Abstract
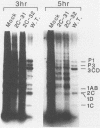
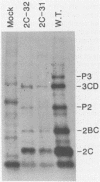
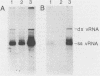
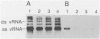
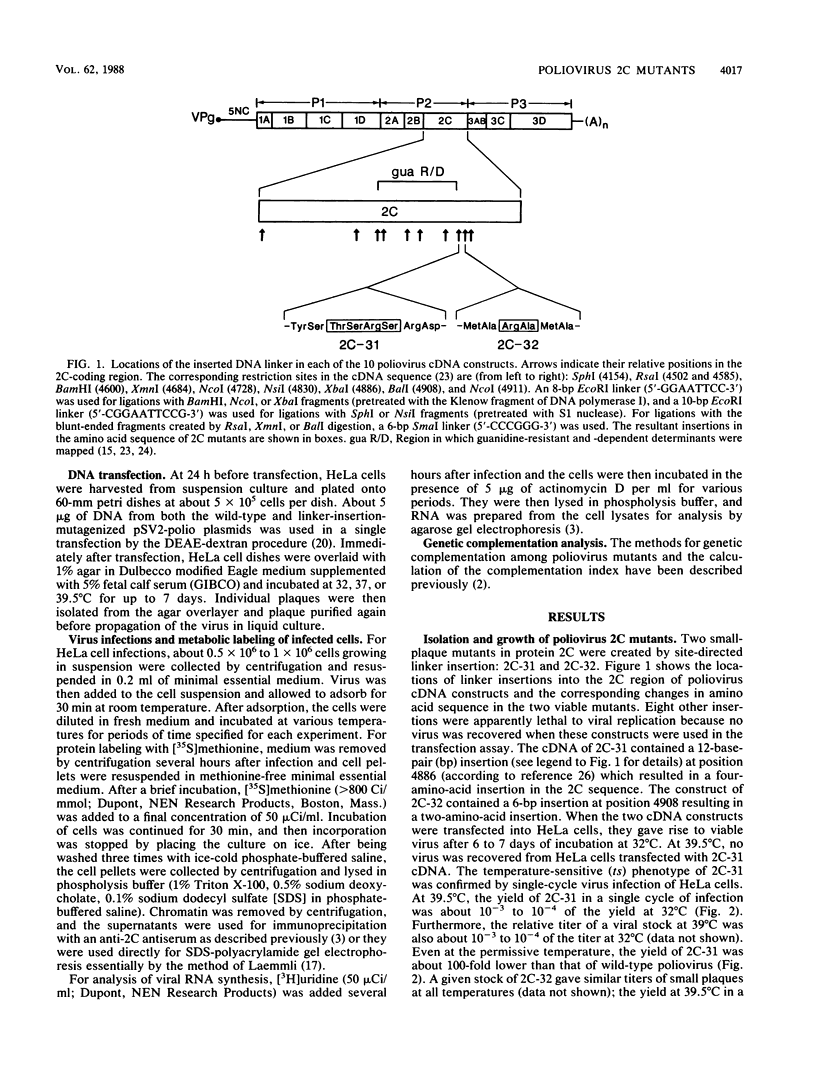
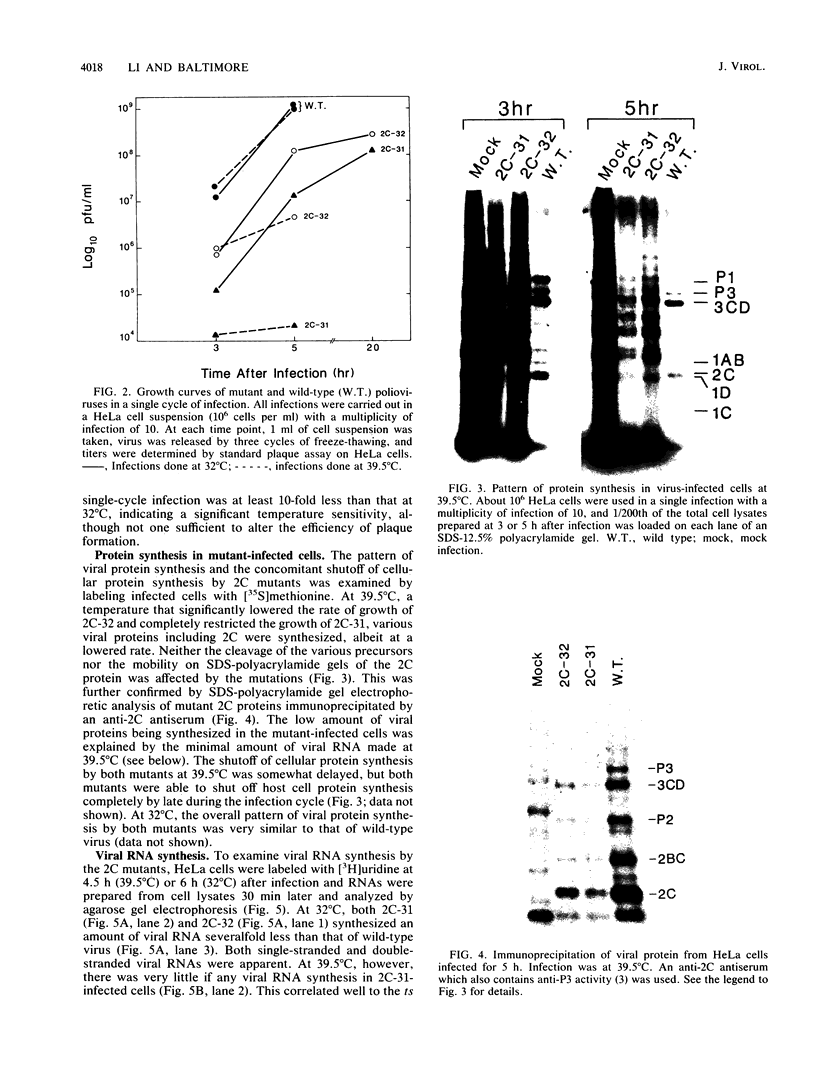
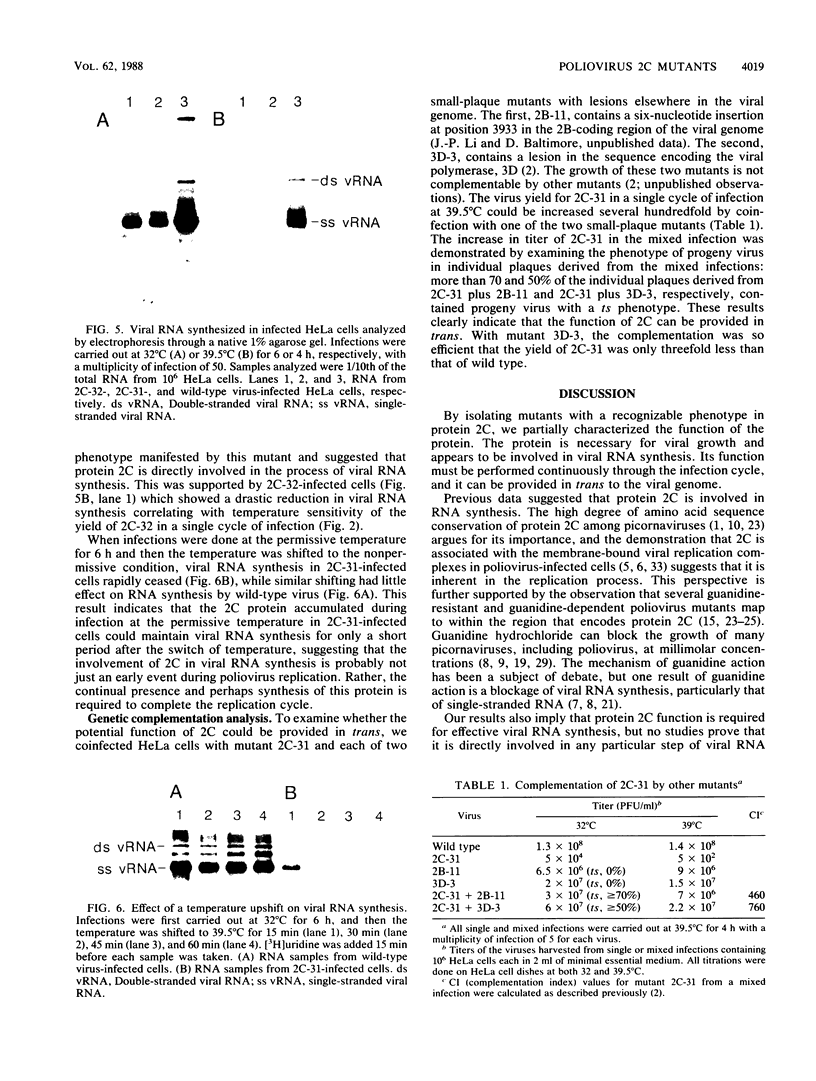
Two poliovirus mutants were isolated that contain an oligonucleotide linker insertion in the 2C-coding region of the viral genome. One, 2C-31, has a strongly temperature-sensitive phenotype and the other, 2C-32, forms small plaques on HeLa cell monolayers at all temperatures. Both mutants have a severe temperature-sensitive defect in viral RNA synthesis but little effect on the types of viral protein that are made. Temperature shift experiments showed that the 2C function is continuously required for viral RNA synthesis to proceed. The 2C mutants could be complemented in trans by mutants with mutations in other viral proteins. Protein 2C is also the locus of the guanidine resistance and dependence mutants, a drug whose action also affects viral RNA synthesis. Thus, protein 2C is one that is needed continually for viral RNA synthesis and, at least with these temperature-sensitive alleles, can be provided in trans.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Kamer G., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Similarity in gene organization and homology between proteins of animal picornaviruses and a plant comovirus suggest common ancestry of these virus families. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7251–7267. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz K., Egger D., Pasamontes L. Association of polioviral proteins of the P2 genomic region with the viral replication complex and virus-induced membrane synthesis as visualized by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry and autoradiography. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz K., Egger D., Rasser Y., Bossart W. Intracellular distribution of poliovirus proteins and the induction of virus-specific cytoplasmic structures. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90531-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Shimshick E. J., Yin F. H. Association of the polioviral RNA polymerase complex with phospholipid membranes. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):457–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.457-466.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWTHER D., MELNICK J. L. Studies of the inhibitory action of guanidine on poliovirus multiplication in cell cultures. Virology. 