Abstract
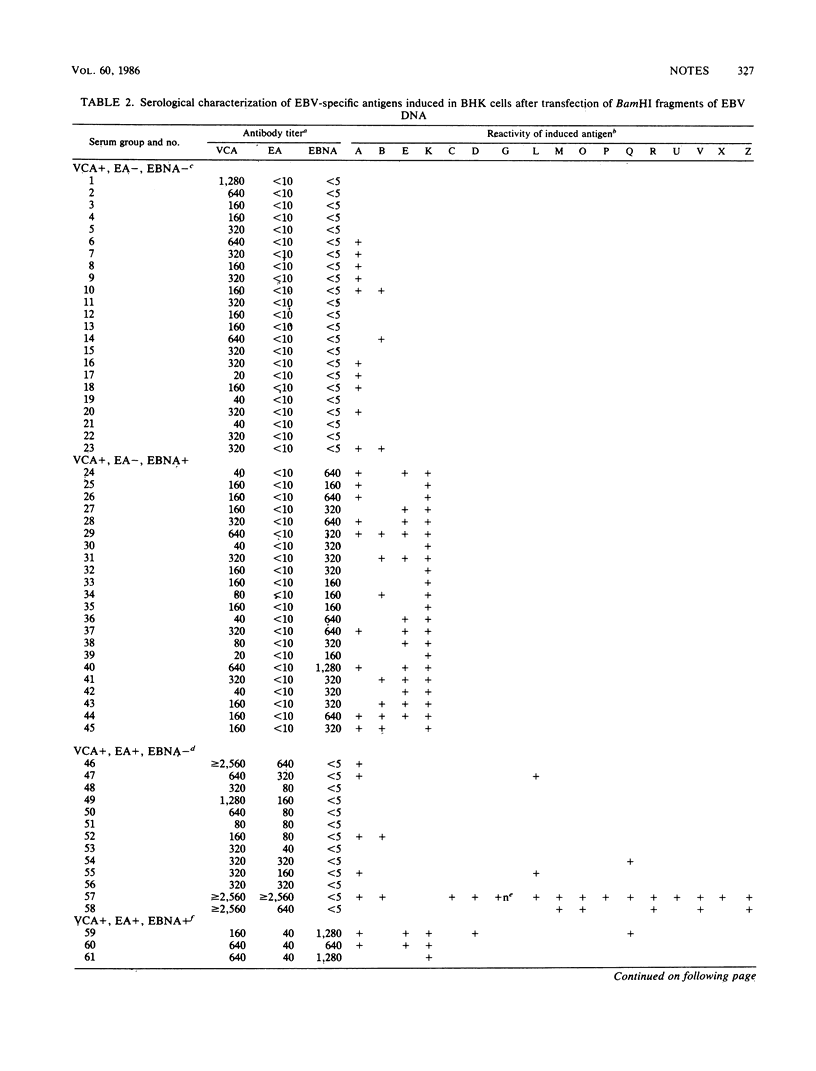
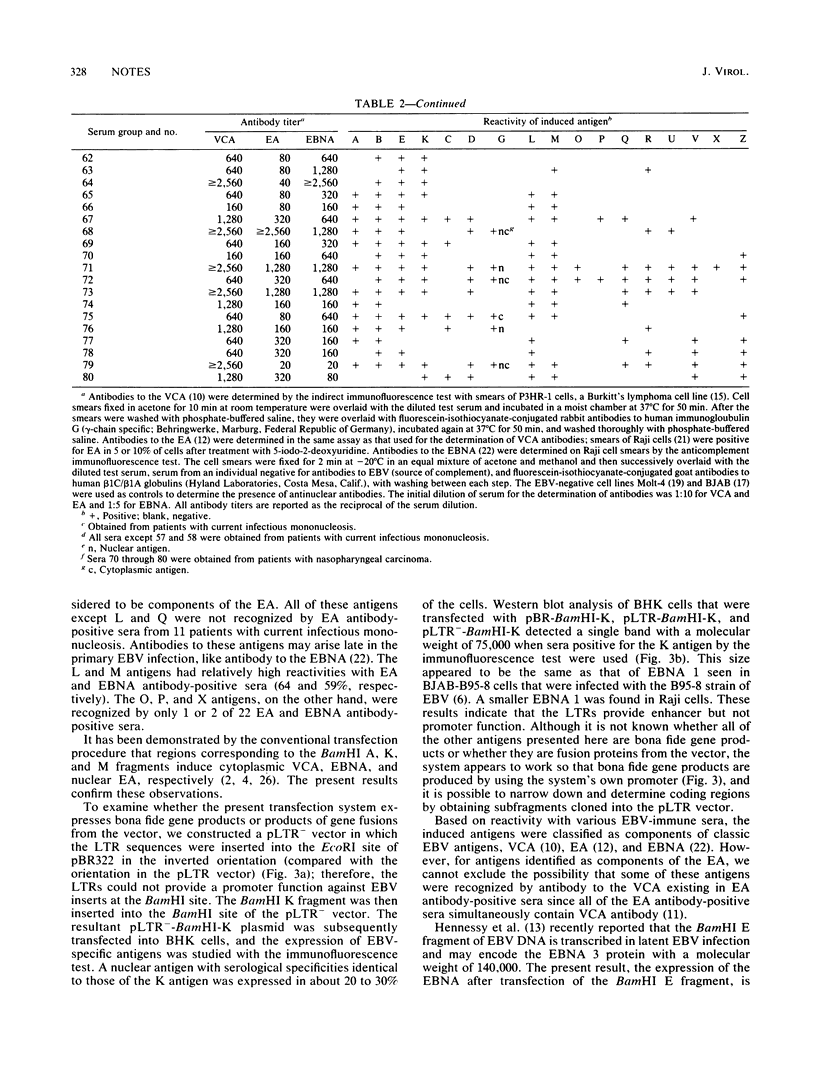
Baby hamster kidney cells were transfected with BamHI fragments of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA (B95-8 strain) cloned into the pLTR vector containing retroviral enhancer and promoter sequences. Seventeen fragments (BamHI-A, -B, -C, -D, -E, -G, -K, -L, -M, -O, -P, -Q, -R, -U, -V, -X, and -Z) expressed antigenically distinct EBV-specific products recognized by EBV-immune human sera.
Full text
PDF
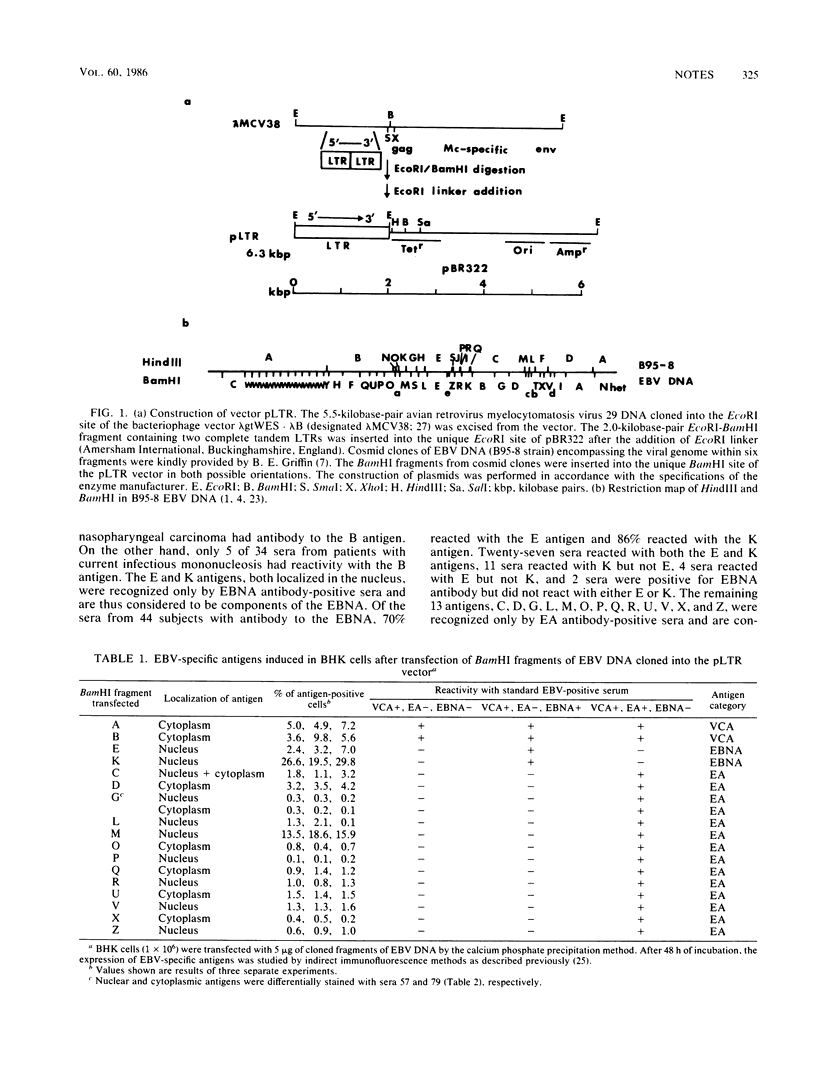
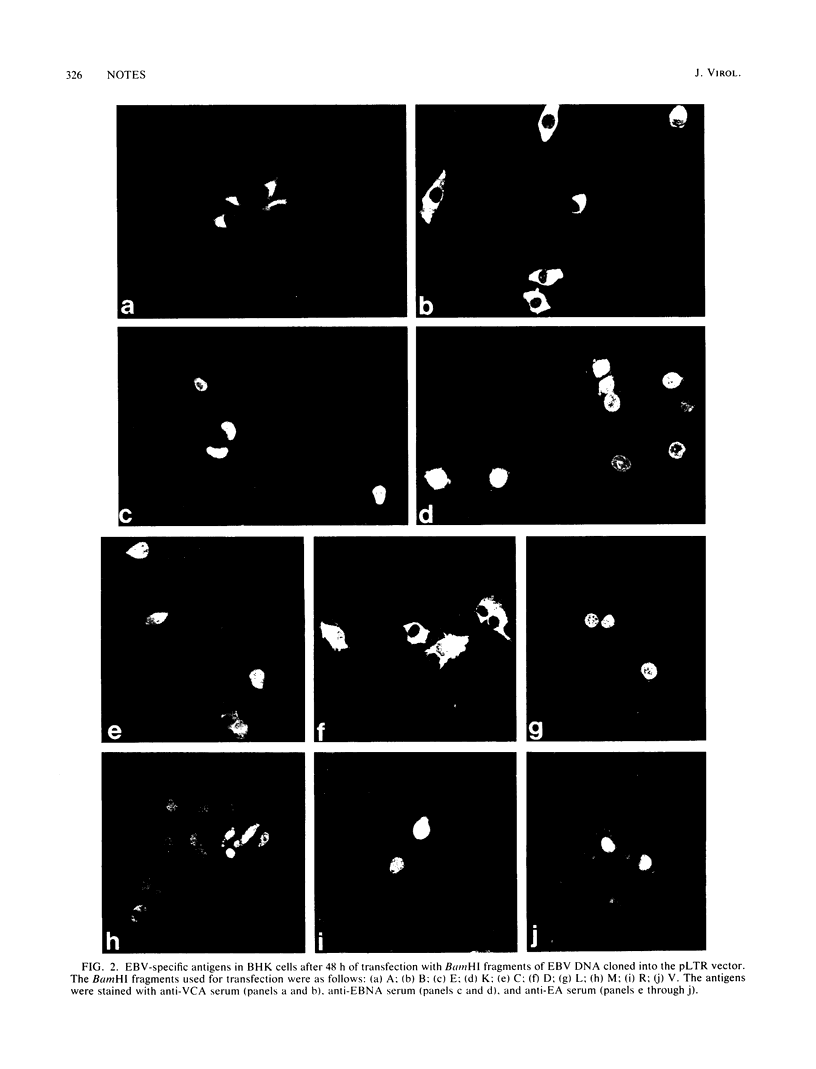


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cho M. S., Gissmann L., Hayward S. D. Epstein-Barr virus (P3HR-1) defective DNA codes for components of both the early antigen and viral capsid antigen complexes. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Transcriptional activity of avian retroviral long terminal repeats directly correlates with enhancer activity. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):515–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.515-521.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Beisel C., Hummel M., King W., Fennewald S., Cheung A., Heller M., Raab-Traub N., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (B95-8) DNA VII: molecular cloning and detailed mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D. K., Robert M. F., Shedd D., Summers W. P., Robinson J. E., Wolak J., Stefano J. E., Miller G. Identification