Abstract
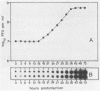
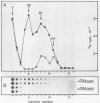
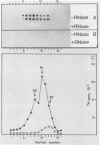
The replication of hepatitis A virus (HAV) in BS-C-1 cells was examined under single-cycle growth conditions by using strand-specific probes for detection of viral RNA species. No measurable lag phase was demonstrated between accumulation of positive-strand HAV RNA and production of infectious virions, indicating that replication of virion RNA is rate limiting for the production of infectious virus. Intracellular viral RNA was further analyzed by using 2 M LiCl to fractionate the insoluble nonvirion 35S RNA and replicative intermediates (RI) from the soluble virions and double-stranded replicative forms, in conjunction with sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation to separate the different forms of viral RNA. Throughout the productive phase of HAV infection, 95 to 97% of positive-strand HAV RNA was soluble in 2 M LiCl and was shown to be contained in mature virions. Of the LiCl-insoluble HAV RNA, more than 99% was positive-stranded 35S RNA, whereas 0.4% was negative stranded and had the sedimentation and partial RNase resistance characteristics of RI. The pattern of RNA accumulation in HAV-infected cells is thus very different from that seen in poliovirus-infected cells, where large pools of RI and mRNA are produced before RNA is sequestered into mature virions. The results of this study suggest that encapsidation of positive-strand HAV RNA inhibits transcription at all times during the growth cycle, thereby reducing the pool of replicating RNA and the final yield of infectious HAV.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
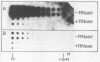
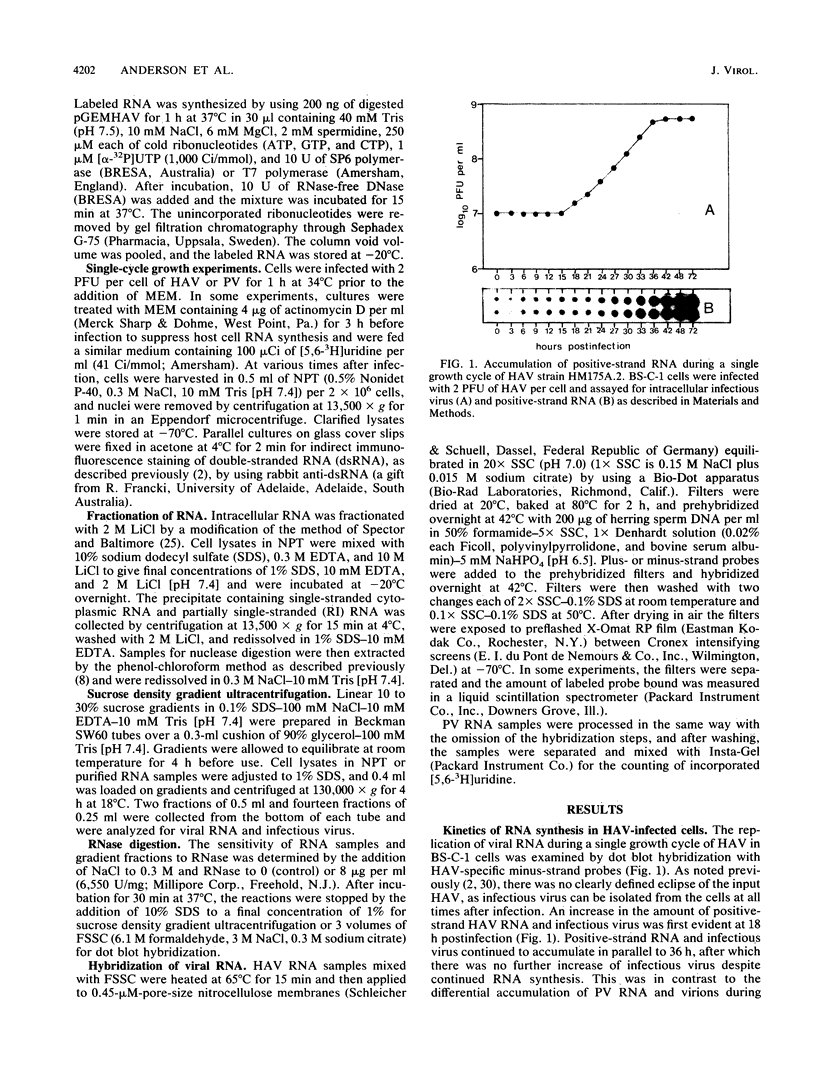
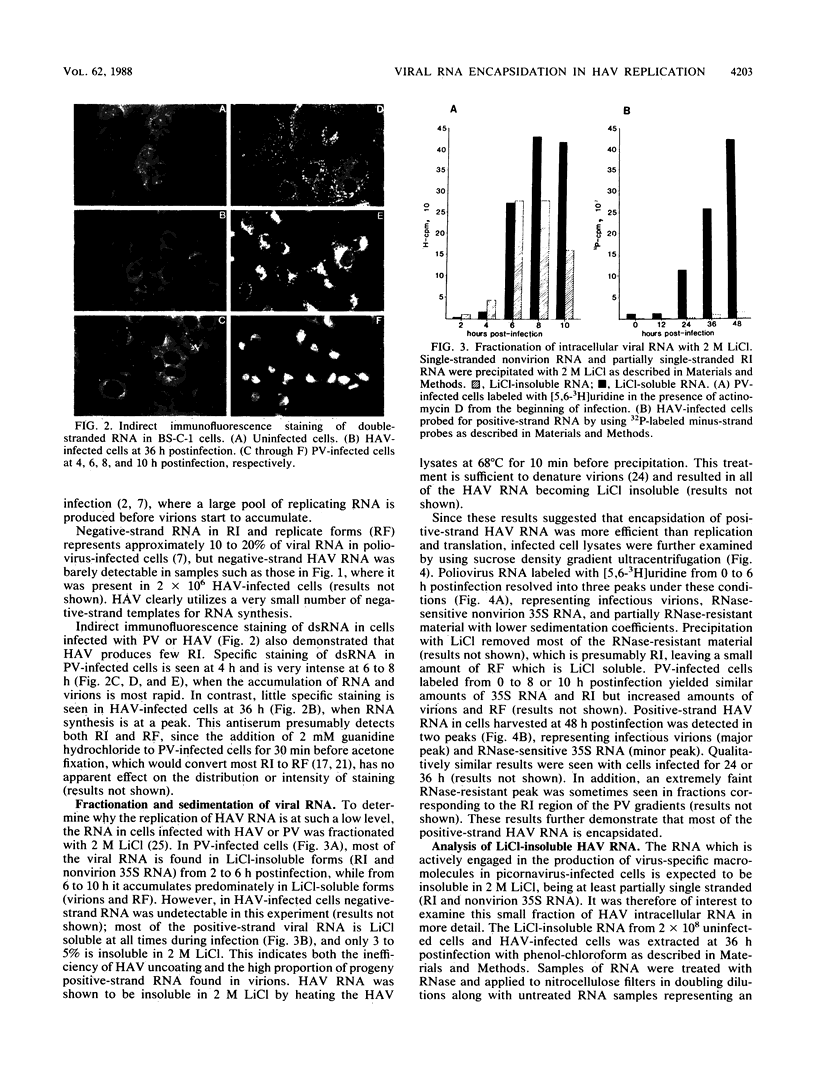
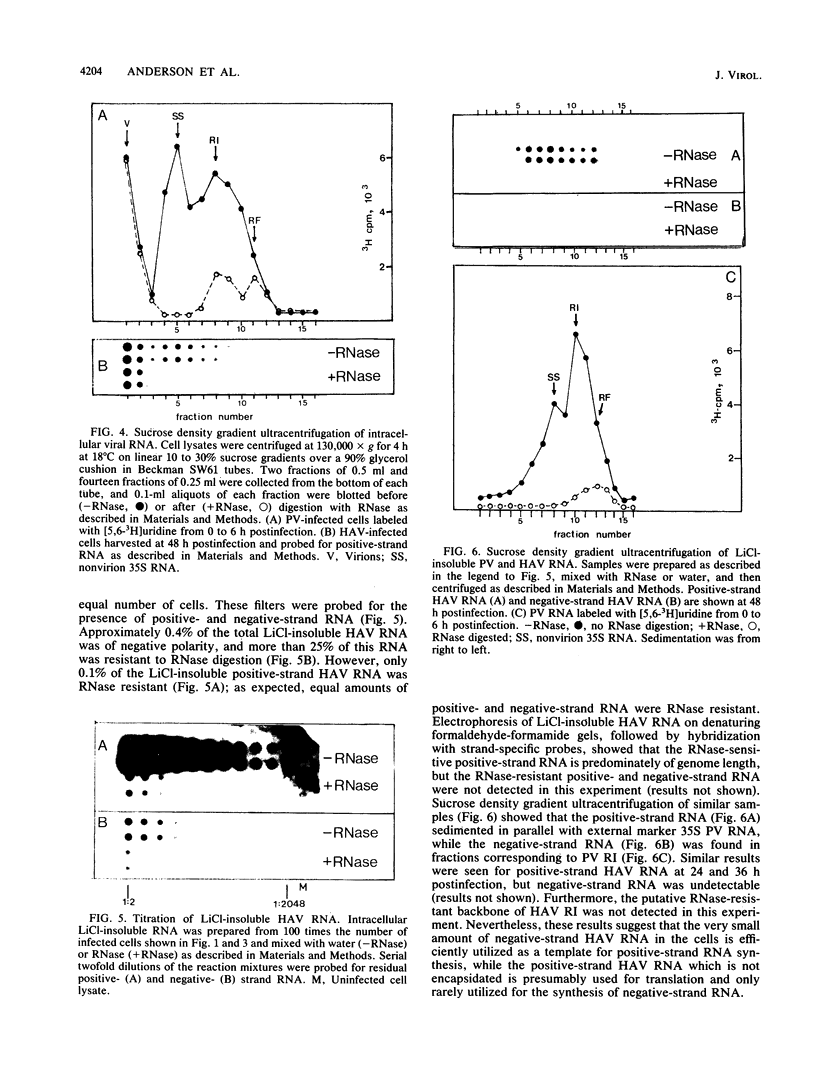
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. A. Cytopathology, plaque assay, and heat inactivation of hepatitis A virus strain HM175. J Med Virol. 1987 May;22(1):35–44. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890220106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Structure of the poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroudy B. M., Ticehurst J. R., Miele T. A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Purcell R. H., Feinstone S. M. Sequence analysis of hepatitis A virus cDNA coding for capsid proteins and RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2143–2147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Feinstone S. M., Rosenblum B., Purcell R. H. Hepatitis A virus cDNA and its RNA transcripts are infectious in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3035–3039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3035-3039.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Steiner-Pryor A., Wright P. J. A proposed regulator for poliovirus: the equestron. Intervirology. 