Abstract
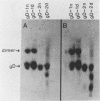
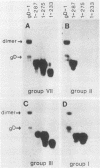
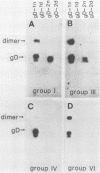
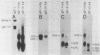
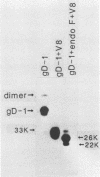
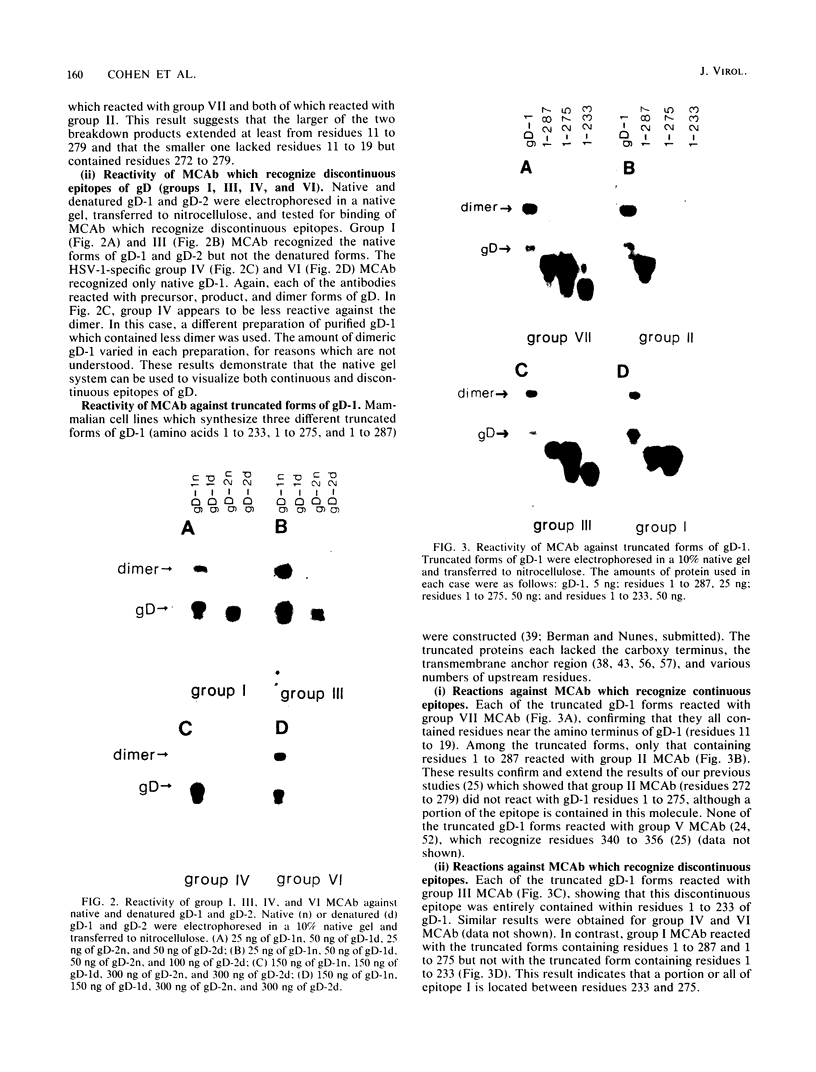
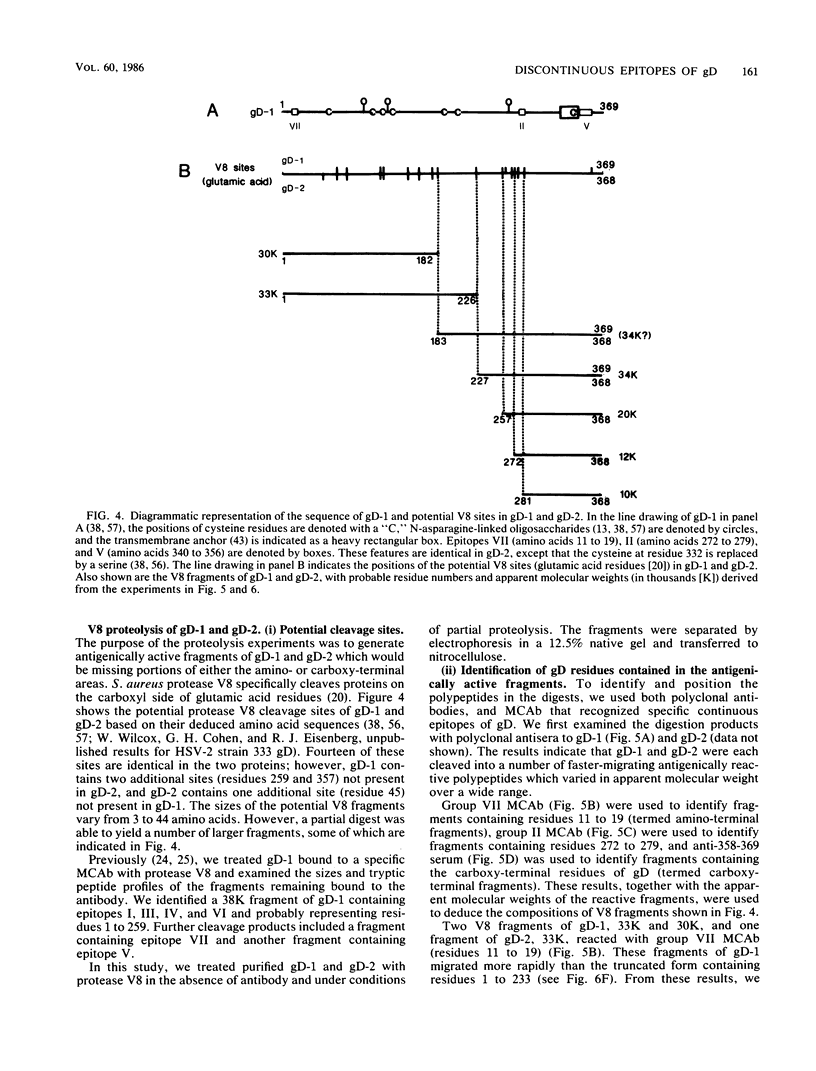
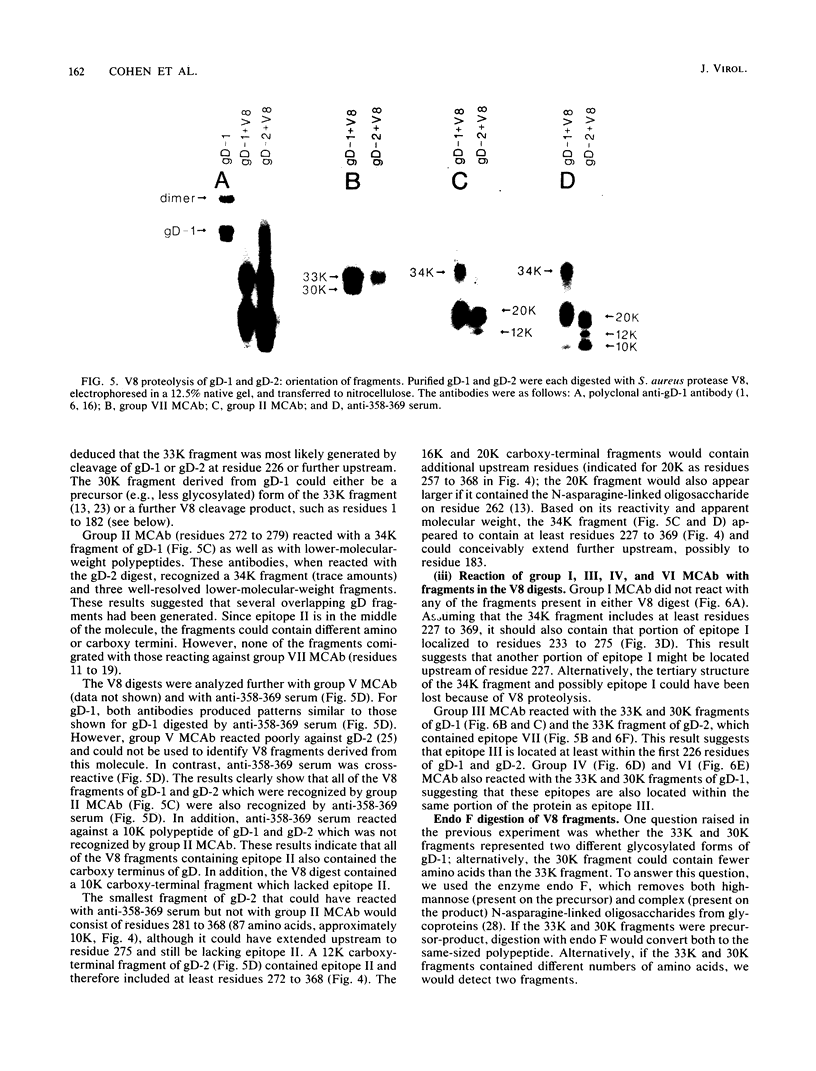
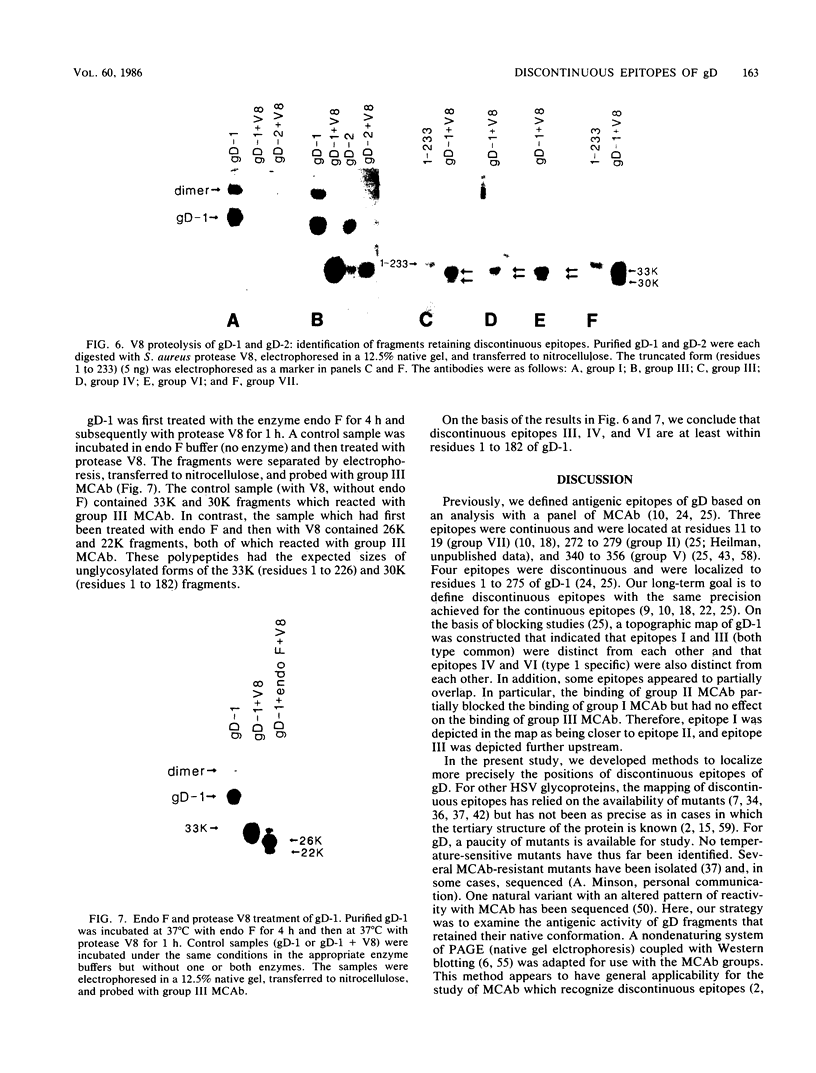
Previously, a panel of monoclonal antibodies (MCAb) was used to define specific epitopes of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D (gD) (R. J. Eisenberg et al., J. Virol. 53:634-644, 1985). Three groups of antibodies recognized continuous epitopes; group VII reacted with residues 11 to 19 of the mature protein (residues 36 to 44 of the predicted sequence), group II reacted with residues 272 to 279, and group V reacted with residues 340 to 356. Four additional antibody groups recognized discontinuous epitopes of gD, since their reactivity was lost when the glycoprotein was denatured by reduction and alkylation. Our goal in this study was to localize more precisely the discontinuous epitopes of gD. Using a nondenaturing system of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis ("native" gel electrophoresis) coupled to Western blotting, we analyzed the antigenic activity of truncated forms of gD. These fragments were generated either by recombinant DNA methods or by cleavage of purified native gD-1 (gD obtained from herpes simplex virus type 1) and gD-2 (gD obtained from herpes simplex virus type 2) with Staphylococcus aureus protease V8. Antibodies in groups III, IV, and VI recognized three truncated forms of gD-1 produced by recombinant DNA methods, residues 1 to 287, 1 to 275, and 1 to 233. Antibodies in group I recognized the two larger forms but did not react with the gD-1 fragment of residues 1 to 233. On the basis of these and previous results, we concluded that a protion of epitope I was located within residues 233 to 259 and that epitopes III, IV, and VI were upstream of residue 233. Antibodies to continuous epitopes identified protease V8 fragments of gD-1 and gD-2 that contained portions of either the amino or carboxy regions of the proteins. None of the V8 fragments, including a 34K polypeptide containing residues 227 to 369, reacted with group I antibodies. This result indicated that a second portion of epitope I was located upstream of residue 227. Two amino-terminal fragments of gD-1, 33K and 30K, reacted with group III, IV, and VI antibodies. A 33K fragment of gD-2 reacted with group III antibodies. Based on their size and reactivity with endo-beta-N-acetylglycosaminidase F, we hypothesized that the 33K and 30K molecules represented residues 1 to 226 and 1 to 182 of gD-1, respectively. These results suggest that epitopes III, IV, and VI are located within the first 182 residues of gD.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atassi M. Z. Precise determination of the entire antigenic structure of lysozyme: molecular features of protein antigenic structures and potential of "surface-simulation" synthesis--a powerful new concept for protein binding sites. Immunochemistry. 1978 Dec;15(12):909–936. