Abstract
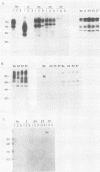
We describe experiments using the swine herpesvirus, pseudorabies virus (PRV), as a vector for expression of hybrid membrane protein genes. In particular, we present the construction and analysis of three infectious PRV mutants expressing chimeric viral membrane proteins composed of portions of the PRV envelope glycoprotein gIII and of the human retrovirus, human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), envelope glycoproteins gp120 and gp41. All of the chimeric genes contain the transcription control sequences and the first 157 codons of PRV gIII (known to contain signals sufficient for efficient export of the encoded peptide out of the cell) fused to different regions of the HIV-1 envelope. The mutant viruses express novel glycosylated fusion proteins that are immunoprecipitated by polyvalent sera specific for gIII, as well as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patient sera. The levels of expression are lower than expected due primarily to instability or altered processing of the hybrid mRNA. We could not detect cleavage of chimeric proteins carrying the gp120-gp41 protease processing site. The use of localization signals contained within herpesvirus membrane proteins to direct chimeric proteins to desired cellular locations is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett L. M., Timmins J. G., Thomsen D. R., Post L. E. The processing of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gX in infected cells and in an uninfected cell line. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):707–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Robert-Guroff M., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Moss B. Expression of the HTLV-III envelope gene by a recombinant vaccinia virus. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):535–537. doi: 10.1038/320535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Kamine J., Bakker A., Silva D., Woychik R. P., Sakai D. D., Rottman F. M. Synthesis of bovine growth hormone in primates by using a herpesvirus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2796–2803. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. The human immunodeficiency virus: infectivity and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):617–622. doi: 10.1126/science.3277274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampl H., Ben-Porat T., Ehrlicher L., Habermehl K. O., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of the envelope proteins of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.583-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Holland L. E., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Physical mapping of the mutation in an antigenic variant of herpes simplex virus type 1 by use of an immunoreactive plaque assay. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):649–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.649-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Otal T. M., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Transcriptional control signals of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) gene lie within bases -34 to +124 relative to the 5' terminus of the mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3652–3666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Kosowski S. G., Dalrymple J. M. Expression of AIDS virus envelope gene in recombinant vaccinia viruses. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):537–540. doi: 10.1038/320537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeler C. L., Jr, Whealy M. E., Enquist L. W. Construction of an infectious pseudorabies virus recombinant expressing a glycoprotein gIII-beta-galactosidase fusion protein. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. M., Flomerfelt F. A., Ghrayeb J. Expression of the art/trs protein of HIV and study of its role in viral envelope synthesis. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):837–840. doi: 10.1126/science.3033827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Groopman J. E., Fennie C. W., Benz P. M., Capon D. J., Dowbenko D. J., Nakamura G. R., Nunes W. M., Renz M. E., Berman P. W. Neutralization of the AIDS retrovirus by antibodies to a recombinant envelope glycoprotein. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):209–212. doi: 10.1126/science.3014647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukàcs N., Thiel H. J., Mettenleiter T. C., Rziha H. J. Demonstration of three major species of pseudorabies virus glycoproteins and identification of a disulfide-linked glycoprotein complex. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):166–173. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.166-173.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L. Vaccinia virus expression vectors. J Gen Virol. 1986 Oct;67(Pt 10):2067–2082. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-10-2067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Lukàcs N., Thiel H. J., Schreurs C., Rziha H. J. Location of the structural gene of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein complex gII. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):66–75. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Schreurs C., Zuckermann F., Ben-Porat T. Role of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gI in virus release from infected cells. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2764–2769. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2764-2769.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Watson R. J., Whealy M. E., Hays W. W., Enquist L. W. Characterization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene with homology to herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):339–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.339-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Whealy M. E., Watson R. J., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus gene encoding glycoprotein gIII is not essential for growth in tissue culture. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):635–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.635-645.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Jenkins F. J. Genetic engineering of novel genomes of large DNA viruses. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1208–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.2994215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. G., Doyle C., Sambrook J., Gething M. J. Heterologous transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains direct functional chimeric influenza virus hemagglutinins into the endocytic pathway. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1271–1283. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. P., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Analysis of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII localization and modification by using novel infectious viral mutants carrying unique EcoRI sites. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2962–2972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2962-2972.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer B., Whealy M., Robbins A., Enquist L. Site-specific insertion of DNA into a pseudorabies virus vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9108–9112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Kennell W. L., Lamm D. L. Visualization of minute centers of viral infection in unfixed cell cultures by an enzyme-linked antibody assay. J Immunol Methods. 1981;40(3):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90361-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Marotti K. R., Palermo D. P., Post L. E. Pseudorabies virus as a live virus vector for expression of foreign genes. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII is required for efficient virus growth in tissue culture. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2512–2515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2512-2515.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]