Abstract
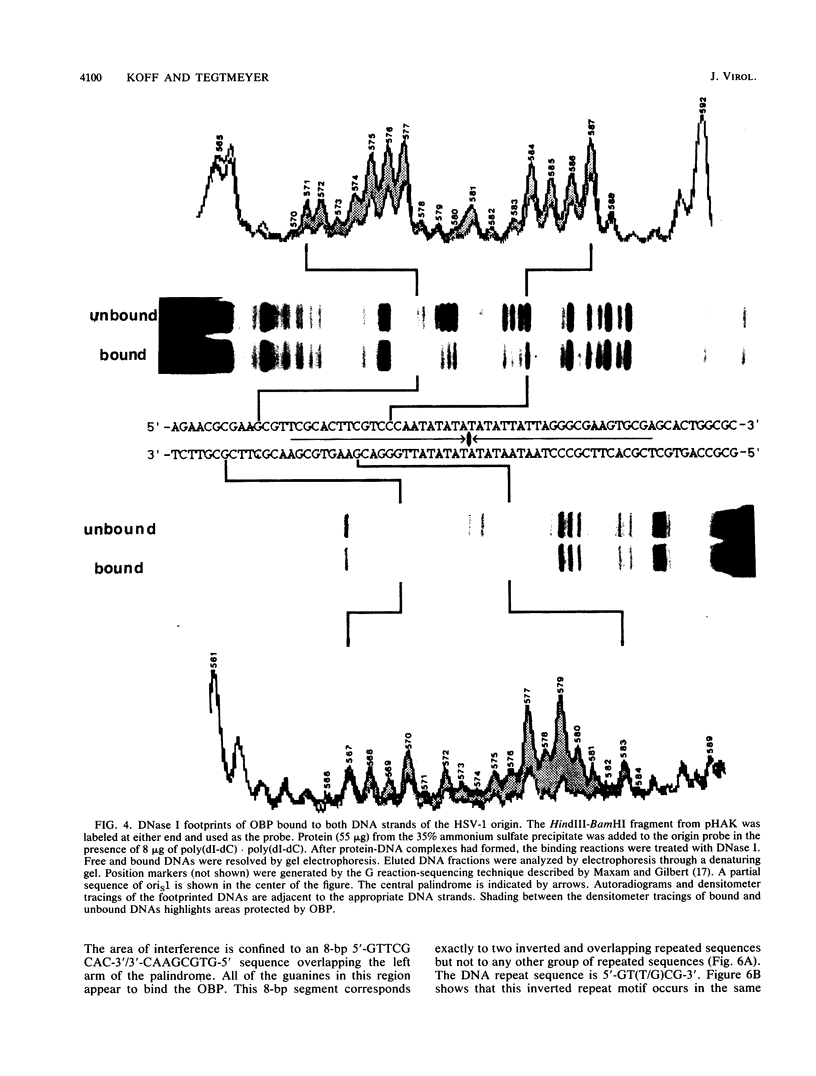
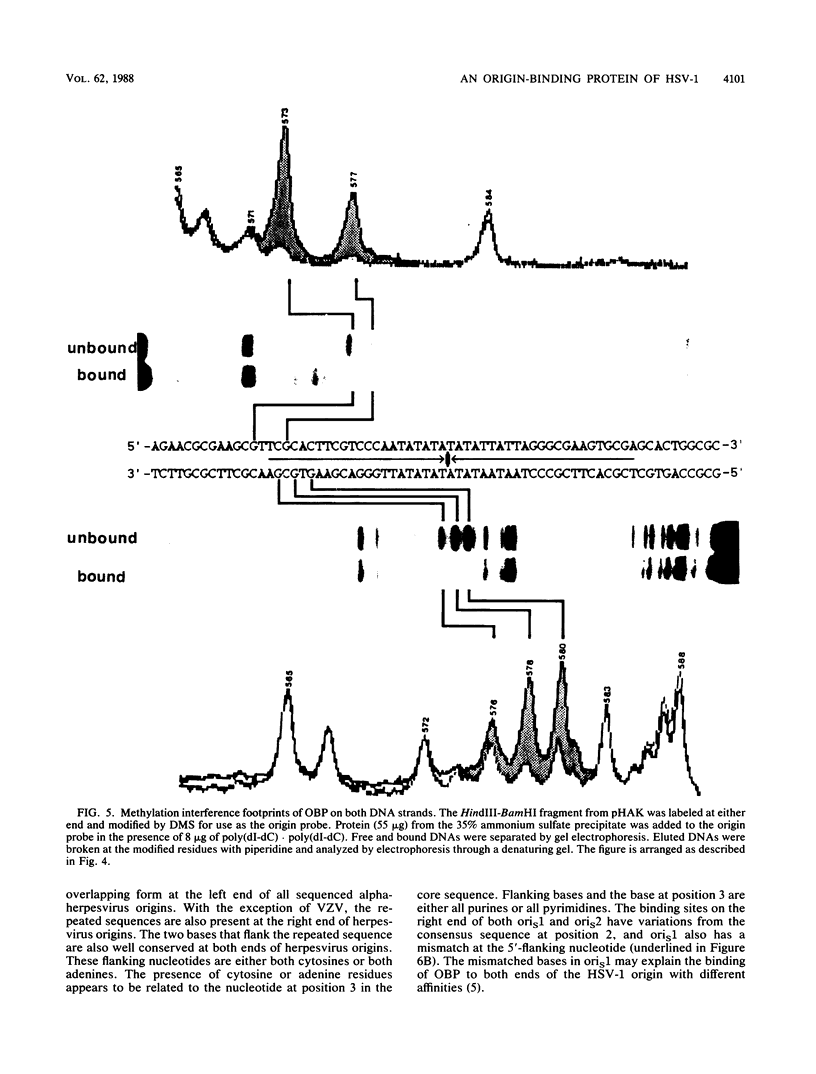
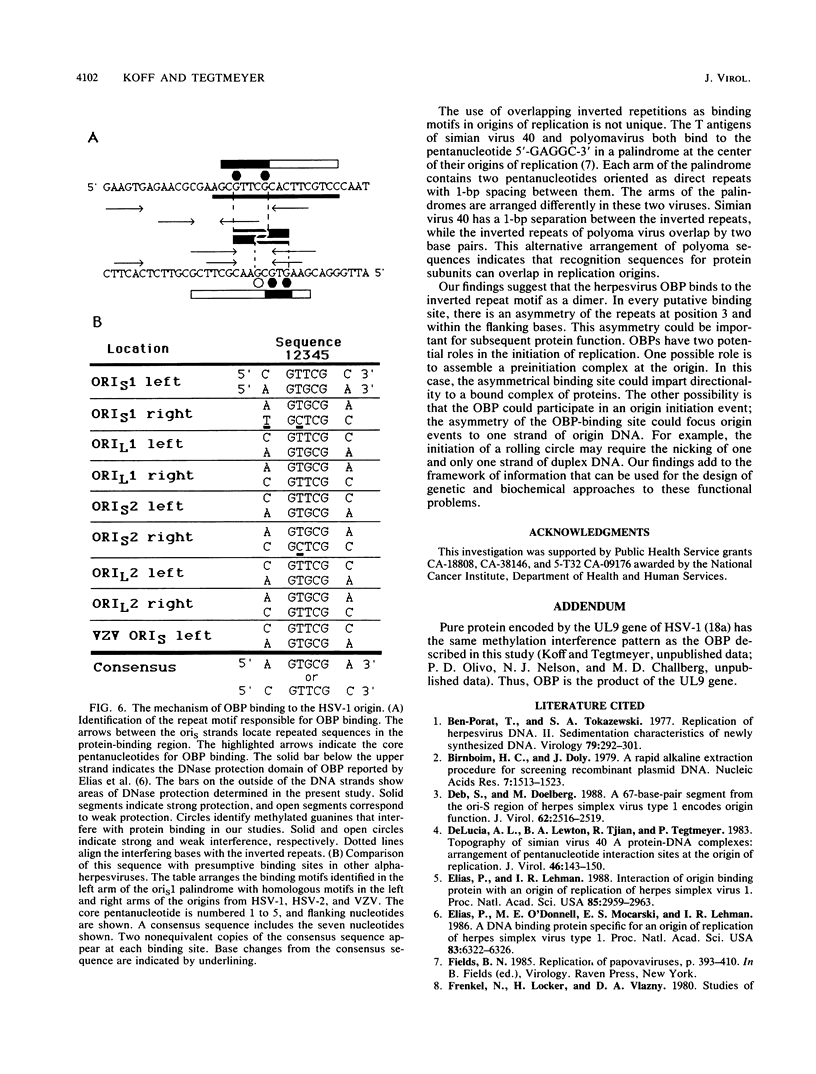
To investigate early initiation events in the replication of herpes simplex virus type 1, we analyzed interactions of proteins from infected cell extracts with the small origin of herpes simplex virus type 1 (oris1). Using the mobility shift assay, we detected two origin-specific binding interactions. We characterized the more prominent interaction on both strands of the DNA duplex with DNase I protection and methylation interference assays. Protein binding protects 17 bases of DNA on each strand from DNase I. These sequences are located at the left end of the central palindrome and are shifted four bases relative to one another. On the basis of the DNase protection pattern, we believe this protein to be related to the origin-binding protein defined by Elias et al. (P. Elias, M.E. O'Donnell, E.S. Mocarski, and I.R. Lehman, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 83:6322-6326, 1986). Our DNase I footprint shows both strong and weak areas of protection. The regions strongly protected from DNase I align with the essential contact residues identified by interference footprinting. Methylation interference defines a small binding domain of 8 base pairs: 5'-GTTCGCAC-3'/3'-CAAGCGTG-5'. This recognition sequence contains two inverted 5'-GT(T/G)CG-3' repeats which share a 2-base overlap; thus, the origin-binding protein probably binds to the inverted repeats as a dimer.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Porat T., Tokazewski S. A. Replication of herpesvirus DNA. II. Sedimentation characteristics of newly synthesized DNA. Virology. 1977 Jun 15;79(2):292–301. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Lewton B. A., Tjian R., Tegtmeyer P. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of pentanucleotide interaction sites at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.143-150.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Doelberg M. A 67-base-pair segment from the Ori-S region of herpes simplex virus type 1 encodes origin function. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2516–2519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2516-2519.