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin D. C., Berzofsky J. A., East I. J., Gurd F. R., Hannum C., Leach S. J., Margoliash E., Michael J. G., Miller A., Prager E. M. The antigenic structure of proteins: a reappraisal. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:67–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. W., Gregory T., Crase D., Lasky L. A. Protection from genital herpes simplex virus type 2 infection by vaccination with cloned type 1 glycoprotein D. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1490–1492. doi: 10.1126/science.2983428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. K., Pereira L., Norrild B., Roizman B. Application of denatured, electrophoretically separated, and immobilized lysates of herpes simplex virus-infected cells for detection of monoclonal antibodies and for studies of the properties of viral proteins. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):103–112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.103-112.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Fox B. A., DeLuca N. A., Person S. Nucleotide sequence of a region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 gB glycoprotein gene: mutations affecting rate of virus entry and cell fusion. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. L. Protective immunization of mice with specific HSV-1 glycoproteins. Immunology. 1983 Jun;49(2):343–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Dietzschold B., Ponce de Leon M., Long D., Golub E., Varrichio A., Pereira L., Eisenberg R. J. Localization and synthesis of an antigenic determinant of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D that stimulates the production of neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):102–108. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.102-108.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Factor M. N., Ponce de Leon M. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 2 replication by thymidine. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):20–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.20-25.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Katze M., Hydrean-Stern C., Eisenberg R. J. Type-common CP-1 antigen of herpes simplex virus is associated with a 59,000-molecular-weight envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):172–181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.172-181.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Long D., Matthews J. T., May M., Eisenberg R. Glycopeptides of the type-common glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):679–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.679-689.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Ponce de Leon M., Nichols C. Isolation of a herpes simplex virus-specific antigenic fraction which stimulates the production of neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1021-1030.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M., Varghese J. N., Laver W. G. Structure of the catalytic and antigenic sites in influenza virus neuraminidase. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):41–44. doi: 10.1038/303041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer K. J., Mackett M., Wohlenberg C., Notkins A. L., Moss B. Vaccinia virus recombinant expressing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D prevents latent herpes in mice. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):737–740. doi: 10.1126/science.2986288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. O., Schneider W. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Visualization of lipoprotein receptors by ligand blotting. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4606–4611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Eisenberg R. J., Ponce de Leon M., Golub E., Hudecz F., Varrichio A., Cohen G. H. Fine structure analysis of type-specific and type-common antigenic sites of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):431–435. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.431-435.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix R. D., Pereira L., Baringer J. R. Use of monoclonal antibody directed against herpes simplex virus glycoproteins to protect mice against acute virus-induced neurological disease. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):192–199. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.192-199.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R., Boily Y., Houmard J. Purification and properties of an extracellular protease of Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6720–6726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Cerini C. P., Heilman C. J., Joseph A. D., Dietzschold B., Golub E., Long D., Ponce de Leon M., Cohen G. H. Synthetic glycoprotein D-related peptides protect mice against herpes simplex virus challenge. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):1014–1017. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.1014-1017.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Hydrean-Stern C., Cohen G. H. Structural analysis of precursor and product forms of type-common envelope glycoprotein D (CP-1 antigen) of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):608–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.608-620.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Long D., Pereira L., Hampar B., Zweig M., Cohen G. H. Effect of monoclonal antibodies on limited proteolysis of native glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):478–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.478-488.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Long D., Ponce de Leon M., Matthews J. T., Spear P. G., Gibson M. G., Lasky L. A., Berman P., Golub E., Cohen G. H. Localization of epitopes of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):634–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.634-644.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Ponce de Leon M., Cohen G. H. Comparative structural analysis of glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):428–435. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.428-435.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Ponce de Leon M., Pereira L., Long D., Cohen G. H. Purification of glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 by use of monoclonal antibody. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1099–1104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1099-1104.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. M., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J., Seidel C. A., Cines D. B. Glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus 1 acts as a receptor for the C3b complement component on infected cells. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):633–635. doi: 10.1038/309633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Specificities of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies that inhibit adsorption of herpes simplex virus to cells and lack of inhibition by potent neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):475–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.475-482.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson M. G., Spear P. G. Insertion mutants of herpes simplex virus have a duplication of the glycoprotein D gene and express two different forms of glycoprotein D. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):396–404. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.396-404.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbrink P., Van Bussel F. J., Warnaar S. O. The antigen spot test (AST): a highly sensitive assay for the detection of antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(3):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. Antigenic variants of herpes simplex virus selected with glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):672–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.672-682.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kümel G., Kaerner H. C., Levine M., Schröder C. H., Glorioso J. C. Passive immune protection by herpes simplex virus-specific monoclonal antibodies and monoclonal antibody-resistant mutants altered in pathogenicity. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):930–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.930-937.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Dowbenko D. J. DNA sequence analysis of the type-common glycoprotein-D genes of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. DNA. 1984;3(1):23–29. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. T., Para M. F., Spear P. G. Location of the structural genes for glycoproteins gD and gE and for other polypeptides in the S component of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):41–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.41-49.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long D., Madara T. J., Ponce de Leon M., Cohen G. H., Montgomery P. C., Eisenberg R. J. Glycoprotein D protects mice against lethal challenge with herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):761–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.761-764.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin S. D., Holland T. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Epitopes of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein gC are clustered in two distinct antigenic sites. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):128–136. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.128-136.