Abstract
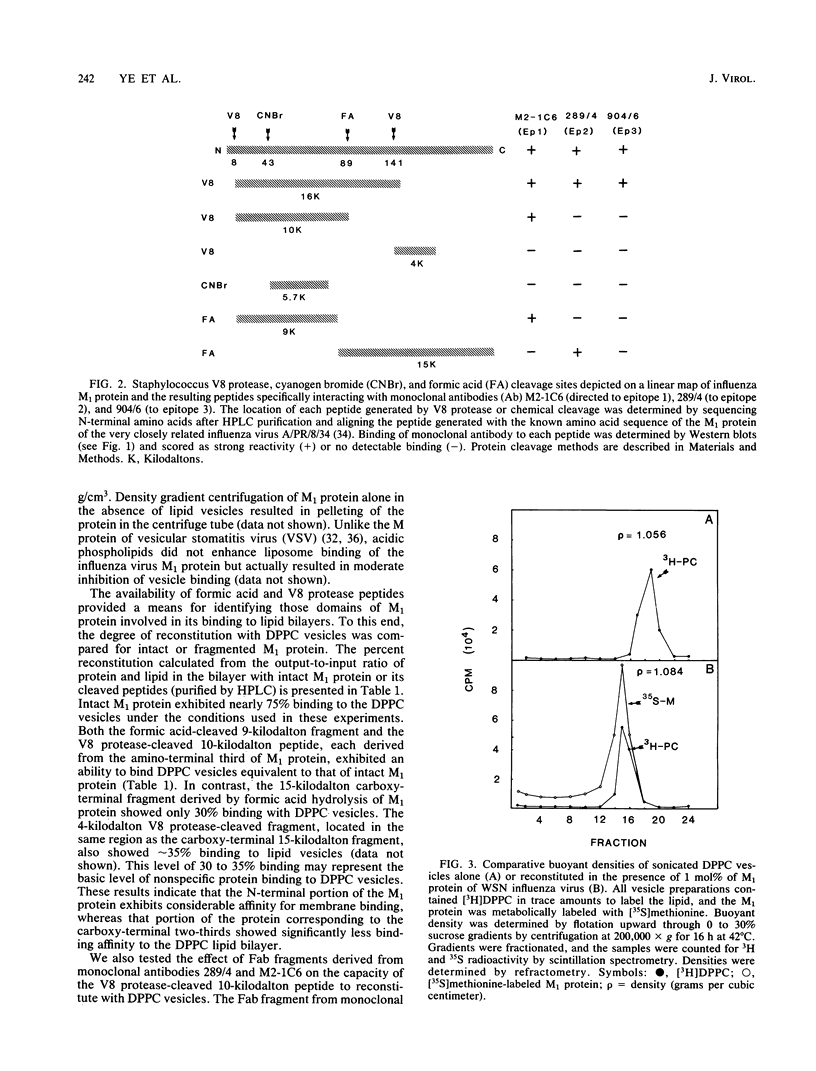
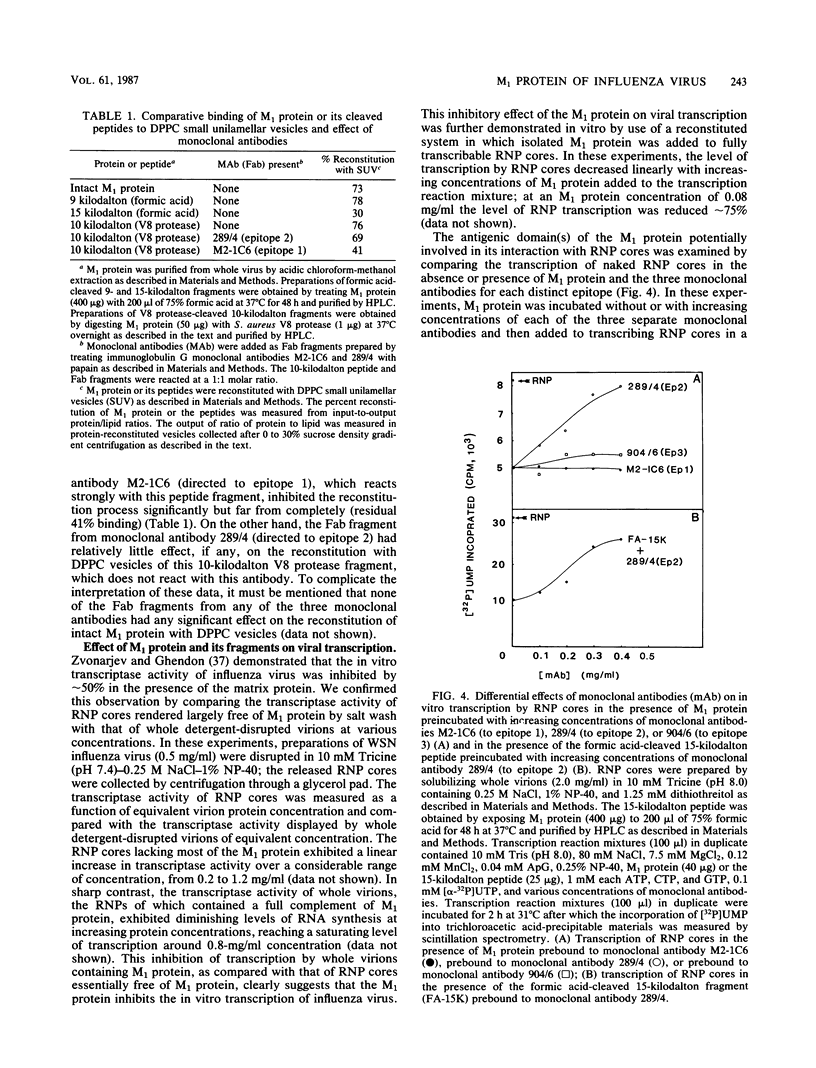
The membrane- and ribonucleocapsid (RNP)-binding domains of the matrix (M1) protein of influenza A virus (WSN strain) were partially mapped and characterized by reactivity with monoclonal antibodies (MAb) as well as by proteolytic cleavages and amino acid sequencing of the resulting peptides. Of two peptides formed by formic acid hydrolysis, a 9-kilodalton fragment at the amino-terminal third of the M1 protein was recognized by MAb M2-1C6 (to epitope 1), and a 15-kilodalton fragment at the carboxy-terminal two-thirds was recognized by MAb 289/4 (to epitope 2). Partial cleavage by staphylococcal V8 protease gave rise to a 16-kilodalton peptide, mapping to amino acid 8, which was recognized by MAbs to all three epitopes but rather weakly by MAb 904/6 to epitope 3. These studies suggest that epitope 1 of the M1 protein resides between amino acids 8 and 89, whereas epitopes 2 and possibly 3 are located between amino acids 89 and 141 or somewhat more carboxy distal. The intact M1 protein and its N-terminal 9- and 10-kilodalton peptides generated by formic acid or V8 protease cleavage, respectively, reconstituted with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles, but these N-terminal peptides had little effect on in vitro transcription of the RNP core. In sharp contrast, both intact M1 protein and the C-terminal 15-kilodalton formic acid fragment were able to inhibit viral transcription markedly. Moreover, MAb 289/4 (to epitope 2) reversed this inhibited transcription significantly. These studies suggest that the lipid-binding domain of the M1 protein is located within the amino-terminal third, whereas the site involved in the interaction of the M1 protein with RNP cores is located within the carboxy-terminal two-thirds.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen H., McCauley J., Waterfield M., Gething M. J. Influenza virus RNA segment 7 has the coding capacity for two polypeptides. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):548–551. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apostolov K., Flewett T. H. Further observations on the structure of influenza viruses A and C. J Gen Virol. 1969 Apr;4(3):365–370. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-3-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher D. J., Kharitonenkov I. G., Zakomirdin J. A., Grigoriev V. B., Klimenko S. M., Davis J. F. Incorporation of influenza virus M-protein into liposomes. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):586–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.586-590.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. R., Wagner R. R. Role of the membrane (M) protein in endogenous inhibition of in vitro transcription by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.134-142.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Little S. P., Hagen F. S., Huang A. S. The matrix (M) protein of vesicular stomatitis virus regulates transcription. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1455–1462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combard A., Printz Ane C. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus transcriptase complex by the virion envelope M protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 14;88(1):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91704-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einck L., Bustin M. Inhibition of transcription in somatic cells by microinjection of antibodies to chromosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6735–6739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Karadaghi S., Zakomirdin J. A., Shimane C., Bucher D. J., Tverdislov V. A., Kharitonenkov I. G. Interaction of influenza virus proteins with planar bilayer lipid membranes. I. Characterization of their adsorption and incorporation into lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 5;778(2):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90368-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriades A., Frangione B. Insertion of influenza M protein into the viral lipid bilayer and localization of site of insertion. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):323–328. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.323-328.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriades A. Interaction of influenza M protein with viral lipid and phosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):470–479. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.470-479.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriades A. The membrane protein of influenza virus: extraction from virus and infected cell with acidic chloroform-methanol. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):369–383. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson N. J., Lloyd C. E., Mortimore G. E. Degradation of intra- and extrahepatic protein by livers of normal and diabetic mice: differential responses to starvation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1737–1741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharitonenkov I. G., ElKaradahgi S., Bucher D. J., Zakomirdin J. A., Tverdislov V. A. Interaction of influenza virus proteins with planar lipid bilayers: a model for virion assembly. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):308–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91522-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. The gene structure and replication of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:467–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Lai C. J., Choppin P. W. Sequences of mRNAs derived from genome RNA segment 7 of influenza virus: colinear and interrupted mRNAs code for overlapping proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Zebedee S. L., Richardson C. D. Influenza virus M2 protein is an integral membrane protein expressed on the infected-cell surface. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):627–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon Cleavage at aspartyl-prolyl bonds. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:145–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Grinnell B. W., Snyder R. M., Wiener J. R., Volk W. A., Wagner R. R. Monoclonal antibodies to the M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana serotype) and to a cDNA M gene expression product. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):298–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.298-306.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney D. F., Emerson S. U. In vitro synthesis of triphosphate-initiated N-gene mRNA oligonucleotides is regulated by the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):897–904. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.897-904.