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Lehman I. R. Interaction of origin binding protein with an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., O'Donnell M. E., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA binding protein specific for an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel N., Locker H., Vlazny D. A. Studies of defective herpes simplex viruses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:347–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann A., Shlomai J., Becker Y. Electron microscopy of herpes simplex virus DNA molecules isolated from infected cells by centrifugation in CsCl density gradients. J Gen Virol. 1977 Mar;34(3):507–522. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-3-507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes A. M., Wietstock S. M., Ruyechan W. T. Identification and characterization of a DNA primase activity present in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1038–1045. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1038-1045.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. J., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA VIII. Properties of the replicating DNA. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):394–411. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.394-411.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Galloway D. A. Cloning and characterization of oriL2, a large palindromic DNA replication origin of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):513–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.513-521.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Campbell M. E., Haarr L., Frame M. C., Parris D. S., Murphy M., Hope R. G., Muller M. T., Preston C. M. The 65,000-Mr DNA-binding and virion trans-inducing proteins of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2428–2437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2428-2437.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M. E., Elias P., Funnell B. E., Lehman I. R. Interaction between the DNA polymerase and single-stranded DNA-binding protein (infected cell protein 8) of herpes simplex virus 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4260–4266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poffenberger K. L., Roizman B. A noninverting genome of a viable herpes simplex virus 1: presence of head-to-tail linkages in packaged genomes and requirements for circularization after infection. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):587–595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.587-595.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Spear P. G. Preparation of herpes simplex virus of high titer. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):83–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.83-84.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Davison A. J. Identification of a varicella-zoster virus origin of DNA replication and its activation by herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1613–1623. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Localization of an origin of DNA replication within the TRS/IRS repeated region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):863–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Mutagenesis of a herpes simplex virus origin of DNA replication and its effect on viral interference. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jan;66(Pt 1):31–42. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. J., Banks L. M., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. Interactions between herpes simplex virus DNA-binding proteins. J Gen Virol. 1984 Nov;65(Pt 11):2033–2041. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-11-2033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Frenkel N. Replication of herpes simplex virus DNA: localization of replication recognition signals within defective virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Aschman D. P., Sacks W. R., Coen D. M., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants of HSV-1: the combined use of complementation and physical mapping for cistron assignment. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):290–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. J., DeLucia A. L., Tegtmeyer P. Sequence-specific binding of simian virus 40 A protein to nonorigin and cellular DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2631–2638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]