1973;1(1):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000148826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulepis A. G., Tannock G. A., Locarnini S. A., Gust I. D. Evidence that the genome of hepatitis A virus consists of single-stranded RNA. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.473-477.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromeans T., Sobsey M. D., Fields H. A. Development of a plaque assay for a cytopathic, rapidly replicating isolate of hepatitis A virus. J Med Virol. 1987 May;22(1):45–56. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890220107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Chastonay J., Siegl G. Replicative events in hepatitis A virus-infected MRC-5 cells. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):268–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss-Müller V., Deinhardt F. Effect of hepatitis A virus infection on cell metabolism in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1984 Jan;175(1):10–15. doi: 10.3181/00379727-175-41757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss-Müller V., Lottspeich F., Deinhardt F. Characterization of hepatitis A virus structural proteins. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):732–736. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90234-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiernan R. E., Marshall J. A., Coulepis A. G., Anderson D. A., Gust I. D. Cellular changes associated with persistent hepatitis A infection in vitro. Arch Virol. 1987;94(1-2):81–95. doi: 10.1007/BF01313727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Coulepis A. G., Westaway E. G., Gust I. D. Restricted replication of human hepatitis A virus in cell culture: intracellular biochemical studies. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):216–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.216-225.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Dasgupta A. Antibody to a synthetic nonapeptide corresponding to the NH2 terminus of poliovirus genome-linked protein VPg reacts with native VPg and inhibits in vitro replication of poliovirus RNA. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):429–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.429-439.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Lundquist R. E., Maizel J. V., Jr Absence of subviral particles and assembly activity in HeLa cells infected with defective-interfering (DI) particles of poliovirus. Virology. 1980 Jan 15;100(1):116–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Hilleman M. R. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in cell culture in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Feb;160(2):213–221. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. C., Anderson B. N., Coulepis A. G., Chenoweth M. P., Gust I. D. Molecular cloning of cDNA from hepatitis A virus strain HM-175 after multiple passages in vivo and in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1741–1744. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Weitz M., Kronauer G. Stability of hepatitis A virus. Intervirology. 