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews J. T., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J. Synthesis and processing of glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 in an in vitro system. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):521–533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.521-533.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery P. C., Dorrington K. J., Rockey J. H. Equine antihapten antibody. The molecular weights of the subunits of equine immunoglobulins. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):1247–1258. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble A. G., Lee G. T., Sprague R., Parish M. L., Spear P. G. Anti-gD monoclonal antibodies inhibit cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):218–224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90409-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E., Lipinskas B. R., Samsonoff C., Mercer S., Panicali D. Construction of live vaccines using genetically engineered poxviruses: biological activity of vaccinia virus recombinants expressing the hepatitis B virus surface antigen and the herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):193–197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D. V., Gallo D., Devlin V., Woodie J. D. Serological analysis of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):363–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.363-367.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Klassen T., Baringer J. R. Type-common and type-specific monoclonal antibody to herpes simplex virus type 1. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):724–732. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.724-732.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Balachandran N., Sisson G., Watson R. J. Localization of a type-specific antigenic site on herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein D. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):263–265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.263-265.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector J. T., Lausch R. N., Oakes J. E. Identification of infected cell-specific monoclonal antibodies and their role in host resistance to ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):657–661. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J. DNA sequence of the Herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein D gene. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Weis J. H., Salstrom J. S., Enquist L. W. Bacterial synthesis of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 glycoprotein D antigens. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jul;83(1 Suppl):102s–111s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12281828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Weis J. H., Salstrom J. S., Enquist L. W. Herpes simplex virus type-1 glycoprotein D gene: nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):381–384. doi: 10.1126/science.6289440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):373–378. doi: 10.1038/289373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]