of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen polypeptide in mouse and monkey cells after gene transfer with a cloned 2.9-kilobase-pair subfragment of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E., Karran L. Immortalization of monkey epithelial cells by specific fragments of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):78–82. doi: 10.1038/309078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E. A., Summers W. P., Dowling S., Shedd D., Gradoville L., Miller G. Two Epstein-Barr viral nuclear neoantigens distinguished by gene transfer, serology, and chromosome binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7650–7653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E., Miller G., Henle W., Rabson M., Shedd D., Niederman J. C. Expression of Epstein-Barr viral early antigen in monolayer tissue cultures after transfection with viral DNA and DNA fragments. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Zajac B. A., Pearson G., Waubke R., Scriba M. Differential reactivity of human serums with early antigens induced by Epstein-Barr virus. Science. 1970 Jul 10;169(3941):188–190. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3941.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Kieff E. A third viral nuclear protein in lymphoblasts immortalized by Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5944–5948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. One of two Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens contains a glycine-alanine copolymer domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Konn M., Yamaguchi J., Wudarski D. J., Blakeslee J. R., Jr, Grace J. T., Jr Immunofluorescence and herpes-type virus particles in the P3HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma cell line. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):1045–1051. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.1045-1051.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Clifford P., Klein E., Stjernswärd J. Search for tumor-specific immune reactions in Burkitt lymphoma patients by the membrane immunofluorescence reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1628–1635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G., Clements G. Establishment and characterization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBC)-negative lymphoblastoid B cell line (BJA-B) from an exceptional, EBV-genome-negative African Burkitt's lymphoma. Biomedicine. 1975 Jul;22(4):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Lantzsch N., Lenoir G. M., Sauter M., Takaki K., Béchet J. M., Kuklik-Roos C., Wunderlich D., Bornkamm G. W. Identification of the coding region for a second Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA 2) by transfection of cloned DNA fragments. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1805–1811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. A STUDY OF MALIGNANT TUMOURS IN NIGERIA BY SHORT-TERM TISSUE CULTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:261–273. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Strominger J. L. Cloning and mapping of BamHi endonuclease fragments of DNA from the transforming B95-8 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3860–3864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Grogan E. A., Shedd D., Robert M., Liu C. R., Miller G. Stable expression in mouse cells of nuclear neoantigen after transfer of a 3.4-megadalton cloned fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Shimizu N., Sakuma S., Ono Y. trans activation of the latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome after transfection of the EBV DNA fragment. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1016–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1016-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaki K., Polack A., Bornkamm G. W. Expression of a nuclear and a cytoplasmic Epstein-Barr virus early antigen after DNA transfer: cooperation of two distant parts of the genome for expression of the cytoplasmic antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4568–4572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Moscovici C., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning of the avian myelocytomatosis virus genome and recovery of infectious virus by transfection of chicken cells. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):625–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.625-631.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]