1984;22(4):218–226. doi: 10.1159/000149554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., deChastonay J., Kronauer G. Propagation and assay of hepatitis A virus in vitro. J Virol Methods. 1984 Aug;9(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(84)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. II. poly(A) on intracellular RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1418–1431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1418-1431.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Yang C. F., Takeda N., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. Analysis of RNA synthesis of type 1 poliovirus by using an in vitro molecular genetic approach. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2816–2822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2816-2822.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Hofmann L., Wurster K. G., Flehmig B. Persistent infection of human fibroblasts by hepatitis A virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):609–615. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venuti A., Di Russo C., del Grosso N., Patti A. M., Ruggeri F., De Stasio P. R., Martiniello M. G., Pagnotti P., Degener A. M., Midulla M. Isolation and molecular cloning of a fast-growing strain of human hepatitis A virus from its double-stranded replicative form. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):579–588. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.579-588.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitz M., Baroudy B. M., Maloy W. L., Ticehurst J. R., Purcell R. H. Detection of a genome-linked protein (VPg) of hepatitis A virus and its comparison with other picornaviral VPgs. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):124–130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.124-130.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler C. M., Fields H. A., Schable C. A., Meinke W. J., Maynard J. E. Adsorption, purification, and growth characteristics of hepatitis A virus strain HAS-15 propagated in fetal rhesus monkey kidney cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):434–440. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.434-440.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler C. M., Robertson B. H., Van Nest G., Dina D., Bradley D. W., Fields H. A. Structure of the hepatitis A virion: peptide mapping of the capsid region. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):307–313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.307-313.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widell A., Hansson B. G., Nordenfelt E., Oberg B. Enhancement of hepatitis A propagation in tissue culture with 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. J Med Virol. 1988 Apr;24(4):369–376. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890240403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin F. H. Involvement of viral procapsid in the RNA synthesis and maturation of poliovirus. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]