Abstract
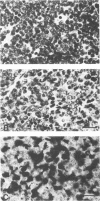
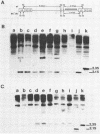
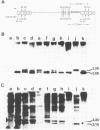
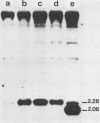
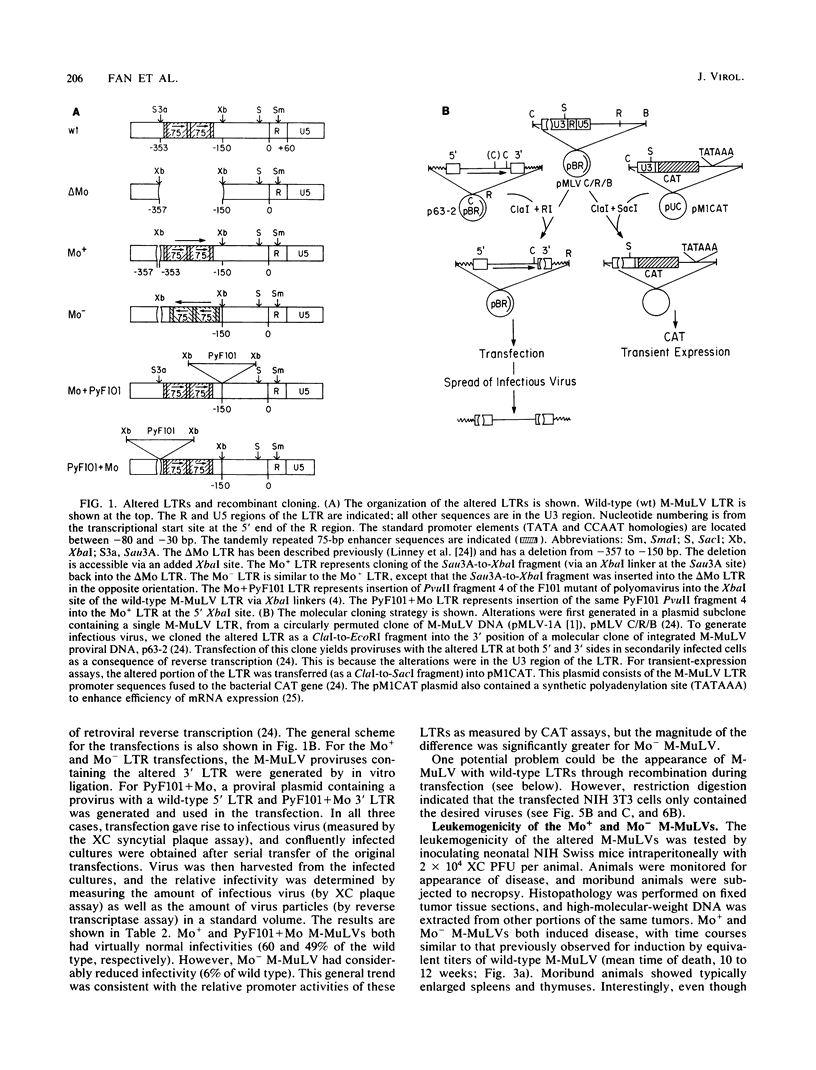
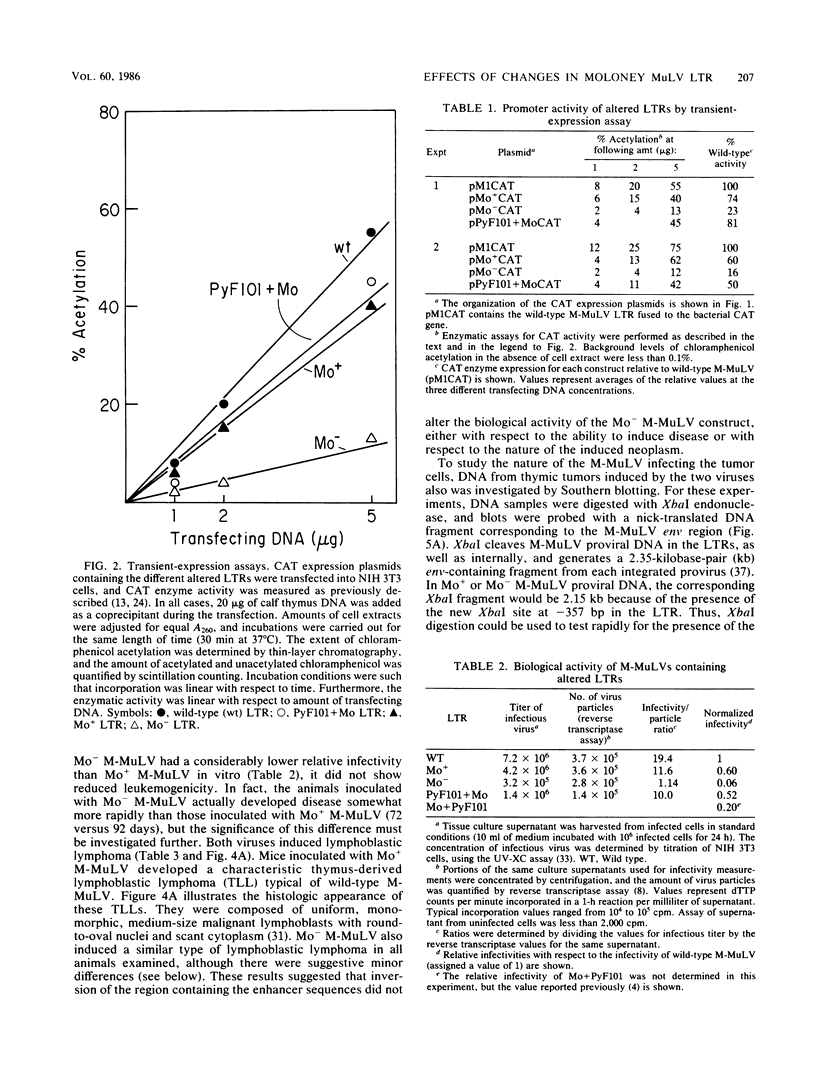
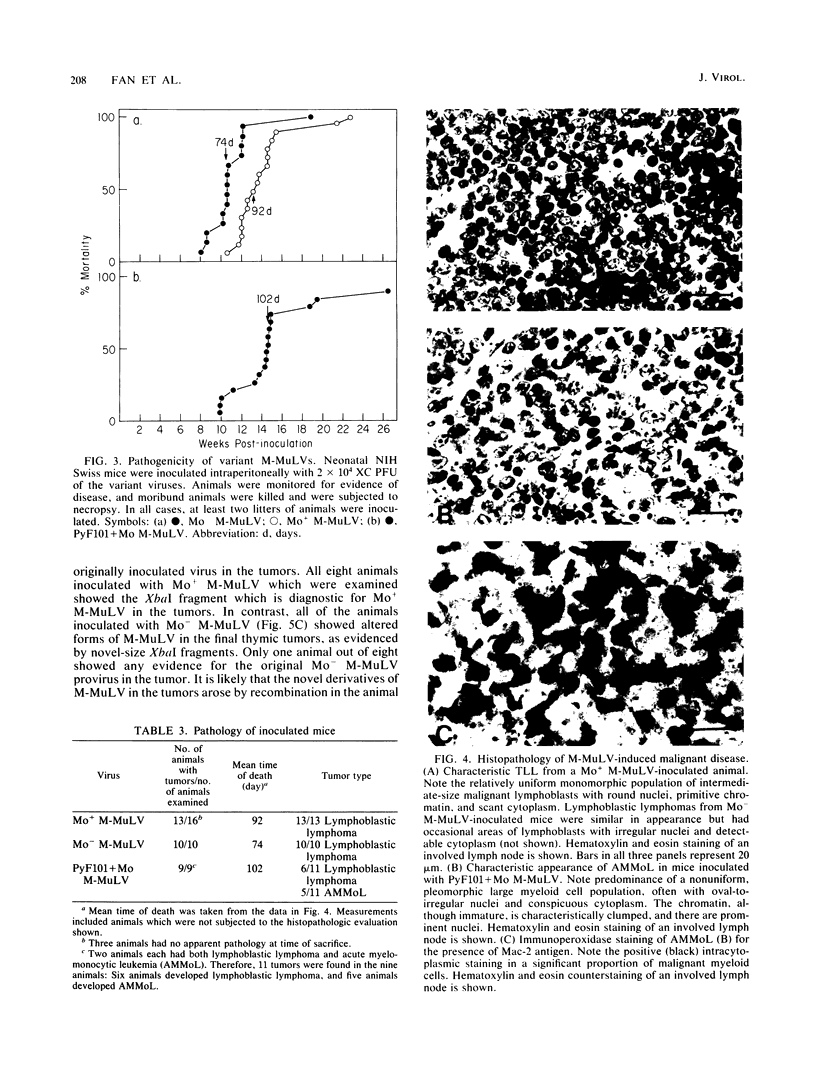
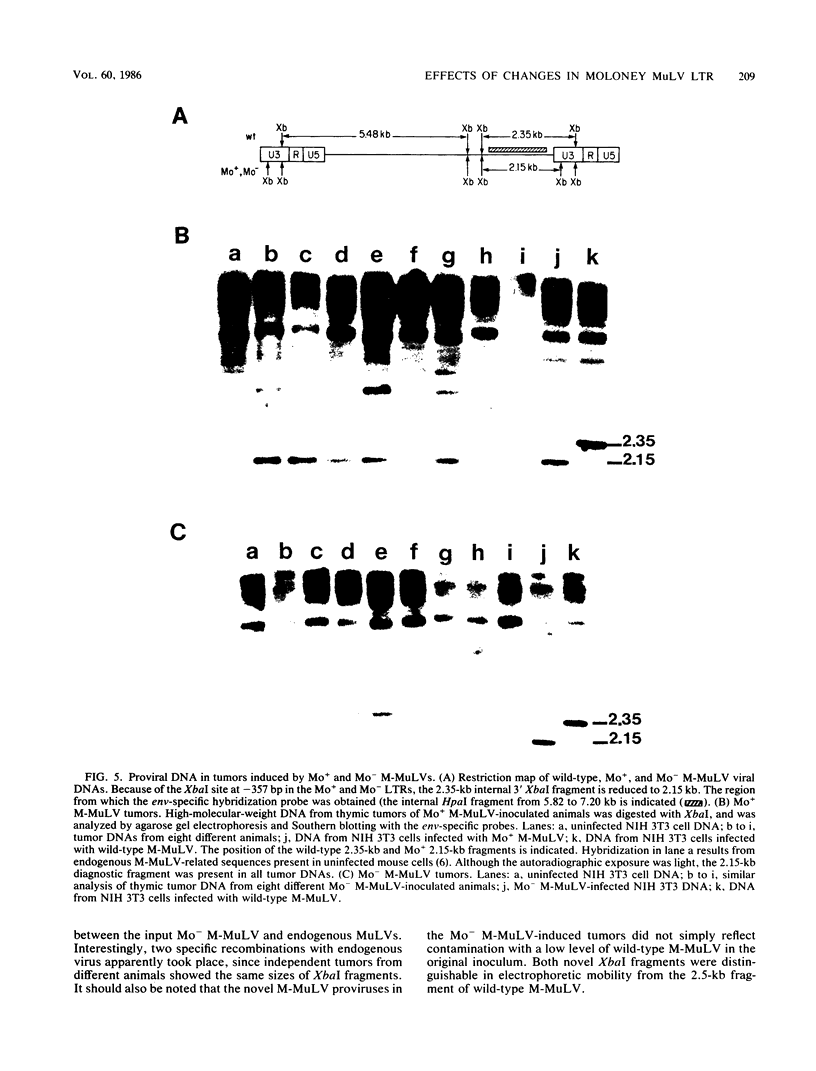
The effects of rearrangement and insertion of sequences in the Moloney murine leukemia virus (M-MuLV) long terminal repeat (LTR) were investigated. The alterations were made by recombinant DNA manipulations on a plasmid subclone containing an M-MuLV LTR. Promoter activity of altered LTRs was measured by fusion to the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene, followed by transient expression assay in NIH 3T3 cells. M-MuLV proviral organizations containing the altered LTRs were also generated, and infectious virus was recovered by transfection. Infectivity of the resulting virus was quantified by XC plaque assay, and pathogenicity was determined by inoculating neonatal NIH Swiss mice. Inversion of sequences in the U3 region containing the tandemly repeated enhancer sequences (-150 to -353 base pairs [bp]) reduced promoter activity approximately fivefold in the transient-expression assays. Infectious virus containing the inverted sequences (Mo- M-MuLV) showed a 20-fold reduction in relative infectivity compared with wild-type M-MuLV, but the virus still induced thymus-derived lymphoblastic lymphoma or leukemia in mice, with essentially the same kinetics as for wild-type M-MuLV. We previously derived an M-MuLV which carried inserted enhancer sequences from the F101 strain of polyomavirus (Mo + PyF101 M-MuLV) and showed that this virus is nonleukemogenic. In Mo + PyF101 M-MuLV, the PyF101 sequences were inserted between the M-MuLV promoter and the M-MuLV enhancers (at -150 bp). A new LTR was generated in which the PyF101 sequences were inserted to the 5' side of the M-MuLV enhancers (at -353 bp, PyF101 + Mo M-MuLV). The PyF101 + Mo LTR exhibited promoter activity similar (40 to 50%) to that of wild-type M-MuLV, and infectious PyF101 + Mo M-MuLV had high infectivity on NIH 3T3 cells (50% of wild type). In contrast to the nonleukemogenic Mo + PyF101 M-MuLV, PyF101 + Mo M-MuLV induced leukemia