Abstract
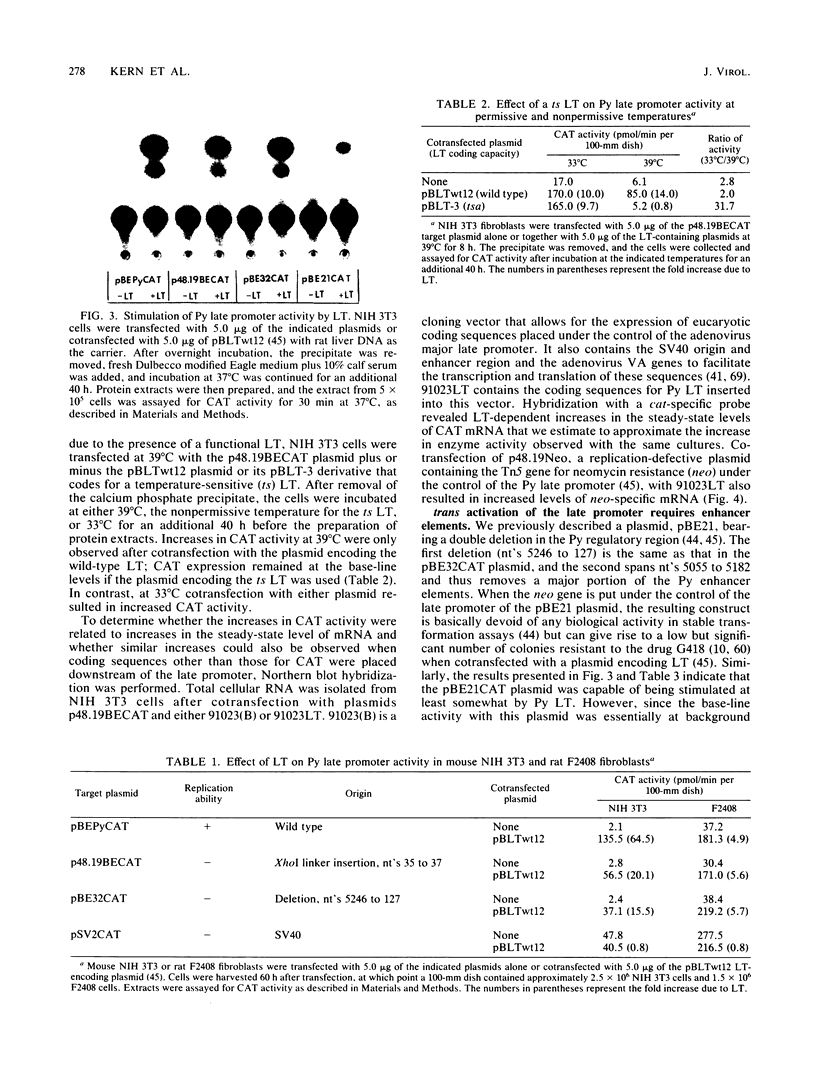
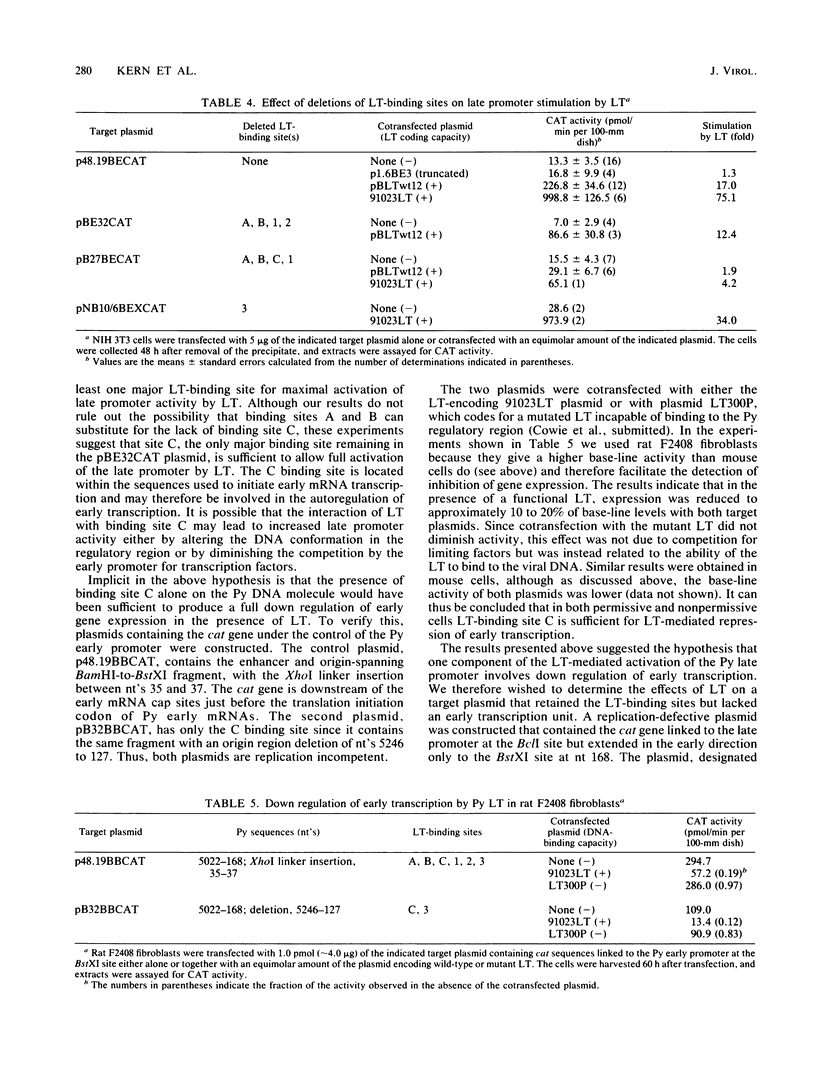
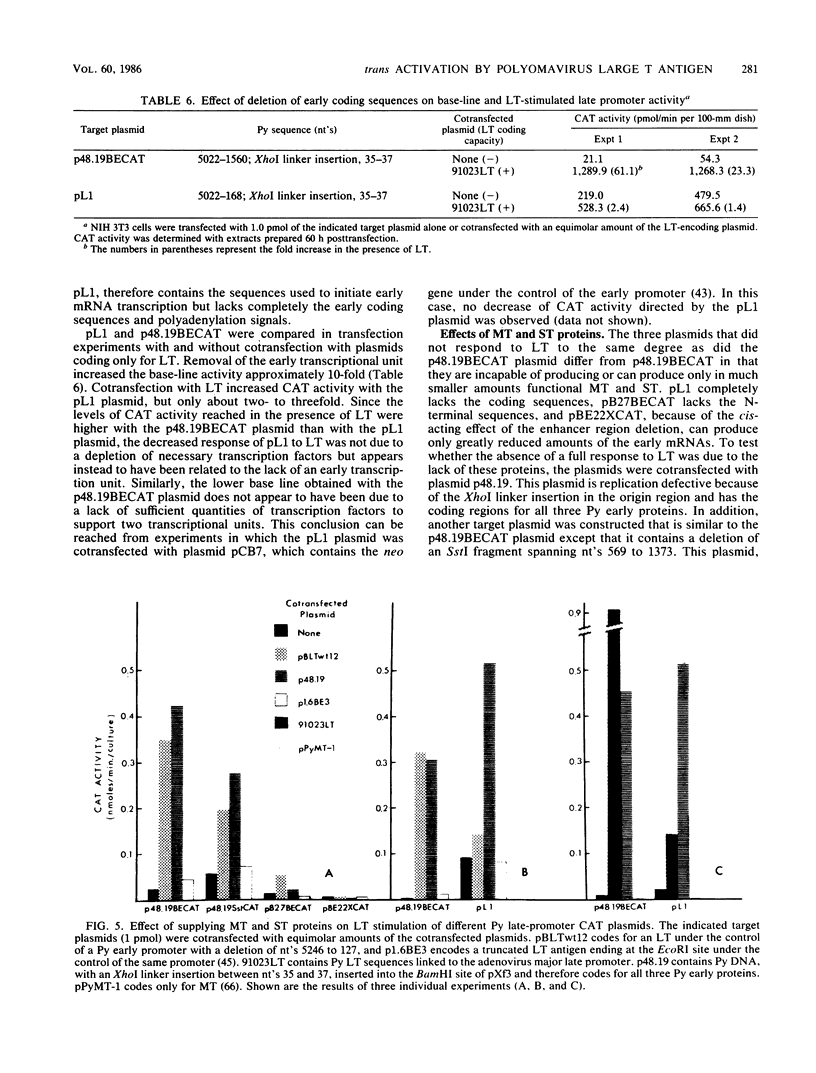
To assess the effect of the polyomavirus (Py) early proteins, the large T (LT), middle T (MT), and small T (ST) antigens, on gene expression from the Py late promoter, replication-defective plasmid constructs with the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (cat) gene linked to this promoter were cotransfected into mouse or rat cells with plasmids capable of producing either LT, MT, or all three early proteins. When target CAT plasmids contained a truncated early region and thus had the coding potential for MT and ST, base-line CAT activities were low, whereas cotransfection with an LT plasmid resulted in up to 70-fold stimulation of CAT activity that was also reflected in similar increases in the level of steady-state mRNA. Studies with target plasmids with deletions within the Py regulatory region indicated that at least the major LT-binding site C and a functional enhancer region were both required for maximal stimulation of CAT activity. However, although enhancer deletions totally suppressed the ability of target plasmids to be trans activated, a consistent two- to fourfold stimulation of CAT activity by LT was still observed with a plasmid in which all three major LT-binding sites were deleted. Of four mutant LTs incapable of binding Py DNA but retaining immortalization potential, only one showed a low but significant trans-activating ability. When the early coding region was completely eliminated from the target plasmid, base-line CAT activity was increased 10-fold. LT failed to stimulate CAT activity to the same levels observed with target plasmid containing the truncated early region, but this limited response could be enhanced by supplying, in addition, MT and ST. Our results suggest that LT trans activation may involve the formation of a complex of transcriptional factors which interacts with the enhancer, an interaction that is facilitated both by the binding of LT to the Py regulatory region and by the presence of MT or ST or both, and that a significant portion of LT stimulation of late gene expression is a result of the removal of the competing early transcriptional unit via autoregulation. In addition, our results suggest that LT trans activation involves a second indirect component acting independently of LT binding and that the immortalization and trans activation functions of LT can be dissociated.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C. Transient gene expression control: effects of transfected DNA stability and trans-activation by viral early proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1034–1042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E., Ludwig G., Auerswald E. A., Reiss B., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Bolen J. B., Radonovich M., Salzman N., Khoury G. Stimulation of simian virus 40 late gene expression by simian virus 40 tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2040–2044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Khoury G. trans Activation of the simian virus 40 late transcription unit by T-antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1391–1399. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Loeken M. R., Khoury G. Interaction between two transcriptional control sequences required for tumor-antigen-mediated simian virus 40 late gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7299–7303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome S., Gilbert W. Rous sarcoma virus encodes a transcriptional activator. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Slamon D. J., Rosenblatt J. D., Shah N. P., Quan S. G., Wachsman W. The x gene is essential for HTLV replication. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):54–58. doi: 10.1126/science.2990037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Kamen R. Multiple binding sites for polyomavirus large T antigen within regulatory sequences of polyomavirus DNA. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):750–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.750-760.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Tyndall C., Kamen R. Sequences at the capped 5'-ends of polyoma virus late region mRNAs: an example of extreme terminal heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6305–6322. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Basilico C. Sequences in the polyomavirus DNA regulatory region involved in viral DNA replication and early gene expression. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):739–749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.739-749.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Caradonna S. J., Casey J. W. Bovine leukemia virus long terminal repeat: a cell type-specific promoter. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):317–320. doi: 10.1126/science.2981431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth S. M., Cowie A., Kamen R. I., Griffin B. E. DNA binding activity of polyoma virus large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1941–1945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmerie W. G., Folk W. R. Regulation of polyomavirus transcription by large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6919–6923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L., Rixon F. J., Jean J. H., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Transcription of the genome of pseudorabies virus (A herpesvirus) is strictly controlled. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):316–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton R. G., Basilico C. Changes in the topography of early region transcription during polyoma virus lytic infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7142–7146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton R. G., Basilico C. Regulation of polyoma virus early transcription in transformed cells by large T-antigen. Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):384–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke B., Eckhart W. Polyoma gene function required for viral DNA synthesis. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcea R. L., Benjamin T. L. Host range transforming gene of polyoma virus plays a role in virus assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3613–3617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudray P., Tyndall C., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The high affinity binding site on polyoma virus DNA for the viral large-T protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5697–5710. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Hillman D., Berk A. J. Adenovirus early region 1A protein activates transcription of a nonviral gene introduced into mammalian cells by infection or transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1193–1197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman E., Hattori J., Benjamin T. Cellular and C-type viral factors in infections by polyoma virus hr-t mutants. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90492-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation of cloned human beta-globin genes by viral immediate-early gene products. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell S. W., Byrne B. J., Subramanian K. N. The simian virus 40 minimal origin and the 72-base-pair repeat are required simultaneously for efficient induction of late gene expression with large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6335–6339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Saragosti S., Blangy D., Yaniv M. Fine structure of the origin-proximal DNAase I-hypersensitive region in wild-type and EC mutant polyoma. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):651–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara S., Feldman L., Watanabe S., Ben-Porat T. Characterization of the immediate-early functions of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):437–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Activation of gene expression by adenovirus and herpesvirus regulatory genes acting in trans and by a cis-acting adenovirus enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Essential contact residues within SV40 large T antigen binding sites I and II identified by alkylation-interference. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Jat P., Treisman R., Favaloro J., Folk W. R. 5' termini of polyoma virus early region transcripts synthesized in vivo by wild-type virus and viable deletion mutants. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 5;159(2):189–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90493-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M., Yaniv M. DNA replication origin of polyoma virus: early proximal boundary. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):244–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.244-248.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J. Identification of the components necessary for adenovirus translational control and their utilization in cDNA expression vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):689–693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern F. G., Basilico C. Transcription from the polyoma late promoter in cells stably transformed by chimeric plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):797–807. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern F. G., Dailey L., Basilico C. Common regulatory elements control gene expression from polyoma early and late promoters in cells transformed by chimeric plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2070–2079. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Sharp P. A. Transcription control by oncogenes. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Cowie A., Morimoto R. I., Gwinn K. A. Binding of polyomavirus large T antigen to the human hsp70 promoter is not required for trans activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3180–3190. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Nilsson M. G., Magnusson G. Non-contiguous segments of the polyoma genome required in cis for DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 15;161(4):533–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maione R., Passananti C., De Simone V., Delli-Bovi P., Augusti-Tocco G., Amati P. Selection of mouse neuroblastoma cell-specific polyoma virus mutants with stage differentiative advantages of replication. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3215–3221. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04068.