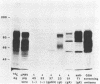
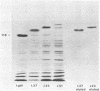
Abstract
A library of pseudorabies virus (PRV) DNA fragments was constructed in the expression cloning vector lambda gt11. The library was screened with antisera which reacted with mixtures of PRV proteins to isolate recombinant bacteriophages expressing PRV proteins. By the nature of the lambda gt11 vector, the cloned proteins were expressed in Escherichia coli as beta-galactosidase fusion proteins. The fusion proteins from 35 of these phages were purified and injected into mice to raise antisera. The antisera were screened by several different assays, including immunoprecipitation of [14C]glucosamine-labeled PRV proteins. This method identified phages expressing three different PRV glycoproteins: the secreted glycoprotein, gX; gI; and a glycoprotein that had not been previously identified, which we designate gp63. The gp63 and gI genes map adjacent to each other in the small unique region of the PRV genome. The DNA sequence was determined for the region of the genome encoding gp63 and gI. It was found that gp63 has a region of homology with a herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) protein, encoded by US7, and also with varicella-zoster virus (VZV) gpIV. The gI protein sequence has a region of homology with HSV-1 gE and VZV gpI. It is concluded that PRV, HSV, and VZV all have a cluster of homologous glycoprotein genes in the small unique components of their genomes and that the organization of these genes is conserved.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEN-PORAT T., KAPLAN A. S. The chemical composition of herpes simplex and pseudorabies viruses. Virology. 1962 Mar;16:261–266. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. V. Identification of an Fc-binding glycoprotein. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., DeMarchi J., Pendrys J., Veach R. A., Kaplan A. S. Proteins specified by the short unique region of the genome of pseudorabies virus play a role in the release of virions from certain cells. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):191–196. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.191-196.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Veach R. A., Ihara S. Localization of the regions of homology between the genomes of herpes simplex virus, type 1, and pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):194–204. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns A., van den Ouweland A., Quint W., van Oirschot J., Gielkens A. Presence of markers for virulence in the unique short region or repeat region or both of pseudorabies hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):89–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.89-93.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmaster E. A., Gompels U., Minson A. Characterisation and physical mapping of an HSV-1 glycoprotein of approximately 115 X 10(3) molecular weight. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90387-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., Williams J. L., McCutchan T. F., Weber J. L., Wirtz R. A., Hockmeyer W. T., Maloy W. L., Haynes J. D., Schneider I., Roberts D. Structure of the gene encoding the immunodominant surface antigen on the sporozoite of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):593–599. doi: 10.1126/science.6204383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J. DNA sequence of the US component of the varicella-zoster virus genome. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2203–2209. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Edson C. M., Ellis R. W., Forghani B., Gilden D., Grose C., Keller P. M., Vafai A., Wroblewska Z., Yamanishi K. New common nomenclature for glycoprotein genes of varicella-zoster virus and their glycosylated products. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1195–1197. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1195-1197.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Waters D. J., Edson C. M. Identification of the products of a varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein gene. J Gen Virol. 1985 Oct;66(Pt 10):2237–2242. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-10-2237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Wilkie N. M. Location and orientation of homologous sequences in the genomes of five herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1983 Sep;64(Pt 9):1927–1942. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-9-1927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Keller P. M., Lowe R. S., Zivin R. A. Use of a bacterial expression vector to map the varicella-zoster virus major glycoprotein gene, gC. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):81–88. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.81-88.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Baron L. S. Genetic characterization of a bacterial locus involved in the activity of the N function of phage lambda. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. M., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J., Seidel C. A., Cines D. B. Glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus 1 acts as a receptor for the C3b complement component on infected cells. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):633–635. doi: 10.1038/309633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Specificities of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies that inhibit adsorption of herpes simplex virus to cells and lack of inhibition by potent neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):475–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.475-482.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb L. D., Wellinghoff W. J., Martin J. H., Huang J. J. Varicella-zoster virus fails to induce immunoglobulin G Fc receptors in infected human cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1981 Nov;168(2):228–232. doi: 10.3181/00379727-168-41265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gielkens A. L., Van Oirschot J. T., Berns A. J. Genome differences among field isolates and vaccine strains of pseudorabies virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jan;66(Pt 1):69–82. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampl H., Ben-Porat T., Ehrlicher L., Habermehl K. O., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of the envelope proteins of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.583-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak R., Andiman W. A., Tucker G. Absence of IgG Fc receptors on varicella-zoster virus-infected cells. J Med Virol. 1984;13(3):261–267. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890130308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalnins A., Otto K., Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of the lacZ gene of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):593–597. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01468.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B., Blankenship M. L., Ben-Porat T. Deletions in the genomes of pseudorabies virus vaccine strains and existence of four isomers of the genomes. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):970–979. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.970-979.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B., Watanabe S., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Genetic basis of the neurovirulence of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):198–205. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.198-205.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J. On the predictive recognition of signal peptide sequences. Virus Res. 1985 Oct;3(3):271–286. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Lukacs N., Rziha H. J. Mapping of the structural gene of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein A and identification of two non-glycosylated precursor polypeptides. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):52–57. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.52-57.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Lukàcs N., Rziha H. J. Pseudorabies virus avirulent strains fail to express a major glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):307–311. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.307-311.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montalvo E. A., Parmley R. T., Grose C. Structural analysis of the varicella-zoster virus gp98-gp62 complex: posttranslational addition of N-linked and O-linked oligosaccharide moieties. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):761–770. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.761-770.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble A. G., Lee G. T., Sprague R., Parish M. L., Spear P. G. Anti-gD monoclonal antibodies inhibit cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):218–224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90409-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Shigeta S. Appearance of immunoglobulin G Fc receptor in cultured human cells infected with varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):770–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.770-774.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Armentrout M. A., Marchioli C. C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Post L. E. DNA sequence of the gene for pseudorabies virus gp50, a glycoprotein without N-linked glycosylation. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):216–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.216-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. J., Timmins J. G., Long G. W., Post L. E. Mapping and sequence of the gene for the pseudorabies virus glycoprotein which accumulates in the medium of infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):21–29. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.21-29.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Buckmaster A., Bell S., Hodgman C., Minson A. C. Identification of a new glycoprotein of herpes simplex virus type 1 and genetic mapping of the gene that codes for it. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):647–655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.647-655.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Watson R. J., Whealy M. E., Hays W. W., Enquist L. W. Characterization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene with homology to herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):339–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.339-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Weis J. H., Enquist L. W., Watson R. J. Construction of E. coli expression plasmid libraries: localization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(5):485–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli A. C., Fischer D. S., Downs W. G. Use of sarcoma 180/TG to prepare hyperimmune ascitic fluid in the mouse. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):676–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmins J. G., Petrovskis E. A., Marchioli C. C., Post L. E. A method for efficient gene isolation from phage lambda gt11 libraries: use of antisera to denatured, acetone-precipitated proteins. Gene. 1985;39(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90112-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Wathen L. M. Isolation, characterization, and physical mapping of a pseudorabies virus mutant containing antigenically altered gp50. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):57–62. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.57-62.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]