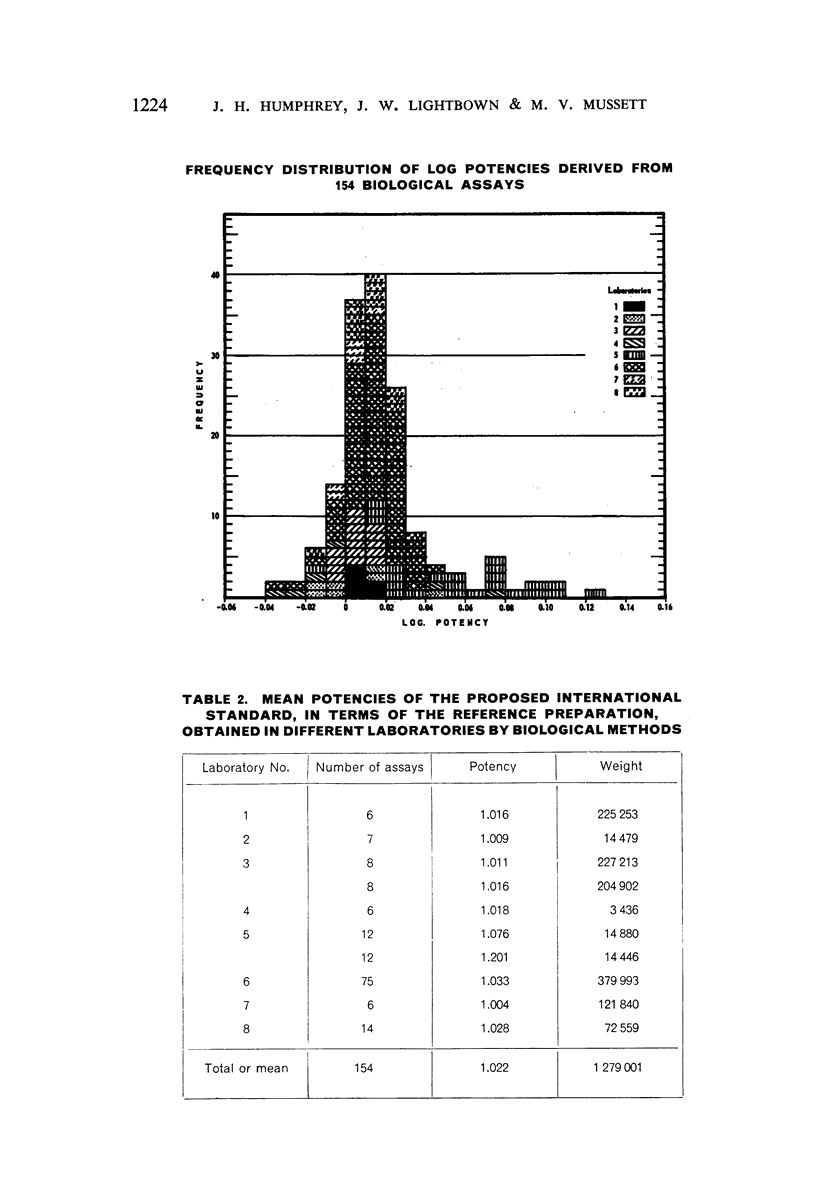
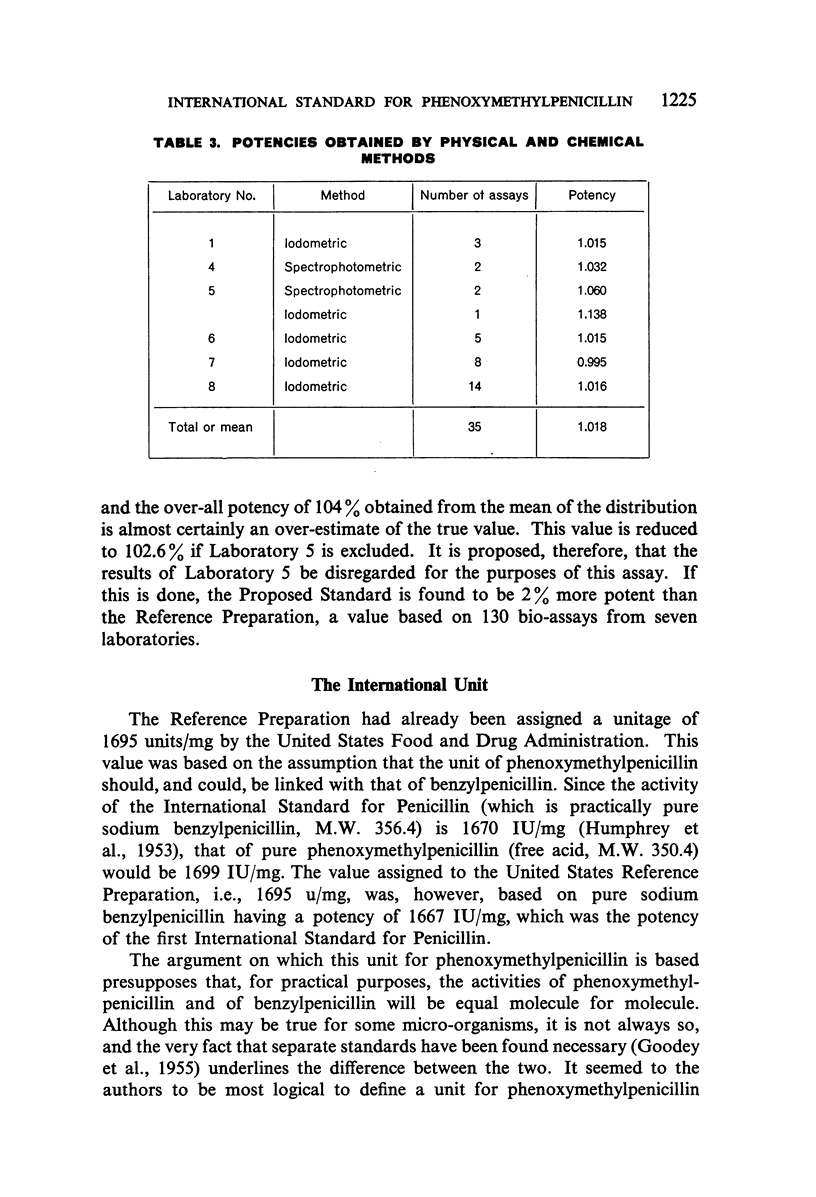
A batch of highly purified phenoxymethylpenicillin has been examined by eight laboratories in seven different countries, and has been assayed against the phenoxymethylpenicillin standard of the Food and Drug Administration of the US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare. The material examined has been established as the International Standard for Phenoxymethylpenicillin, and the International Unit of Phenoxymethylpenicillin is defined as the activity contained in 0.000590 mg of the International Standard.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GOODEY R., REED K. N., STEPHENS J. Chemical and microbiological assay of penicillin V. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1955 Oct;7(10):692–701. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1955.tb12082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H., LIGHTBOWN J. W., MUSSETT M. V. International standard for erythromycin. Bull World Health Organ. 1957;17(4-5):527–535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER G., COX R. J., RICHARDS D. The purification and characterisation of penicillin V. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1955 Oct;7(10):683–691. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1955.tb12081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEPHENS J., GRAINGER A. Paper chromatography of penicillin V. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1955 Oct;7(10):702–705. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1955.tb12083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