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K., Fried M. Construction of the genetic map of the polyoma genome. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):824–832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.824-832.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz B. J., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus and simian virus 40 large T antigens bind to common DNA sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):925–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.925-937.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz B. J., Mueller C. R., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus large T antigen binds independently to multiple, unique regions on the viral genome. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):600–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.600-610.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Naghashfar Z., Cowie A., Carr A., Grisoni M., Kamen R., Cuzin F. Expression of the large T protein of polyoma virus promotes the establishment in culture of "normal" rodent fibroblast cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4354–4358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Kettman R., Burny A., Haseltine W. A. Trans activation of the bovine leukemia virus long terminal repeat in BLV-infected cells. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):320–322. doi: 10.1126/science.2981432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller A., Prives C. Simian virus 40 and polyomavirus large tumor antigens have different requirements for high-affinity sequence-specific DNA binding. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):532–545. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.532-545.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of human T lymphotropic viruses in infected cells. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):381–385. doi: 10.1126/science.6330891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Transactivation of a bovine papilloma virus transcriptional regulatory element by the E2 gene product. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):183–191. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneloni R. J., Fluck M. M., Benjamin T. L. Host range selection of transformation-defective hr-t mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):598–609. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90485-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Adenovirus 2 early region 1A stimulates expression of both viral and cellular genes. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):789–794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Andersen B., Shaw S. B., Wilson V. G. Alternative interactions of the SV40 A protein with DNA. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Characterisation of polyoma late mRNA leader sequences by molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):4867–4888. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.4867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Novak U., Favaloro J., Kamen R. Transformation of rat cells by an altered polyoma virus genome expressing only the middle-T protein. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):595–600. doi: 10.1038/292595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Moran B., Maruyama K., Moomaw J., Grodzicker T., Ruley H. E. Adenovirus E1A coding sequences that enable ras and pmt oncogenes to transform cultured primary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):887–899. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]