Abstract
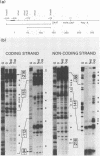
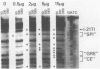
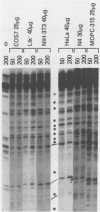
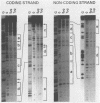
The long terminal repeats (LTRs) of cloned intracisternal A particles (IAPs) can function as effective promoters in heterologous and homologous cell types (K. K. Lueders, J. W. Fewell, E. L. Kuff, and T. Koch, Mol. Cell. Biol. 4:2128-2135, 1984) and respond to transcriptional factors induced by various nuclear oncogene products (S. Luria and M. Horowitz, J. Virol. 57:998-1003, 1986). Using the first 139 base pairs of the U3 region of a cloned mouse IAP LTR as probe, we demonstrated multiple exonuclease III stop sites which appeared specifically in the presence of nuclear extract protein. Various extracts gave similar footprints, but the amount of nuclear protein required varied up to 10-fold. Cell lines transformed with known nuclear oncogenes, such as adenovirus E1a and E1b (293 cells), simian virus 40 large T antigen (COS7 cells), and c-myc (MOPC-315 cells) had more and/or higher-affinity factors for the IAP LTR than extracts from HeLa, CV1, and NIH 3T3 cells did. DNase I footprinting revealed at least five distinct protein-binding domains within the 139-base-pair region. These domains correspond to segments of highly conserved nucleotide sequence among a number of IAP LTRs. Gel retardation studies with oligonucleotides encompassing the DNase I footprint sites showed that the nuclear factors are present in different proportions and different absolute levels in extracts from different cell types. Moreover, the oligonucleotide probes indicate that individual motifs can be occupied independently of one another. Three of the DNase I footprints include a sequence with homology to the simian virus 40 core enhancer and sequence motifs that closely resemble the binding sites for transcription factors SP1 and AP-1. The other two binding sites are not obviously related to previously recognized motifs. The multiple protein-binding sites in close proximity indicate the complex regulatory mechanism for IAP transcription.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augenlicht L. H., Kobrin D., Pavlovec A., Royston M. E. Elevated expression of an endogenous retroviral long terminal repeat in a mouse colon tumor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt D. W., Reith A. D., Brammar W. J. A retroviral provirus closely associated with the Ren-2 gene of DBA/2 mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8579–8593. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani E., Dreazen O., Klar A., Rechavi G., Ram D., Cohen J. B., Givol D. Activation of the c-mos oncogene in a mouse plasmacytoma by insertion of an endogenous intracisternal A-particle genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7118–7122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Brown A. R., Gourlie B. B., Huang R. C. Nucleotide sequences of murine intracisternal A-particle gene LTRs have extensive variability within the R region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):289–302. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Huang R. C. Functional analysis of the long terminal repeats of intracisternal A-particle genes: sequences within the U3 region determine both the efficiency and direction of promoter activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1093–1102. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Unger T., Rechavi G., Canaani E., Givol D. Rearrangement of the oncogene c-mos in mouse myeloma NSI and hybridomas. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):797–799. doi: 10.1038/306797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Josephs S. F., Curran T. The Fos complex and Fos-related antigens recognize sequence elements that contain AP-1 binding sites. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1150–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.2964084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni-Celli S., Hsiao W. L., Weinstein I. B. Rearranged c-mos locus in a MOPC 21 murine myeloma cell line and its persistence in hybridomas. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):795–796. doi: 10.1038/306795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. G., Shulman M. J., Hozumi N. Transposition of two different intracisternal A particle elements into an immunoglobulin kappa-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2565–2572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. G., Shulman M. J., Murialdo H., Gibson D. M., Hozumi N. Mutant immunoglobulin genes have repetitive DNA elements inserted into their intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7425–7429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M., Luria S., Rechavi G., Givol D. Mechanism of activation of the mouse c-mos oncogene by the LTR of an intracisternal A-particle gene. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2937–2941. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C. C., Overton G. C. Expression of the intracisternal A-particle is elevated during differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):150–157. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Feenstra A., Lueders K., Rechavi G., Givol D., Canaani E. Homology between an endogenous viral LTR and sequences inserted in an activated cellular oncogene. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):547–548. doi: 10.1038/302547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Feenstra A., Lueders K., Smith L., Hawley R., Hozumi N., Shulman M. Intracisternal A-particle genes as movable elements in the mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1992–1996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Fewell J. W. Intracisternal A-particle gene expression in normal mouse thymus tissue: gene products and strain-related variability. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):474–483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Smith L. A., Lueders K. K. Intracisternal A-particle genes in Mus musculus: a conserved family of retrovirus-like elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):216–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnel B., Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Functional analysis of the glucocorticoid regulatory elements present in the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat. A synthetic distal binding site can replace the proximal binding domain. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Fewell J. W., Kuff E. L., Koch T. The long terminal repeat of an endogenous intracisternal A-particle gene functions as a promoter when introduced into eucaryotic cells by transfection. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2128–2135. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Intracisternal A-particle genes: identification in the genome of Mus musculus and comparison of multiple isolates from a mouse gene library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3571–3575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Sequences associated with intracisternal A particles are reiterated in the mouse genome. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):963–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S., Horowitz M. The long terminal repeat of the intracisternal A particle as a target for transactivation by oncogene products. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):998–1003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.998-1003.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietz J. A., Grossman Z., Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Nucleotide sequence of a complete mouse intracisternal A-particle genome: relationship to known aspects of particle assembly and function. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3020–3029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3020-3029.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., Jardieu P., Mietz J. A., Trounstine M. L., Kuff E. L., Ishizaka K., Martens C. L. Rodent IgE-binding factor genes are members of an endogenous, retrovirus-like gene family. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4283–4290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled simian virus 40 DNA contains Z-DNA segments within transcriptional enhancer sequences. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):674–679. doi: 10.1038/303674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Kitasato H., Ohishi H., Motobayashi-Nakajima Y. Molecular cloning and long terminal repeat sequences of intracisternal A-particle genes in Mus caroli. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):352–358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.352-358.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Toh H., Miyata T., Awaya T. Nucleotide sequence of the Syrian hamster intracisternal A-particle gene: close evolutionary relationship of type A particle gene to types B and D oncovirus genes. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):387–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.387-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Yaniv M. Two different factors bind to the alpha-domain of the polyoma virus enhancer, one of which also interacts with the SV40 and c-fos enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1331–1337. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Holbrook N., Levens D. Binding of a cellular protein to the gibbon ape leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2735–2744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sambucetti L. C., Curran T., Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Common DNA binding site for Fos protein complexes and transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechavi G., Givol D., Canaani E. Activation of a cellular oncogene by DNA rearrangement: possible involvement of an IS-like element. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):607–611. doi: 10.1038/300607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey L., Chalkley R. At least two nuclear proteins bind specifically to the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):787–798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Ben-Levy R. Multiple nuclear proteins in liver cells are bound to hepatitis B virus enhancer element and its upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1913–1920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Cole M. D. Amplification of a specific set of intracisternal A-particle genes in a mouse plasmacytoma. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):171–177. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.171-177.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Cole M. D. Differing populations of intracisternal A-particle genes in myeloma tumors and mouse subspecies. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):411–421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.411-421.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topol J., Ruden D. M., Parker C. S. Sequences required for in vitro transcriptional activation of a Drosophila hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. Form and function of retroviral proviruses. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):812–820. doi: 10.1126/science.6177038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wujcik K. M., Morgan R. A., Huang R. C. Transcription of intracisternal A-particle genes in mouse myeloma and Ltk- cells. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):29–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.29-36.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S., Tucker W. Q., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Nucleotide sequence of the intracisternal A-particle genome inserted 5' to the interleukin-3 gene of the leukemia cell line WEHI-3B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5901–5918. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yotsuyanagi Y., Szöllösi D. Early mouse embryo intracisternal particle: Fourth type of retrovirus-like particle associated with the mouse. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Sep;67(3):677–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]