1961 Sep;15:65–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Action of guanidine on the replication of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):408–417. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franssen H., Leunissen J., Goldbach R., Lomonossoff G., Zimmern D. Homologous sequences in non-structural proteins from cowpea mosaic virus and picornaviruses. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):855–861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Balitmore D. Initiation of polyribosome formation in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):275–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90302-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IKEGAMI N., EGGERS H. J., TAMM I. RESCUE OF DRUG-REQUIRING AND DRUG-INHIBITED ENTEROVIRUSES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1419–1426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Asso J., Baltimore D. Further evidence on the formation of poliovirus proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Polypeptide cleavages in the formation of poliovirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):77–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Baltimore D. The mechanism of RNA recombination in poliovirus. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):433–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90600-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LODDO B., FERRARI W., BROTZU G., SPANEDDA A. In vitro inhibition of infectivity of polio viruses by guanidine. Nature. 1962 Jan 6;193:97–98. doi: 10.1038/193097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., Bestwick R. K., Spiro C., Kabat D. The membrane glycoprotein of Friend spleen focus-forming virus: evidence that the cell surface component is required for pathogenesis and that it binds to a receptor. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2782–2792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2782-2792.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J., Levintow L. Dynamics of poliovirus-specific RNA synthesis and the effects of inhibitors of virus replication. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):634–642. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallansch M. A., Kew O. M., Semler B. L., Omilianowski D. R., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E., Rueckert R. R. Protein processing map of poliovirus. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):873–880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.873-880.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. E., Diamond D. C., Emini E. A., Wimmer E. Guanidine-selected mutants of poliovirus: mapping of point mutations to polypeptide 2C. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):638–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.638-646.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. E., Rohl H., Wimmer E. Guanidine-dependent mutants of poliovirus: identification of three classes with different growth requirements. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90316-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. E., Wimmer E. Production of guanidine-resistant and -dependent poliovirus mutants from cloned cDNA: mutations in polypeptide 2C are directly responsible for altered guanidine sensitivity. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):793–796. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.793-796.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGHTSEL W. A., DICE J. R., McALPINE R. J., TIMM E. A., McLEAN I. W., Jr, DIXON G. J., SCHABEL F. M., Jr Antiviral effect of guanidine. Science. 1961 Aug 25;134(3478):558–559. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3478.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Meriam C. Poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutant containing a single nucleotide deletion in the 5'-noncoding region of the viral RNA. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):498–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Bernstein H. D., Baltimore D. A poliovirus temperature-sensitive RNA synthesis mutant located in a noncoding region of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):571–575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. C., Atkinson T., Smith M., Pawson T. Identification of functional regions in the transforming protein of Fujinami sarcoma virus by in-phase insertion mutagenesis. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90385-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr Evidence for large precursor proteins in poliovirus synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):966–971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane fractions active in poliovirus RNA replication contain VPg precursor polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):33–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tershak D. R. Inhibition of poliovirus polymerase by guanidine in vitro. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):313–318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.313-318.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Flanegan J. B. Identification of poliovirus polypeptide P63 as a soluble RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.732-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]