Abstract
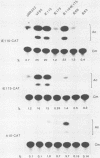
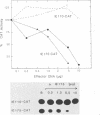
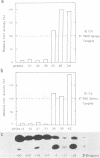
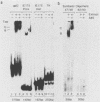
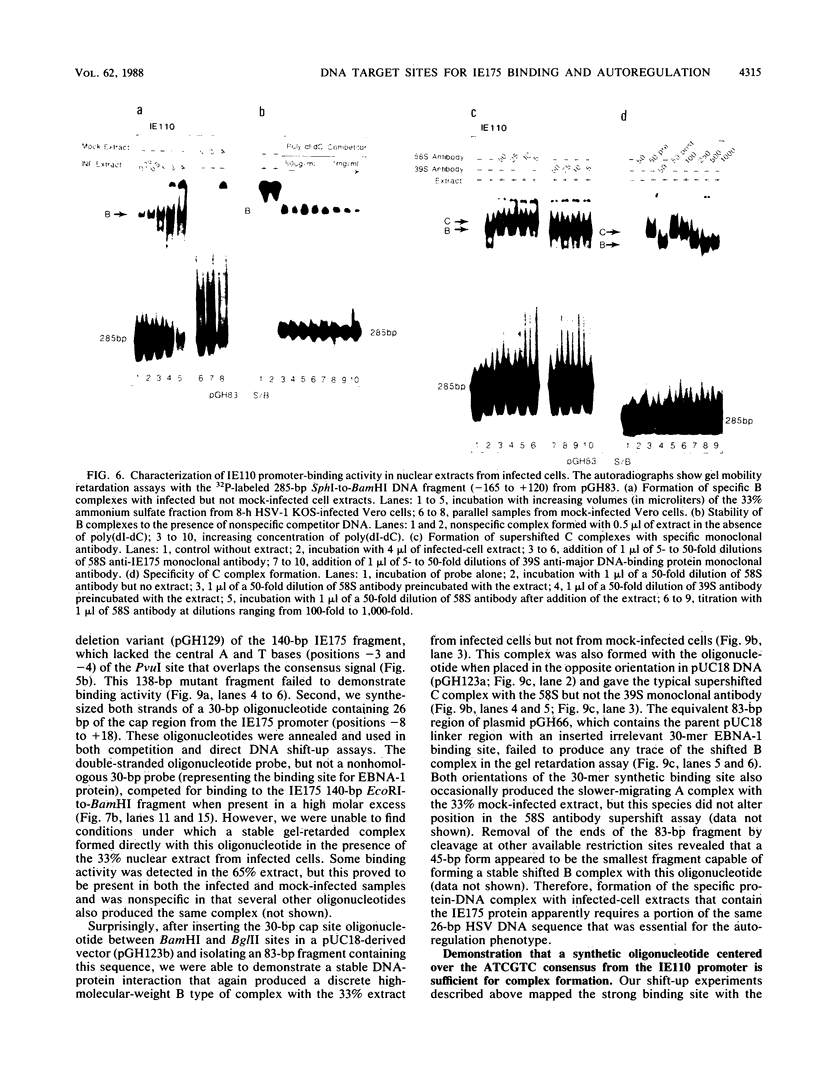
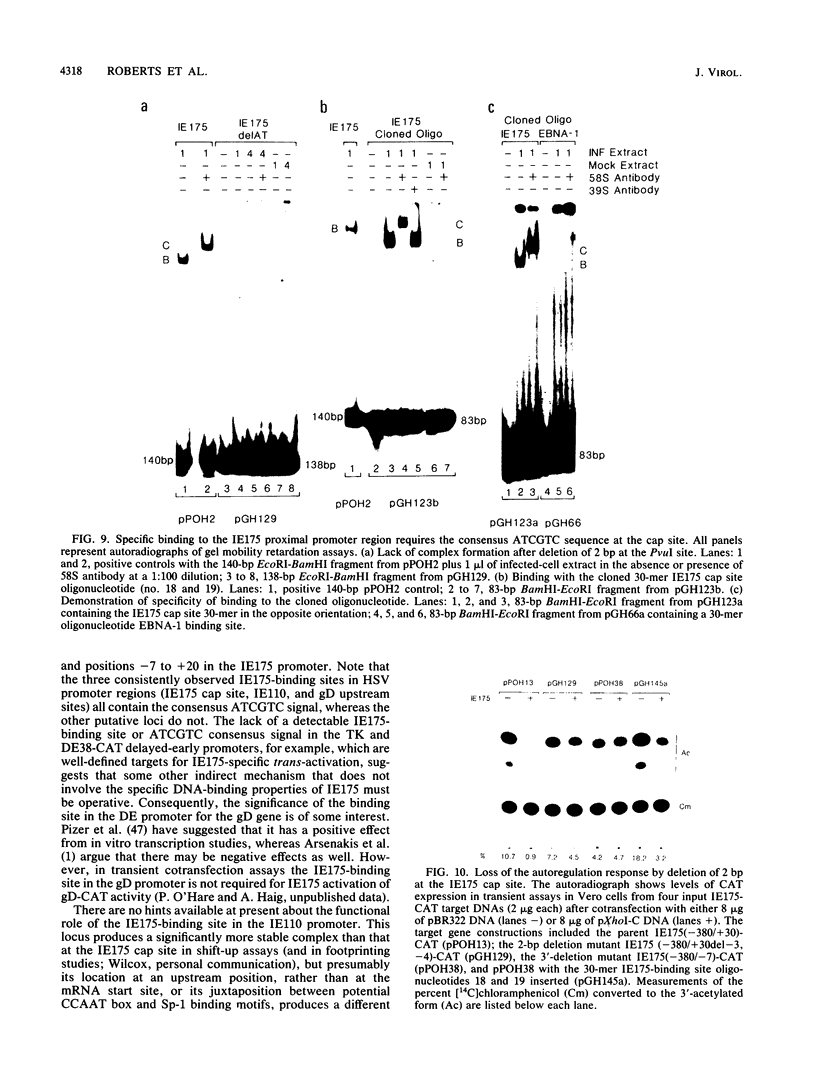
In transient-expression assays, the IE175 (alpha 4) promoter region of herpes simple virus is down-regulated after cotransfection with DNA encoding its own protein product (IE175 or ICP4). The inhibition by IE175 proved to be highly specific for its own promoter region and did not act on either the herpes simplex virus type 1 IE110 (alpha 0) or human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoters. Furthermore, the inhibition was still exhibited by IE175 effector plasmids driven by strong heterologous promoters and therefore must be a direct autoregulatory response that cannot be explained by promoter competition effects. In gel mobility retardation assays with infected-cell nuclear extracts, a prominent and specific DNA-protein complex was formed with DNA fragments containing sequences from -108 to +30 in the IE175 promoter region. This activity was not present in mock-infected samples. Even stronger binding occurred with a fragment containing sequences from -128 to +120 in the IE110 promoter, but this second locus was not associated with any detectable response phenotype in cotransfection assays. Supershift experiments with an anti-IE175 monoclonal antibody confirmed the presence of the IE175 protein in both DNA-protein complexes. In the IE175 promoter, specific binding correlated closely with the presence of an intact autoregulatory signal near the cap site as judged by the loss of both activities in a 3'-deleted promoter fragment lacking sequences from -7 to +30. Insertion of a cloned 30-mer synthetic oligonucleotide sequence from positions -8 to +18 in IE175 restored both IE175 binding activity and the down-regulation phenotype. Direct shift-up assays with a similar 30-base-pair (bp) oligonucleotide containing 21 bp from positions -75 to -55 of IE110 (which encompasses a consensus ATCGTC motif) also produced a specific DNA-protein complex containing the IE175 protein. This ATCGTC motif proved to be a necessary component of both the IE110 and IE175 binding sites, but was insufficient on its own for complex formation. Finally, deletion of 2 bp from positions -3 and -4 within the ATCGTC sequence in the IE175 cap site region abolished both binding activity and the IE175-dependent autoregulation phenotype.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arsenakis M., Campadelli-Fiume G., Roizman B. Regulation of glycoprotein D synthesis: does alpha 4, the major regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus 1, regulate late genes both positively and negatively? J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):148–158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.148-158.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The terminal a sequence of the herpes simplex virus genome contains the promoter of a gene located in the repeat sequences of the L component. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):629–637. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.629-637.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. A genetic approach to promoter recognition during trans induction of viral gene expression. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3018926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple M. A., McGeoch D. J., Davison A. J., Preston C. M. DNA sequence of the herpes simplex virus type 1 gene whose product is responsible for transcriptional activation of immediate early promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7865–7879. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., McCarthy A. M., Schaffer P. A. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate-early regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):558–570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.558-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activation of immediate-early, early, and late promoters by temperature-sensitive and wild-type forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 protein ICP4. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1997–2008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Physical and functional domains of the herpes simplex virus transcriptional regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):732–743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.732-743.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis D., Smiley J. R. Transactivation of a late herpes simplex virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):544–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Kareh A., Silverstein S., Smiley J. Control of expression of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene in biochemically transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jan;65(Pt 1):19–36. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Dunlop M. Trans activation of plasmid-borne promoters by adenovirus and several herpes group viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):5969–5978. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.5969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber S. W., Wilcox K. W. Association of herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 with sequences spanning the ICP4 gene transcription initiation site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):555–570. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber S. W., Wilcox K. W. Association of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 with specific nucleotide sequences in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6067–6083. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. T., Ahlers S. E. Repression of adenovirus early gene expression by coinfection with a temperature-sensitive mutant in the immediate-early gene of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):13–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.13-17.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. J., Powell K. L. DNA-binding properties of a herpes simplex virus immediate early protein. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):1084–1087. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.1084-1087.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Co-ordinate regulation of herpes simplex virus gene expression is mediated by the functional interaction of two immediate early gene products. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):395–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Dissection of immediate-early gene promoters from herpes simplex virus: sequences that respond to the virus transcriptional activators. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3167–3172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3167-3172.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Identification of immediate early genes from herpes simplex virus that transactivate the virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5265–5269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Rawlins D. R., Rosenfeld P. J., Shero J. H., Kelly T. J., Hayward G. S. Multiple tandemly repeated binding sites for cellular nuclear factor 1 that surround the major immediate-early promoters of simian and human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1559–1570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1559-1570.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Alpha 4, the major regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus type 1, is stably and specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes and of selected other viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. DNA-binding site of major regulatory protein alpha 4 specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. C., Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Transcriptional regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene is mediated through an enhancer-type sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Buttyan R., Spear P. G. Herpes simplex virus gene expression in transformed cells. I. Regulation of the viral thymidine kinase gene in transformed L cells by products of superinfecting virus. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):413–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.413-424.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung W. C., Dimock K., Smiley J. R., Bacchetti S. Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase transcripts are absent from both nucleus and cytoplasm during infection in the presence of cycloheximide. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):361–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.361-365.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: transcription-initiation sites and domains of alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7122–7126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler D. W., Wilcox K. W. Isolation of herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 as a homodimeric complex. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):329–337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.329-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Reyes G. R., Pitha P. M., Hayward G. S. Differential activation of hybrid genes containing herpes simplex virus immediate-early or delayed-early promoters after superinfection of stable DNA-transfected cell lines. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):867–878. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.867-878.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T. Binding of the herpes simplex virus immediate-early gene product ICP4 to its own transcription start site. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):858–865. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.858-865.