Abstract
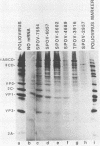
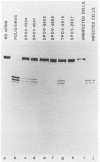
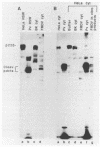
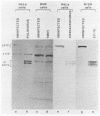
Infection of HeLa cells by poliovirus results in an abrupt inhibition of host cell protein synthesis. It is thought that the mechanism of this inhibition involves proteolytic cleavage of the p220 component of the cap-binding protein complex, thereby causing functional inactivation of the cap-binding protein complex and preventing capped (cellular) mRNAs from binding ribosomes. Current data suggest that the viral proteinase 2A indirectly induces p220 cleavage via alteration or activation of a second proteinase of cellular origin. We present evidence that translation of poliovirus proteinase 2A sequences in vitro activates p220 cleavage. We have also aligned published picornavirus 2A amino acid sequences for maximum homology, and we show that the picornaviruses can be divided into two classes based on the presence or absence of a highly conserved 18-amino acid sequence in the carboxy-terminal portion of 2A. This conserved 2A sequence is homologous with the active site of the cysteine proteinase 3C common to all picornaviruses. We show that picornaviruses which contain the putative 2A active site sequence (e.g., enteroviruses and rhinoviruses) will induce cleavage of p220 in vivo. Conversely, we show that two cardioviruses (encephalomyocarditis virus and Theiler's encephalomyelitis virus) do not encode this putative proteinase sequence in the 2A region and do not induce cleavage of p220 in vivo. The foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) 2A sequence represents an apparent deletion and consists of only 16 amino acids, most homologous with the carboxy terminus of the cardiovirus 2A sequence. It does not contain the putative cysteine proteinase active site. However, FMDV infection induces complete cleavage of BK cell p220, and translation of FMDV RNA in vitro induces an activity that cleaves HeLa cell p220. The data predict that an alternate FMDV viral protease is responsible for the induction of p220 cleavage.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Kamer G., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Similarity in gene organization and homology between proteins of animal picornaviruses and a plant comovirus suggest common ancestry of these virus families. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7251–7267. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan P. L., Mizutani S., Colonno R. J. Molecular cloning and complete sequence determination of RNA genome of human rhinovirus type 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):732–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Purcell R. H., Buckler-White A., Baroudy B. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of wild-type hepatitis A virus: comparison with different strains of hepatitis A virus and other picornaviruses. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):50–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.50-59.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaney M. A., Vakharia V. N., Lloyd R. E., Ehrenfeld E., Grubman M. J. Leader protein of foot-and-mouth disease virus is required for cleavage of the p220 component of the cap-binding protein complex. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4407–4409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4407-4409.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Dorner L. F., Larsen G. R., Wimmer E., Anderson C. W. Identification of the initiation site of poliovirus polyprotein synthesis. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1017-1028.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Semler B. L., Jackson R. J., Hanecak R., Duprey E., Wimmer E. In vitro translation of poliovirus RNA: utilization of internal initiation sites in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):507–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.507-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Etchison J. R. Monoclonal antibody-aided characterization of cellular p220 in uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells: subcellular distribution and identification of conformers. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2702–2710. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2702-2710.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Fout S. Human rhinovirus 14 infection of HeLa cells results in the proteolytic cleavage of the p220 cap-binding complex subunit and inactivates globin mRNA translation in vitro. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):634–638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.634-638.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Baxt B., Bachrach H. L. Foot-and-mouth disease virion RNA: studies on the relation between the length of its 3'-poly(A) segment and infectivity. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):22–31. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Zellner M., Wagner J. Antigenic comparison of the polypeptides of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotypes and other picornaviruses. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Sequence analysis of three Sindbis virus mutants temperature-sensitive in the capsid protein autoprotease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4648–4652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. L., Ehrenfeld E. The effect of poliovirus infection on the translation in vitro of VSV messenger ribonucleoprotein particles. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):415–430. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 2A induces cleavage of eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2711–2718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2711-2718.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Edery I., Hanecak R., Wimmer E., Sonenberg N. Poliovirus protease 3C (P3-7c) does not cleave P220 of the eucaryotic mRNA cap-binding protein complex. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):489–493. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.489-493.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. M., Stålhandske P. O., Pettersson U. Genome of coxsackievirus B3. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):50–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90435-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Etchison D., Ehrenfeld E. Poliovirus protease does not mediate cleavage of the 220,000-Da component of the cap binding protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2723–2727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Jense H. G., Ehrenfeld E. Restriction of translation of capped mRNA in vitro as a model for poliovirus-induced inhibition of host cell protein synthesis: relationship to p220 cleavage. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2480–2488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2480-2488.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E., Ehrenfeld E. Cleavage of the cap binding protein complex polypeptide p220 is not effected by the second poliovirus protease 2A. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosenkis J., Daniels-McQueen S., Janovec S., Duncan R., Hershey J. W., Grifo J. A., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Shutoff of host translation by encephalomyocarditis virus infection does not involve cleavage of the eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide that accompanies poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):643–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.643-645.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitayaphan S., Omilianowski D., Toth M. M., Parks G. D., Rueckert R. R., Palmenberg A. C., Roos R. P. Relationship of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis viruses to the cardiovirus genus of picornaviruses. Intervirology. 1986;26(3):140–148. doi: 10.1159/000149693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozden S., Tangy F., Chamorro M., Brahic M. Theiler's virus genome is closely related to that of encephalomyocarditis virus, the prototype cardiovirus. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1163–1165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1163-1165.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Kirby E. M., Janda M. R., Drake N. L., Duke G. M., Potratz K. F., Collett M. S. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the encephalomyocarditis viral polyprotein coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2969–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevear D. C., Calenoff M., Rozhon E., Lipton H. L. Analysis of the complete nucleotide sequence of the picornavirus Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus indicates that it is closely related to cardioviruses. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1507–1516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1507-1516.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Emmert A. Modulation of the expression of poliovirus proteins in reticulocyte lysates. Virology. 1986 Jan 30;148(2):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. H., Grubman M. J., Weddell G. N., Moore D. M., Welsh J. D., Fischer T., Dowbenko D. J., Yansura D. G., Small B., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide and amino acid sequence coding for polypeptides of foot-and-mouth disease virus type A12. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):651–660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.651-660.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Impact of virus infection on host cell protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:317–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Johnson V. H., Tracy S. A chimeric plasmid from cDNA clones of poliovirus and coxsackievirus produces a recombinant virus that is temperature-sensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton G. J., Langford M. P., Baron S. Effect of interferon, elevated temperature, and cell type on replication of acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis viruses. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):370–376. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.370-376.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Beck E. A second protease of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):893–899. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.893-899.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakharia V. N., Devaney M. A., Moore D. M., Dunn J. J., Grubman M. J. Proteolytic processing of foot-and-mouth disease virus polyproteins expressed in a cell-free system from clone-derived transcripts. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3199–3207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3199-3207.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Semler B. L. In vitro molecular genetics as a tool for determining the differential cleavage specificities of the poliovirus 3C proteinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2069–2088. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]