Abstract
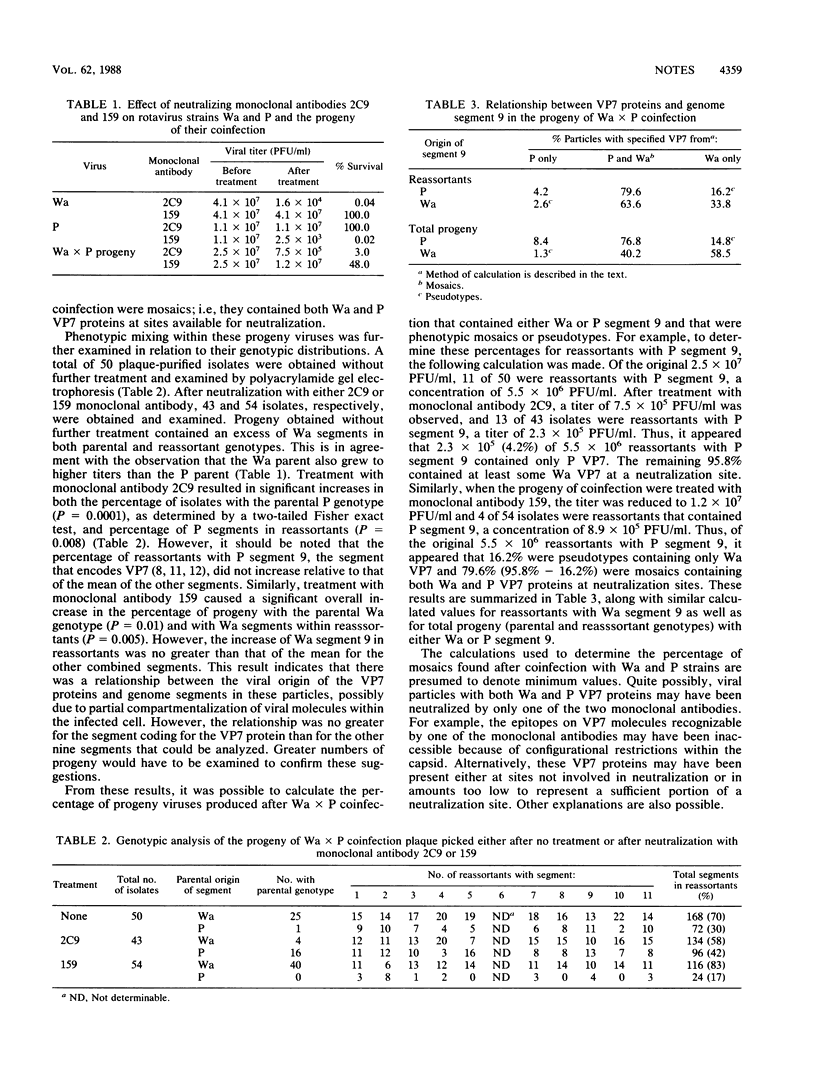
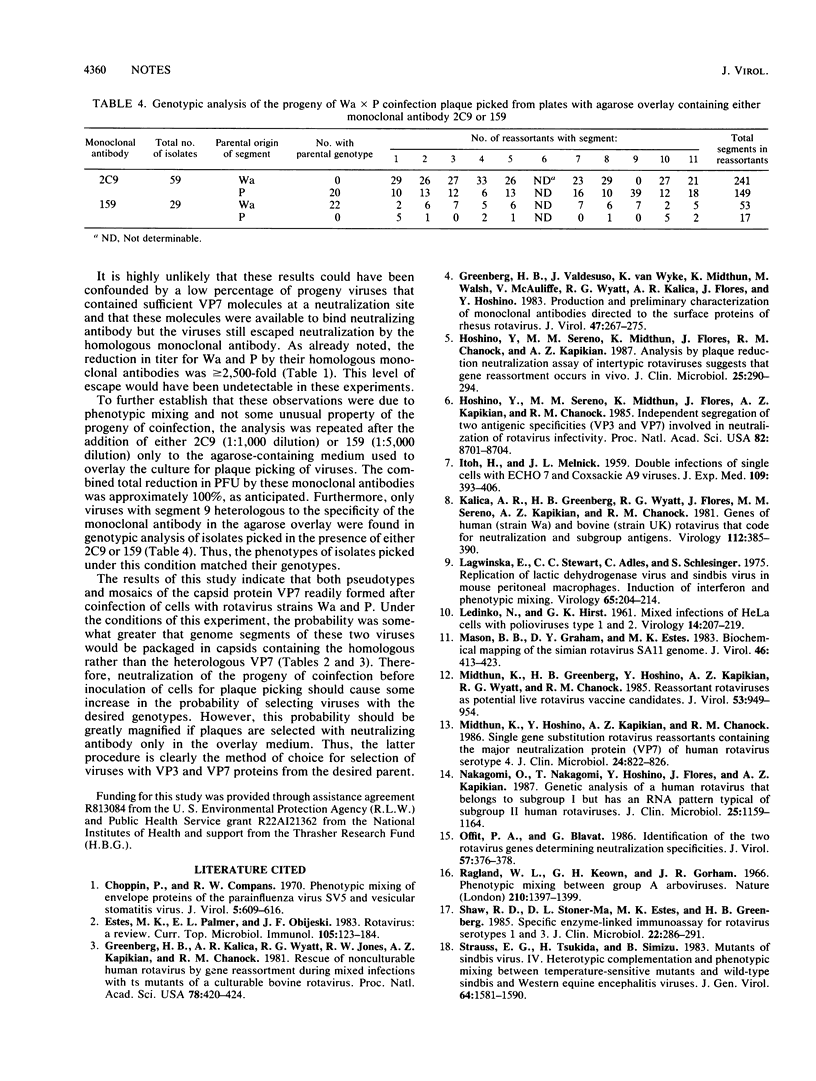
Coinfection of MA-104 cells with serotype 1 (Wa strain) and serotype 3 (P strain) human rotaviruses resulted in progeny viruses that were phenotypically mixed in their major outer-shell structural-protein VP7 and in the genome segment that encodes this protein (segment 9). Segments from the Wa virus predominated in these progeny whether they were of parental or reassortant genotype. Neutralization with monoclonal antibodies specific for VP7 proteins of the coinfecting viruses caused an alteration in genomic distribution favoring the strain heterologous to the neutralizing monoclonal antibody. Because the percentage of change in distribution of segment 9 was similar to that of the other combined segments, there appeared to be no greater association between VP7 and segment 9 than with other segments of the homologous virus during encapsulation. From these results, it was calculated that the progeny of coinfection with P segment 9 were 77.4% mosaic structures and 14.8% pseudotypes; progeny of coinfection with Wa segment 9 were 40.2% mosaic structures and 1.3% pseudotypes. Similar determinations were made for the reassortant progeny alone.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Choppin P. W., Compans R. W. Phenotypic mixing of envelope proteins of the parainfluenza virus SV5 and vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):609–616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.609-616.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F. Rotaviruses: a review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:123–184. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Jones R. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Rescue of noncultivatable human rotavirus by gene reassortment during mixed infection with ts mutants of a cultivatable bovine rotavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):420–424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Valdesuso J., van Wyke K., Midthun K., Walsh M., McAuliffe V., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Hoshino Y. Production and preliminary characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed at two surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):267–275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.267-275.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Analysis by plaque reduction neutralization assay of intertypic rotaviruses suggests that gene reassortment occurs in vivo. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):290–294. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.290-294.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Independent segregation of two antigenic specificities (VP3 and VP7) involved in neutralization of rotavirus infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8701–8704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITOH H., MELNICK J. L. Double infections of single cells with ECHO 7 and Coxsackie A9 viruses. J Exp Med. 1959 Apr 1;109(4):393–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.4.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Sereno M. M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genes of human (strain Wa) and bovine (strain UK) rotaviruses that code for neutralization and subgroup antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDINKO N., HIRST G. K. Mixed infection of HeLa cells with polioviruses types 1 and 2. Virology. 1961 Jun;14:207–219. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90196-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagwinska E., Stewart C. C., Adles C., Schlesinger S. Replication of lactic dehydrogenase virus and Sindbis virus in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Induction of interferon and phenotypic mixing. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):204–214. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason B. B., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Biochemical mapping of the simian rotavirus SA11 genome. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):413–423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.413-423.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Greenberg H. B., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Chanock R. M. Reassortant rotaviruses as potential live rotavirus vaccine candidates. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):949–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.949-954.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Single gene substitution rotavirus reassortants containing the major neutralization protein (VP7) of human rotavirus serotype 4. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):822–826. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.822-826.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Hoshino Y., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic analysis of a human rotavirus that belongs to subgroup I but has an RNA pattern typical of subgroup II human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1159–1164. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1159-1164.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Blavat G. Identification of the two rotavirus genes determining neutralization specificities. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):376–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.376-378.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragland W. L., Keown G. H., Gorham J. R. An epizootic of equine sarcoid. Nature. 1966 Jun 25;210(5043):1399–1399. doi: 10.1038/2101399a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Stoner-Ma D. L., Estes M. K., Greenberg H. B. Specific enzyme-linked immunoassay for rotavirus serotypes 1 and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.286-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Tsukeda H., Simizu B. Mutants of sindbis virus. IV. Heterotypic complementation and phenotypic mixing between temperature-sensitive mutants and wild-type Sindbis and Western equine encephalitis viruses. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jul;64(Pt 7):1581–1590. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-7-1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa S., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K. Genetic reassortment between two human rotaviruses having different serotype and subgroup specificities. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1551–1559. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Knowlton D. R., Hurst P. F. Reassortant formation and selection following coinfection of cultured cells with subgroup 2 human rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):149–162. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Knowlton D. R., Schiff G. M., Hoshino Y., Greenberg H. B. Relative concentrations of serum neutralizing antibody to VP3 and VP7 proteins in adults infected with a human rotavirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1543–1549. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1543-1549.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


