Abstract
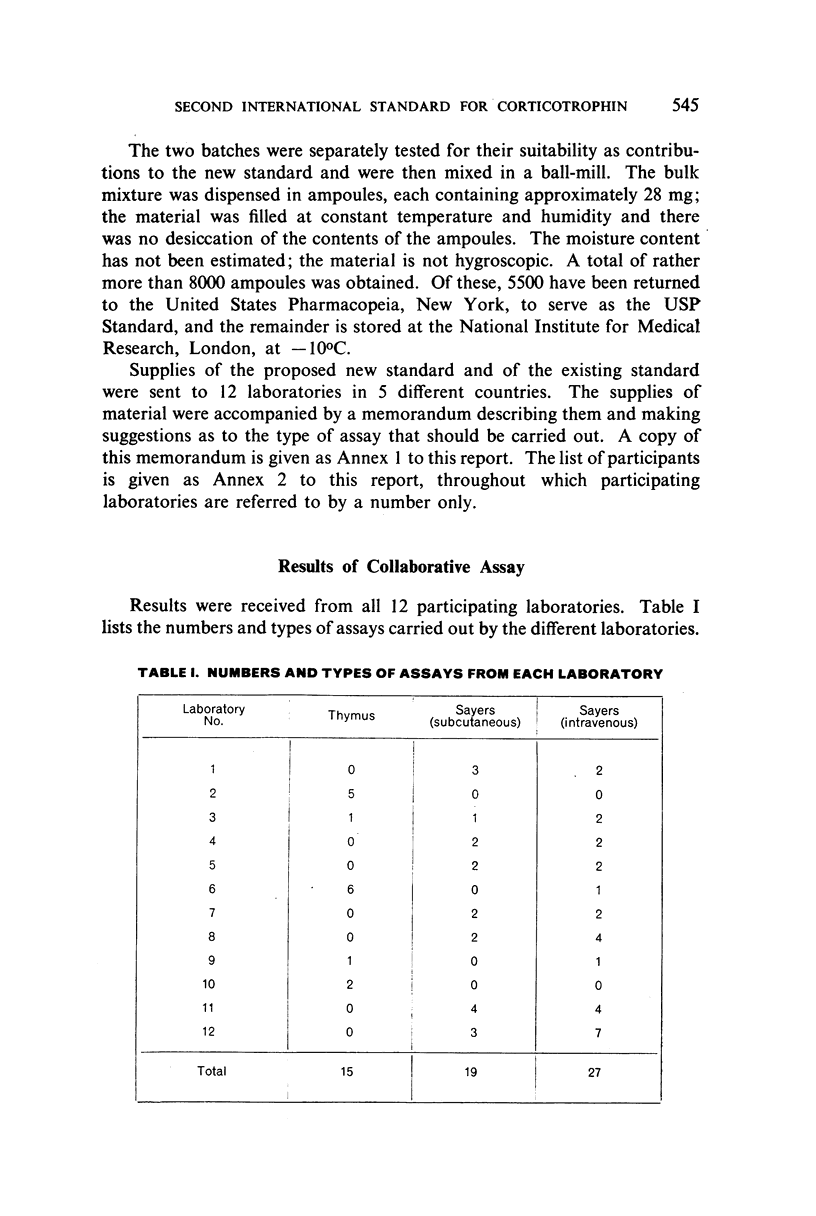
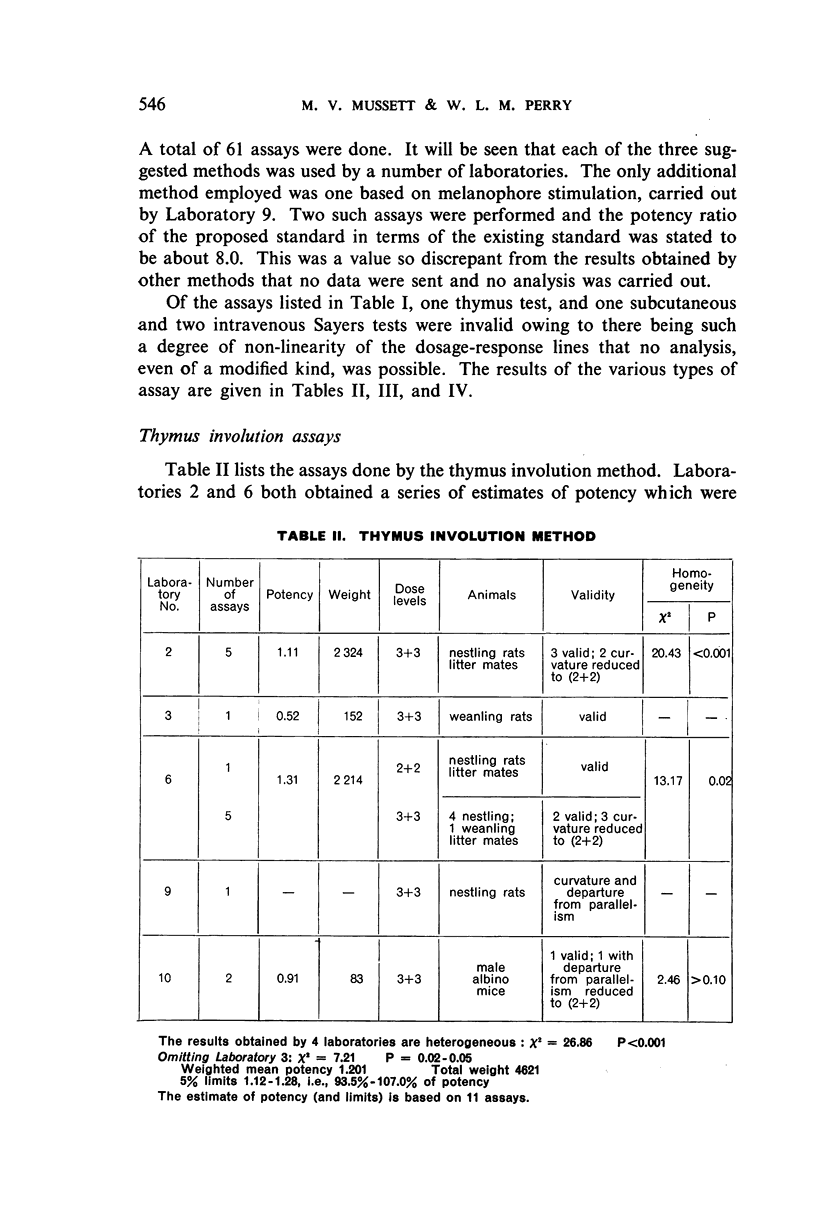
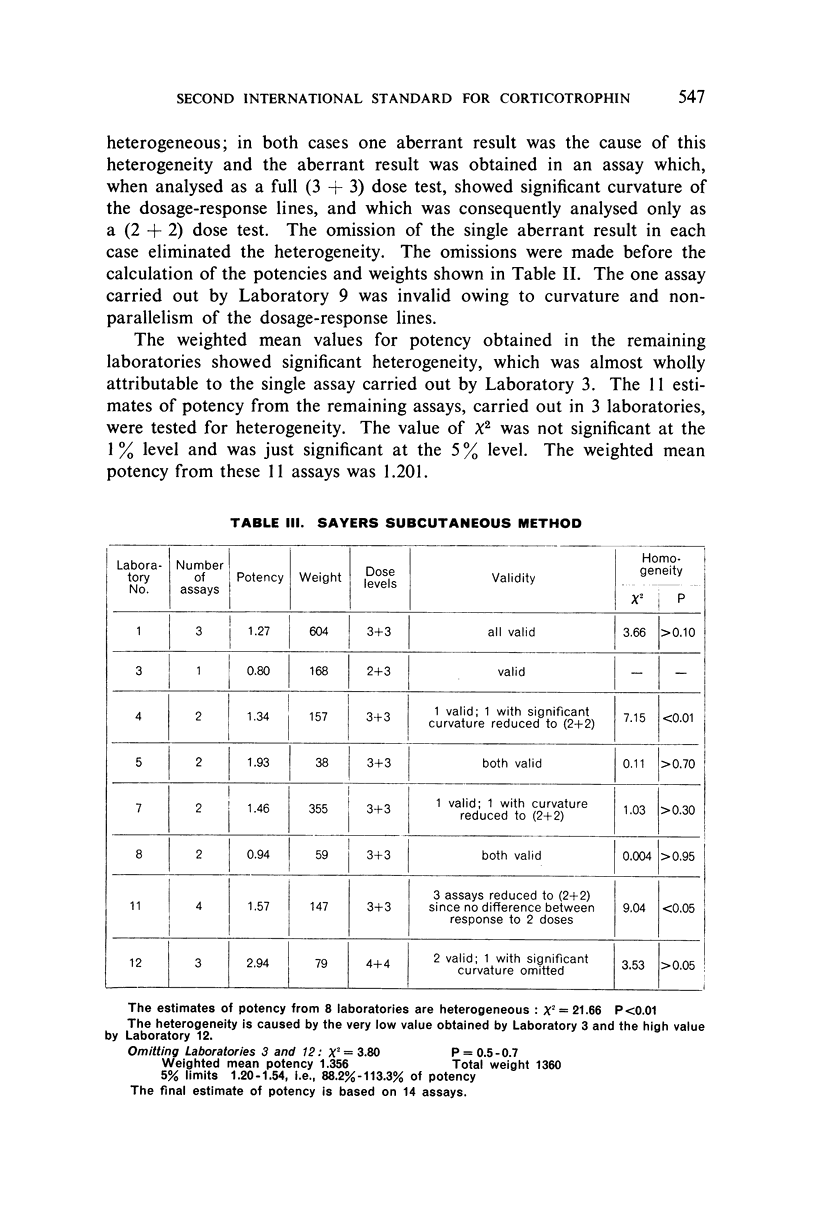
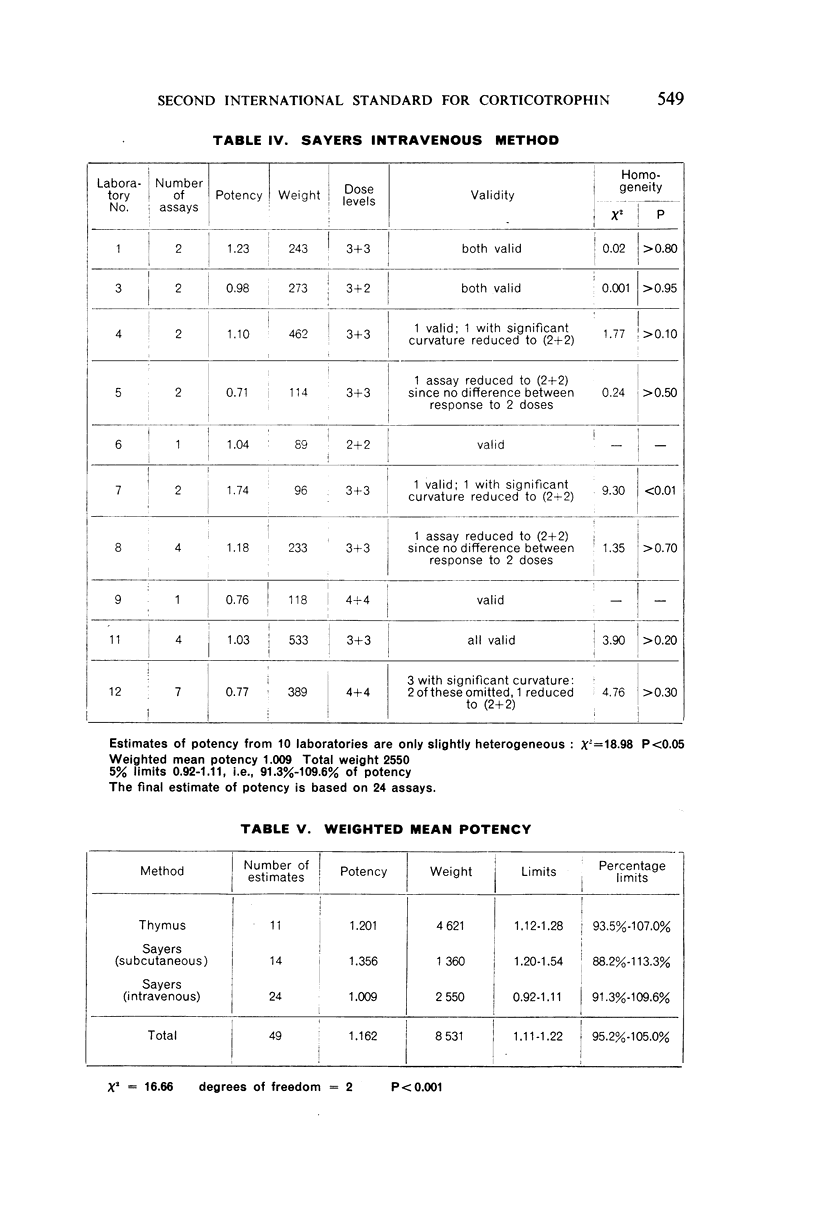
The authors describe the steps taken to establish the Second International Standard for Corticotrophin and discuss the results of the collaborative assay in which it was compared with the First International Standard. Sixty-one assays of the blended material from two batches of crude corticotrophin prepared by the Astwood procedure, but not subjected to oxycellulose purification, were carried out by 12 laboratories in 5 countries. Almost exclusively, the assay methods used were the thymus involution method and the subcutaneous and intravenous Sayers methods. It was estimated from the statistical analysis of the results that the new standard is 1.14 times as potent as the existing standard, and the International Unit has therefore been re-defined as 0.88 mg of the new standard.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- MUSSETT M. V., PERRY W. L. The international standard for thyrotrophin. Bull World Health Organ. 1955;13(5):917–929. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON R. E., FISHER J. D. Correlation of preparative history and method of assay of corticotropin with clinical potency. Endocrinology. 1953 May;52(5):496–509. doi: 10.1210/endo-52-5-496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