with kinetics similar to that of wild-type M-MuLV. Thus, the position of the PyF101 sequences relative to the M-MuLV LTR affected the biological behavior of the molecular construct. Furthermore, PyF101 + Mo M-MuLV induced a different spectrum of neoplastic disease. In comparison with wild-type M-MuLV, which induces a characteristic thymus-derived lymphoblastic lymphoma with extremely high frequency, PyF101 + Mo M-MuLV was capable of inducing both acute myeloid leukemia or thymus-derived lymphoblastic lymphoma, or both. Tumor DNA from both the PyF101 + Mo- and Mo- M-MuLV-inoculated animals contained recombinant proviruses with LTRs that differed from the initially inoculated virus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berns A. J., Lai M. H., Bosselman R. A., McKennett M. A., Bacheler L. T., Fan H., Maandag E. C., van der Putten H. V., Verma I. M. Molecular cloning of unintegrated and a portion of integrated moloney murine leukemia viral DNA in bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):254–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.254-263.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Linney E., Fan H. Suppression of leukaemia virus pathogenicity by polyoma virus enhancers. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):550–553. doi: 10.1038/314550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolberg D. S., Bacheler L. T., Fan H. Endogenous type C retroviral sequences of mice are organized in a small number of virus-like classes and have been acquired recently. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):96–106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.96-106.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Jaenisch R., MacIsaac P. Low-multiplicity infection of Moloney murine leukemia virus in mouse cells: effect on number of viral DNA copies and virus production in producer cells. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):802–809. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.802-809.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerman M. H., Davis B. R., Pattengale P. K., Fan H. Generation of a recombinant Moloney murine leukemia virus carrying the v-src gene of avian sarcoma virus: transformation in vitro and pathogenesis in vivo. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):804–816. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.804-816.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flotte T. J., Springer T. A., Thorbecke G. J. Dendritic cell and macrophage staining by monoclonal antibodies in tissue sections and epidermal sheets. Am J Pathol. 1983 Apr;111(1):112–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Linney E. Mutation near the polyoma DNA replication origin permits productive infection of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):809–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90445-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Rigby P. W., Lane D. P. Negative regulation of viral enhancers in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Eisenman R. N., McKnight S. L. Delineation of transcriptional control signals within the Moloney murine sarcoma virus long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1948–1958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Viral integration near c-myc in 10-20% of mcf 247-induced AKR lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6808–6811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Davis B., Overhauser J., Chao E., Fan H. Non-function of a Moloney murine leukaemia virus regulatory sequence in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):470–472. doi: 10.1038/308470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Donerly S. DNA fragments from F9 PyEC mutants increase expression of heterologous genes in transfected F9 cells. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):693–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Mueller C. R., Mes A. M., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus origin for DNA replication comprises multiple genetic elements. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):586–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.586-599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Fleissner E., Lonial H., Koehne C. F., Reicin A. Early clonality and high-frequency proviral integration into the c-myc locus in AKR leukemias. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):500–503. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.500-503.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overhauser J., Fan H. Generation of glucocorticoid-responsive Moloney murine leukemia virus by insertion of regulatory sequences from murine mammary tumor virus into the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):133–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.133-144.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Taylor C. R. Experimental models of lymphoproliferative disease. The mouse as a model for human non-Hodgkin's lymphomas and related leukemias. Am J Pathol. 1983 Nov;113(2):237–265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Multiple arrangements of viral DNA and an activated host oncogene in bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):209–214. doi: 10.1038/295209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Zijlstra M., Melief C., Berns A. Involvement of c-myc in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas in mice: frequency and mechanisms of activation. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3215–3222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch T. G., Arnstein P., Manohar V., Leiserson W. M., Chused T. M. Proliferation of infected lymphoid precursors before Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Jan;74(1):137–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Rands E., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Verma I. M. Long terminal repeat of murine retroviral DNAs: sequence analysis, host-proviral junctions, and preintegration site. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):542–556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.542-556.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt M. Properties of "mink cell focus-inducing" (MCF) virus isolated from spontaneous lymphoma lines of BALB/c mice carrying Moloney leukemia virus as an endogenous virus. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):226–236. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90290-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Putten H., Quint W., van Raaij J., Maandag E. R., Verma I. M., Berns A. M-MuLV-induced leukemogenesis: integration and structure of recombinant proviruses in tumors. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]