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. H., Bennett J. C., Compans R. W. Selective dansylation of M protein within intact influenza virions. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):871–876. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.871-876.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. H., Bhown A. S., Compans R. W., Bennett J. C. Structure of the membrane protein of influenza virus. I. Isolation and characterization of cyanogen bromide cleavage products. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):759–766. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.759-766.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doolittle R. F., Anilionis A., Curtis P. J., Wunner W. H. Homology between the glycoproteins of vesicular stomatitis virus and rabies virus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):361–364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.361-364.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze I. T. The structure of influenza virus. II. A model based on the morphology and composition of subviral particles. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):181–196. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk W. A., Synder R. M., Benjamin D. C., Wagner R. R. Monoclonal antibodies to the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus: comparative neutralizing activity. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):220–227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.220-227.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., Pal R., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Influence of the peripheral matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus on the membrane dynamics of mixed phospholipid vesicles: fluorescence studies. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2162–2170. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Lenard J. Interaction of wild-type and mutant M protein vesicular stomatitis virus with nucleocapsids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Fields S. Cloning of influenza cDNA ino M13: the sequence of the RNA segment encoding the A/PR/8/34 matrix protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 10;8(9):1965–1974. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.9.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W. Antigenic characterization of viruses by monoclonal antibodies. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:185–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakowski J. J., Petri W. A., Jr, Wagner R. R. Role of matrix protein in assembling the membrane of vesicular stomatitis virus: reconstitution of matrix protein with negatively charged phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3902–3907. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvonarjev A. Y., Ghendon Y. Z. Influence of membrane (M) protein on influenza A virus virion transcriptase activity in vitro and its susceptibility to rimantadine. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):583–586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.583-586.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wyke K. L., Yewdell J. W., Reck L. J., Murphy B. R. Antigenic characterization of influenza A virus matrix protein with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):248–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.248-252.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]