Abstract
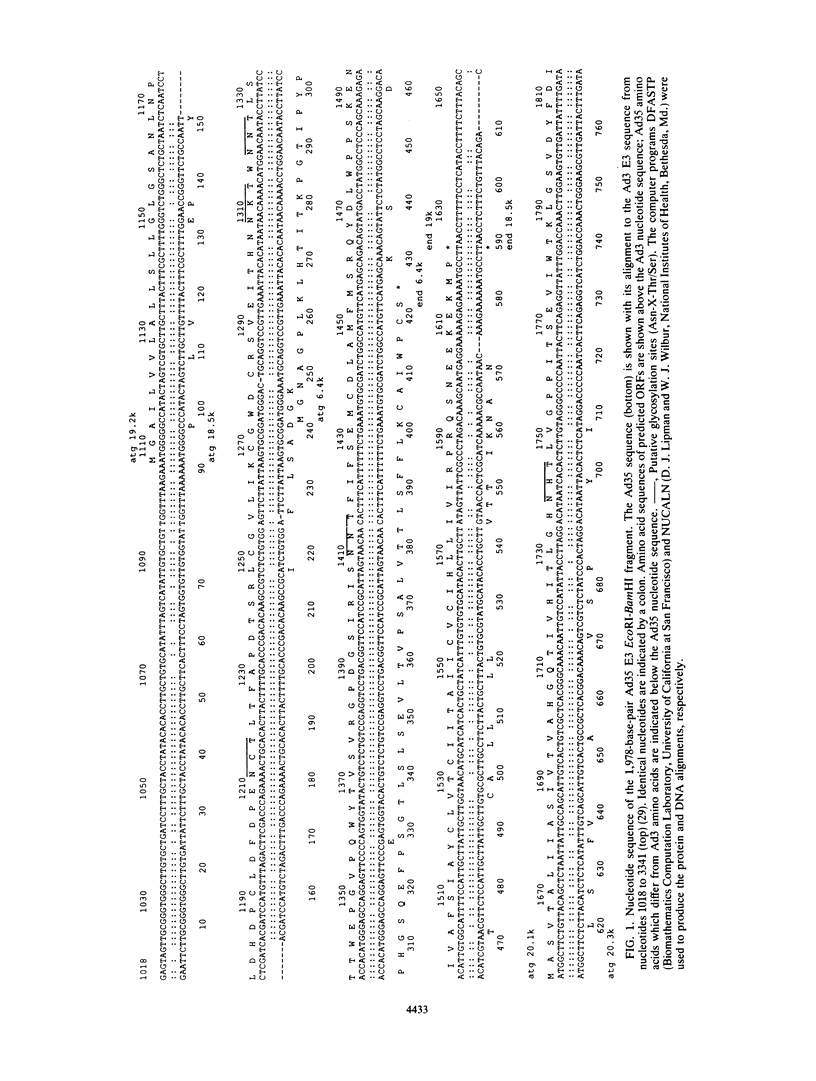
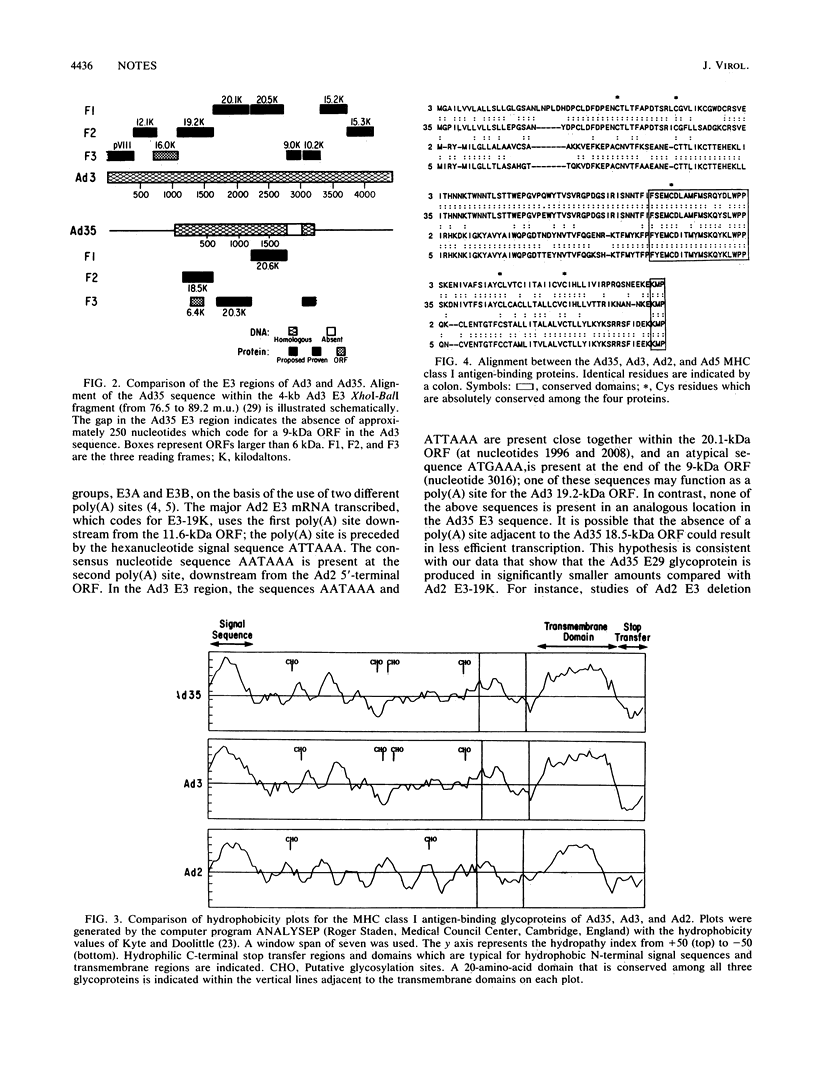
The early transcription region 3 (E3) of group B adenovirus type 35 (Ad35), a serotype isolated primarily from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and other immunodeficiency disorders, has been partially sequenced. We had previously identified an Ad35 29-kilodalton (kDa) early glycoprotein which, analogous to group C Ad2 E3-19K, associated with major histocompatibility complex class I antigens in the endoplasmic reticulum of infected cells. The open reading frame (ORF) of the Ad35 29-kDa protein has now been identified within a 2-kilobase-pair cloned Ad35 E3 fragment. The predicted amino acid sequence was very similar to that of group B Ad3 E3-19K. In contrast, homology between the Ad35 and Ad2 glycoproteins was limited to five cysteines in identical positions and a 20-amino-acid region proximal to the transmembrane domain. In addition, 20.3- and 20.6-kDa ORFs have been identified downstream from the ORF for the Ad35 glycoprotein. Analogous 20-kDa ORFs are present in the Ad3 E3 region but are not present in Ad2 and Ad5. In contrast, the region analogous to an Ad2 11.6-kDa ORF, which is 9 kDa in size in Ad3, was absent from the expected position within the Ad35 E3 region. Because the E3 region is likely to play an important role in the interaction between virus and host, analysis of the function of the Ad35 E3 proteins should further our understanding of adenovirus pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson M., Päbo S., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. Impaired intracellular transport of class I MHC antigens as a possible means for adenoviruses to evade immune surveillance. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat B. M., Wold W. S. A small deletion distant from a splice or polyadenylation site dramatically alters pre-mRNA processing in region E3 of adenovirus. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3938–3945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3938-3945.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgert H. G., Kvist S. An adenovirus type 2 glycoprotein blocks cell surface expression of human histocompatibility class I antigens. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Bhat B., Wold W. S. Mapping the 5' ends, 3' ends, and splice sites of mRNAs from the early E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 5. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):44–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90444-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Wold W. S. DNA sequence of the early E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 5. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):28–43. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Zinkernagel R. M. H-2 compatibility is required for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):502–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fickett J. W. Recognition of protein coding regions in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5303–5318. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flomenberg P. R., Chen M., Horwitz M. S. Characterization of a major histocompatibility complex class I antigen-binding glycoprotein from adenovirus type 35, a type associated with immunocompromised hosts. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3665–3671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3665-3671.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flomenberg P. R., Chen M., Munk G., Horwitz M. S. Molecular epidemiology of adenovirus type 35 infections in immunocompromised hosts. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1127–1134. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooding L. R., Elmore L. W., Tollefson A. E., Brady H. A., Wold W. S. A 14,700 MW protein from the E3 region of adenovirus inhibits cytolysis by tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):341–346. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTLEY J. W., ROWE W. P. A new mouse virus apparently related to the adenovirus group. Virology. 1960 Jul;11:645–647. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. S. Intermediates in the synthesis of type 2 adenovirus deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):675–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.675-683.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérissé J., Courtois G., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the EcoRI D fragment of adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2173–2192. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérissé J., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the EcoRI E fragment of adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1229–1240. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Lewis A. M., Jr Use of nondefective adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrids for mapping the simian virus 40 genome. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):643–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.643-652.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Wold W. S. Structures of the oligosaccharides of the glycoprotein coded by early region E3 of adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):440–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.440-449.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Ostberg L., Persson H., Philipson L., Peterson P. A. Molecular association between transplantation antigens and cell surface antigen in adenovirus-transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5674–5678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin J. E., Lubeck M. D., Barton J. E., Conley A. J., Davis A. R., Hung P. P. Recombinant adenovirus induces antibody response to hepatitis B virus surface antigen in hamsters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4626–4630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Bhat B. M., Wold W. S., Peterson P. A. A short sequence in the COOH-terminus makes an adenovirus membrane glycoprotein a resident of the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90226-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. Adenoviruses of subgenera B, C, D, and E modulate cell-surface expression of major histocompatibility complex class I antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9665–9669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields A. F., Hackman R. C., Fife K. H., Corey L., Meyers J. D. Adenovirus infections in patients undergoing bone-marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 28;312(9):529–533. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502283120901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signäs C., Akusjärvi G., Pettersson U. Region E3 of human adenoviruses; differences between the oncogenic adenovirus-3 and the non-oncogenic adenovirus-2. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder H., Hierholzer J. C., Oxman M. N. New human adenovirus (candidate adenovirus type 35) causing fatal disseminated infection in a renal transplant recipient. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):257–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.257-265.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefson A. E., Wold W. S. Identification and gene mapping of a 14,700-molecular-weight protein encoded by region E3 of group C adenoviruses. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):33–39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.33-39.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valderrama-Leon G., Flomenberg P., Horwitz M. S. Restriction endonuclease mapping of adenovirus 35, a type isolated from immunocompromised hosts. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):647–650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.647-650.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Cladaras C., Magie S. C., Yacoub N. Mapping a new gene that encodes an 11,600-molecular-weight protein in the E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):307–313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.307-313.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong P. J., Valderrama G., Spigland I., Horwitz M. S. Adenovirus isolates from urine of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Lancet. 1983 Jun 11;1(8337):1293–1296. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


