Abstract
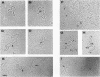
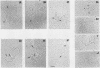
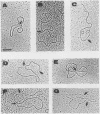
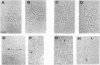
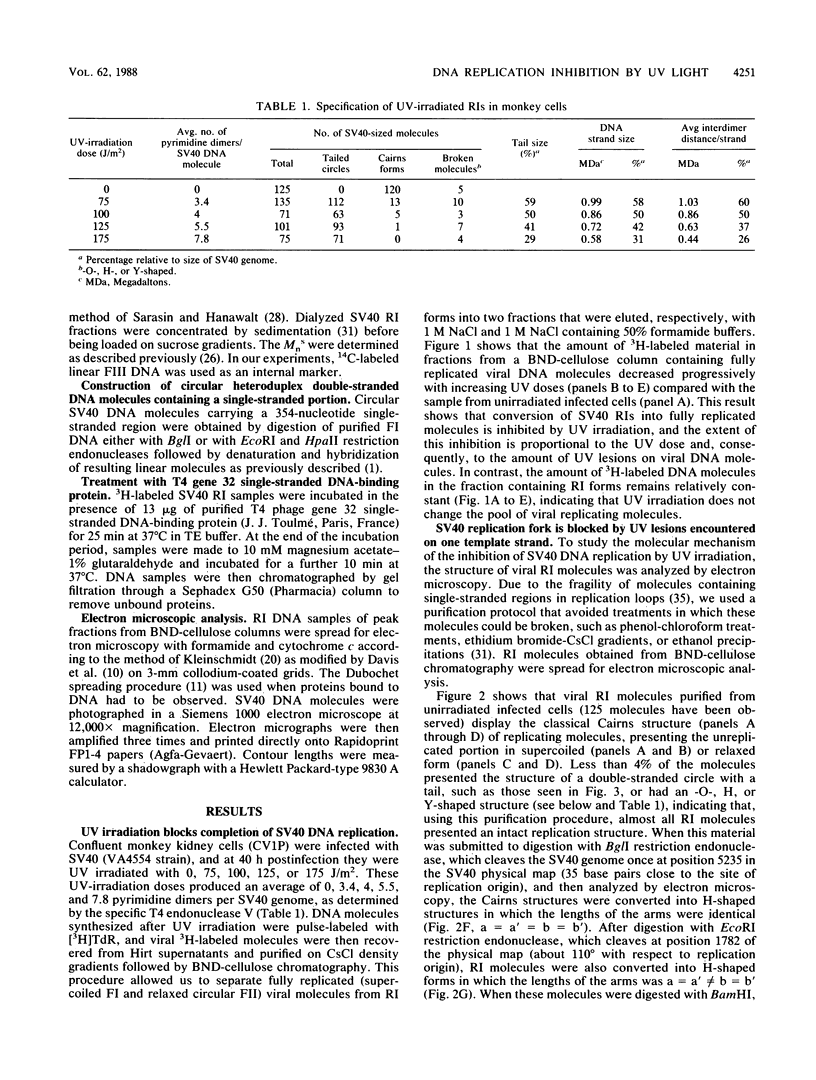
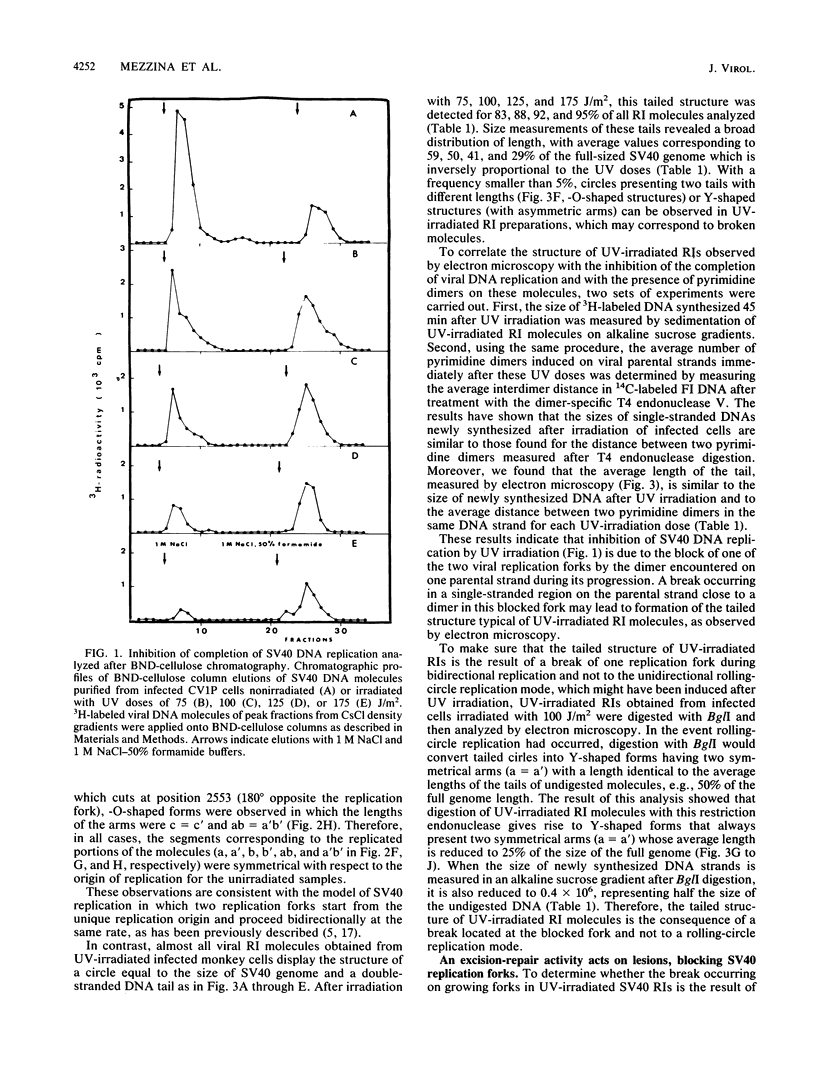
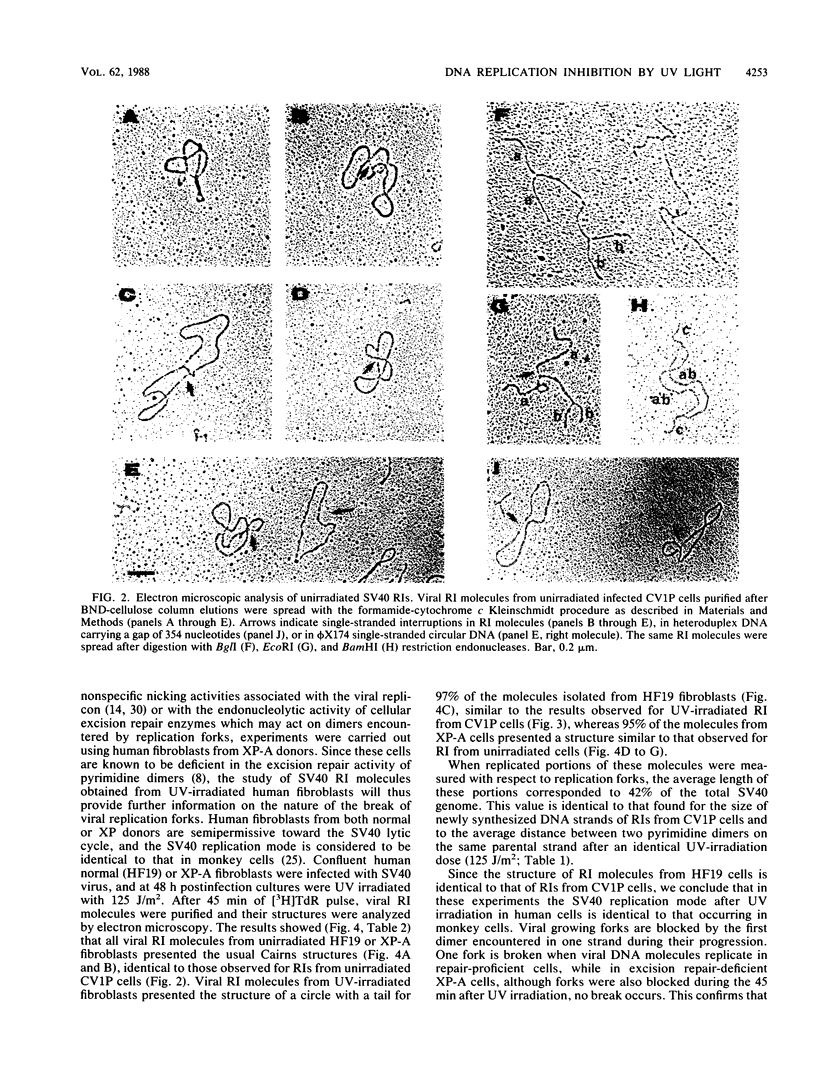
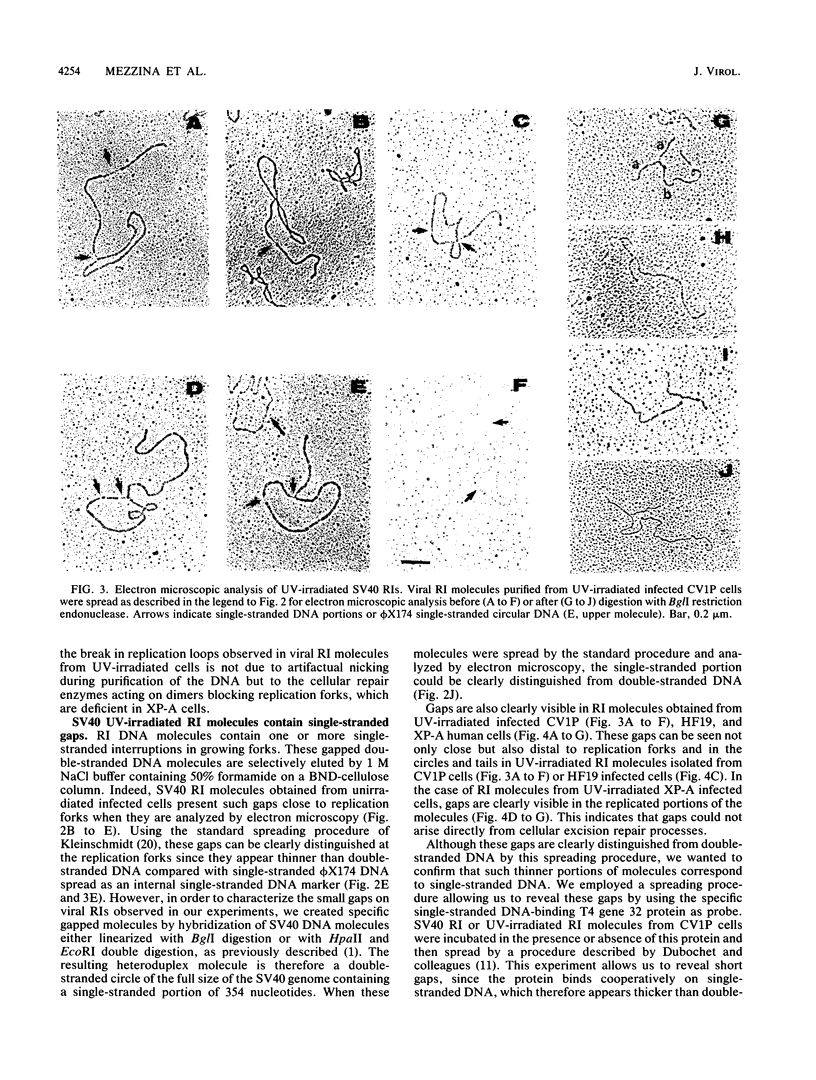
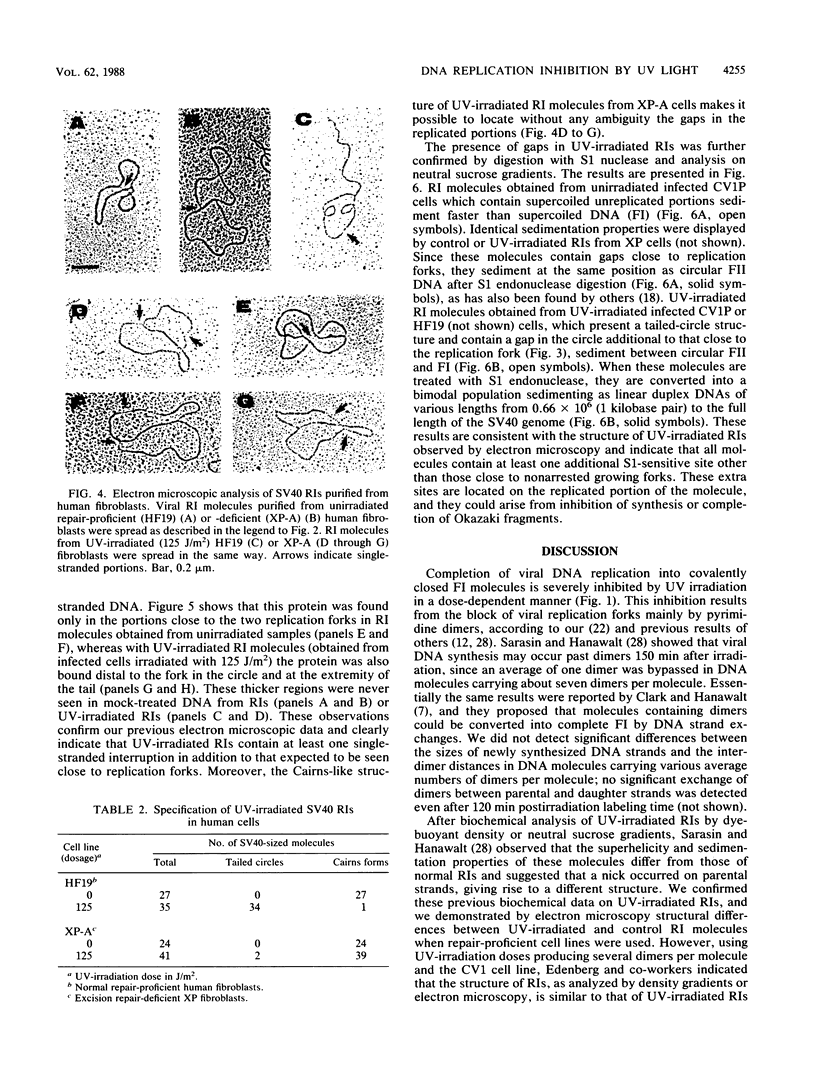
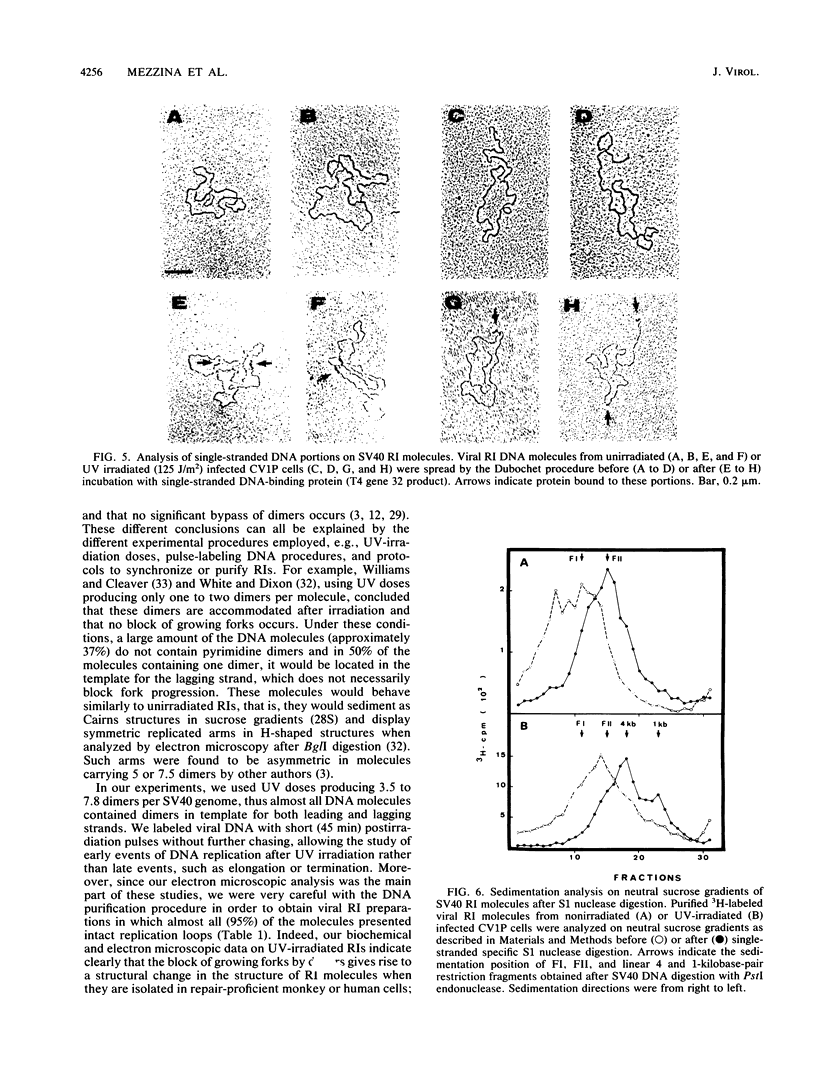
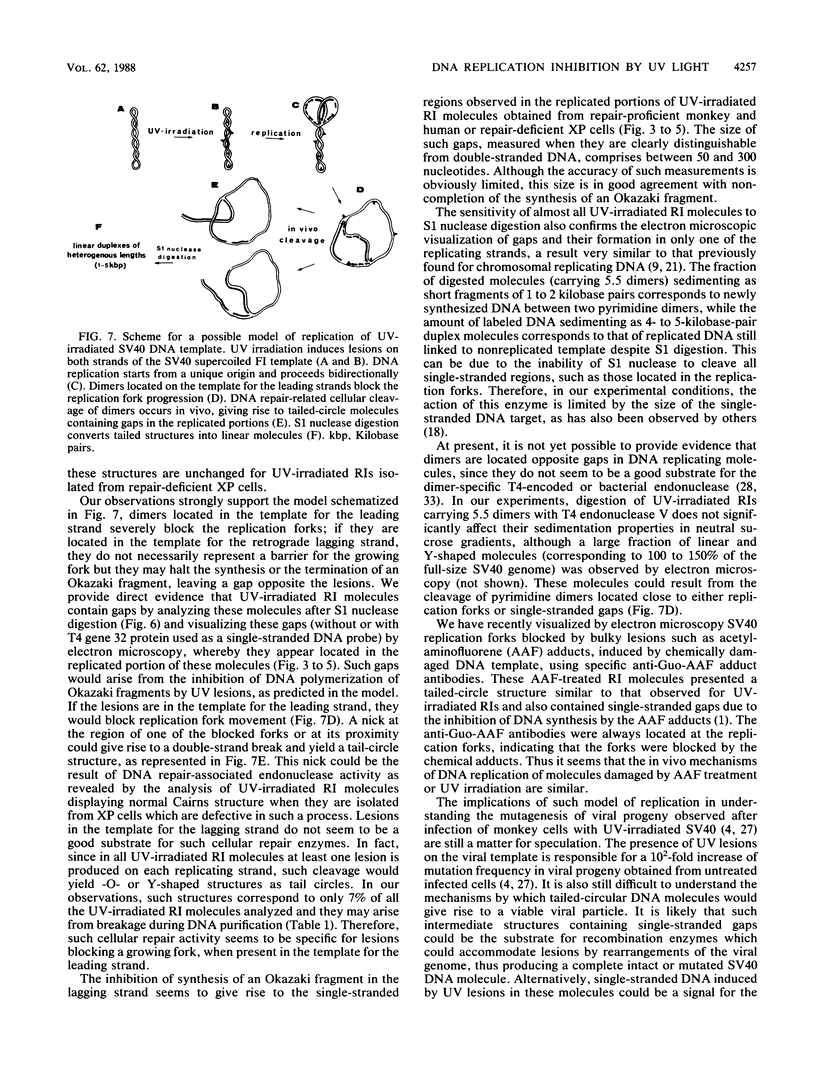
The molecular mechanisms of in vivo inhibition of mammalian DNA replication by exposure to UV light (at 254 nm) was studied in monkey and human cells infected with simian virus 40. Analysis of viral DNA by electron microscopy and sucrose gradients confirmed that the presence of UV-induced lesions severely blocks DNA synthesis, and thus the conversion of replicative intermediates (RIs) into fully replicated form I DNA is inhibited by UV irradiation. These blocked RI molecules present several special features when visualized by electron microscopy. (i) In excision repair-proficient monkey and human cells they are composed of a double-stranded circular DNA with a double-stranded tail whose size corresponds to the average interpyrimidine dimer distance, as determined by the dimer-specific T4 endonuclease V. (ii) In excision repair-deficient human cells from patients with xeroderma pigmentosum, UV-irradiated RIs present a Cairns-like structure similar to that observed for replicating molecules obtained from unirradiated infected cells. (iii) Single-stranded gaps are visualized in