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie M. J., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence analysis of an immediate-early gene region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome (map coordinates 0.950 to 0.978). J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Rio D. C., Robbins A. K., Tjian R. SV40 gene expression is modulated by the cooperative binding of T antigen to DNA. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Comparison of upstream sequence requirements for positive and negative regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate-early gene by three virus-encoded trans-acting factors. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.190-199.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Expression of recombinant genes containing herpes simplex virus delayed-early and immediate-early regulatory regions and trans activation by herpesvirus infection. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.522-531.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Rixon F. J., Everett R. D., Frame M. C., McGeoch D. J. Characterization of the IE110 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2365–2380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson R. H., Bacchetti S., Smiley J. R. Cells that constitutively express the herpes simplex virus immediate-early protein ICP4 allow efficient activation of viral delayed-early genes in trans. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):414–421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.414-421.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer L. I., Tedder D. G., Betz J. L., Wilcox K. W., Beard P. Regulation of transcription in vitro from herpes simplex virus genes. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):950–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.950-959.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., O'Hare P., Sha L., LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. trans-activation and autoregulation of gene expression by the immediate-early region 2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1167–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1167-1179.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G., Stow N. D. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.708-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Knipe D. M. Stimulation of expression of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein by two viral functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):957–963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., Gavis E. R., Buchan A., Raj N. B., Hayward G. S., Pitha P. M. Expression of human beta-interferon cDNA under the control of a thymidine kinase promoter from herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):598–601. doi: 10.1038/297598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Schaffer P. A. Deletion mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 exhibit impaired growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):829–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.829-839.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Holland L. E., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Expression of herpes simplex virus beta and gamma genes integrated in mammalian cells and their induction by an alpha gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2028–2044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G. B., Cook M. L., Feldman L. T. RNA complementary to a herpesvirus alpha gene mRNA is prominent in latently infected neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2434993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Stow E. C. Isolation and characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant containing a deletion within the gene encoding the immediate early polypeptide Vmw110. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2571–2585. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay M. L., Yee S. P., Persson R. H., Bacchetti S., Smiley J. R., Branton P. E. Activation and inhibition of expression of the 72,000-Da early protein of adenovirus type 5 in mouse cells constitutively expressing an immediate early protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90302-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Vande Woude G. F. DNA sequence of an immediate-early gene (IEmRNA-5) of herpes simplex virus type I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):979–991. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls establish the cascade of herpes simplex virus protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):819–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Rixon F. J., Easton A. J., Clements J. B. Immediate-early mRNA-2 of herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2 is unspliced: conserved sequences around the 5' and 3' termini correspond to transcription regulatory signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6271–6287. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]