the replicated portions of UV-irradiated RI molecules; such regions are detected and clearly distinguishable from double-stranded DNA when probed by a specific single-stranded DNA-binding protein such as the bacteriophage T4 gene 32 product. Consistent with the presence of gaps in UV-irradiated RI molecules, single-strand-specific S1 nuclease digestion causes a shift in their sedimentation properties when analyzed in neutral sucrose gradients compared with undamaged molecules. These results are in agreement with and reinforce the model in which UV lesions are a barrier to the replication fork movement when present in the template for the leading strand; when lesions are in the template for the lagging strand they inhibit synthesis or completion of Okazaki fragments, leaving gaps opposite the lesion. Moreover, cellular DNA repair-linked endonucleolytic activity may induce double-stranded breaks in the blocked region of the replication forks, resulting in the tailed structures observed in viral DNA molecules obtained from excision repair-proficient cell lines.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armier J., Mezzina M., Leng M., Fuchs R. P., Sarasin A. N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene-induced damage on SV40 DNA: inhibition of DNA replication and visualization of DNA lesions. Carcinogenesis. 1988 May;9(5):789–795. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailone A., Sommer S., Devoret R. Mini-F plasmid-induced SOS signal in Escherichia coli is RecBC dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5973–5977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. A., Edenberg H. J. Pyrimidine dimers block simian virus 40 replication forks. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3443–3450. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourre F., Sarasin A. Targeted mutagenesis of SV40 DNA induced by UV light. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):68–70. doi: 10.1038/305068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. L. Eukaryotic DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:733–771. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrier W. L., Setlow R. B. Paper strip method for assaying gradient fractions containing radioactive macromolecules. Anal Biochem. 1971 Oct;43(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Hanawalt P. C. Replicative intermediates in UV-irradiated simian virus 40. Mutat Res. 1984 Jul-Aug;132(1-2):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Defective repair replication of DNA in xeroderma pigmentosum. Nature. 1968 May 18;218(5142):652–656. doi: 10.1038/218652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro-Stone M., Schumacher R. I., Meneghini R. Structure of the replication fork in ultraviolet light-irradiated human cells. Biophys J. 1979 Aug;27(2):287–300. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85218-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., Ducommun M., Zollinger M., Kellenberger E. A new preparation method for dark-field electron microscopy of biomacromolecules. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Apr;35(1):147–167. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenberg H. J. Inhibition of simian virus 40 DNA replication by ultraviolet light. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):298–309. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90257-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Huang E. S., Pagano J. S. Structural polypeptides of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):635–641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.635-641.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamelin C., Yaniv M. Nicking-closing enzyme is associated with SV40 DNA in vivo as a sodium dodecyl sulfate-resistant complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):679–687. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A. Ultraviolet light repair and mutagenesis revisited. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., DePamphilis M. L. Initiation of SV40 DNA replication in vivo: location and structure of 5' ends of DNA synthesized in the ori region. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman T. M., DePamphilis M. L., Wassarman P. M. Structure of chromatin at deoxyribonucleic acid replication forks: Okazaki fragments released from replicating SV40 chromosomes by single-strand specific endonucleases are not in nucleosomes. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4563–4571. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneghini R. Gaps in DNA synthesized by ultraviolet light-irradiated WI38 human cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):419–427. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezzina M., Gentil A., Sarasin A. Simian virus 40 as a probe for studying inducible repair functions in mammalian cells. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;17(2):121–131. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.380170203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. D., Bose K. K., Rabkin S. D., Strauss B. S. Sites of termination of in vitro DNA synthesis on ultraviolet- and N-acetylaminofluorene-treated phi X174 templates by prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):110–114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P., Strauss B. S. Sites of inhibition of in vitro DNA synthesis in carcinogen- and UV-treated phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):664–666. doi: 10.1038/278664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozer H. L., Slater M. L., Dermody J. J., Mandel M. Replication of simian virus 40 DNA in normal human fibroblasts and in fibroblasts from xeroderma pigmentosum. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):481–489. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.481-489.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. D., Howard-Flanders P. Discontinuities in the DNA synthesized in an excision-defective strain of Escherichia coli following ultraviolet irradiation. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarasin A. R., Hanawalt P. C. Replication of ultraviolet-irradiated simian virus 40 in monkey kidney cells. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):299–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarasin A., Benoit A. Enhanced mutagenesis of UV-irradiated simian virus 40 occurs in mitomycin C-treated host cells only at a low multiplicity of infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1102–1107. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaria A., Edenberg H. J. Preirradiation of host cells does not alter blockage of simian virus 40 replication forks by pyrimidine dimers. Mutat Res. 1988 Jan;193(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(88)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., DePamphilis M. L. Preferred DNA sites are involved in the arrest and initiation of DNA synthesis during replication of SV40 DNA. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. H., Dixon K. Gap filling and not replication fork progression is the rate-limiting step in the replication of UV-damaged simian virus 40 DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1286–1292. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. I., Cleaver J. E. Perturbations in simian virus 40 DNA synthesis by ultraviolet light. Mutat Res. 1978 Dec;52(3):301–311. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(78)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis-Hadjopoulos M., Persico M., Martin R. G. The remarkable instability of replication loops provides a general method for the isolation of origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]