Abstract
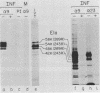
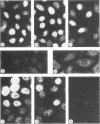
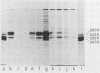
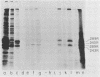
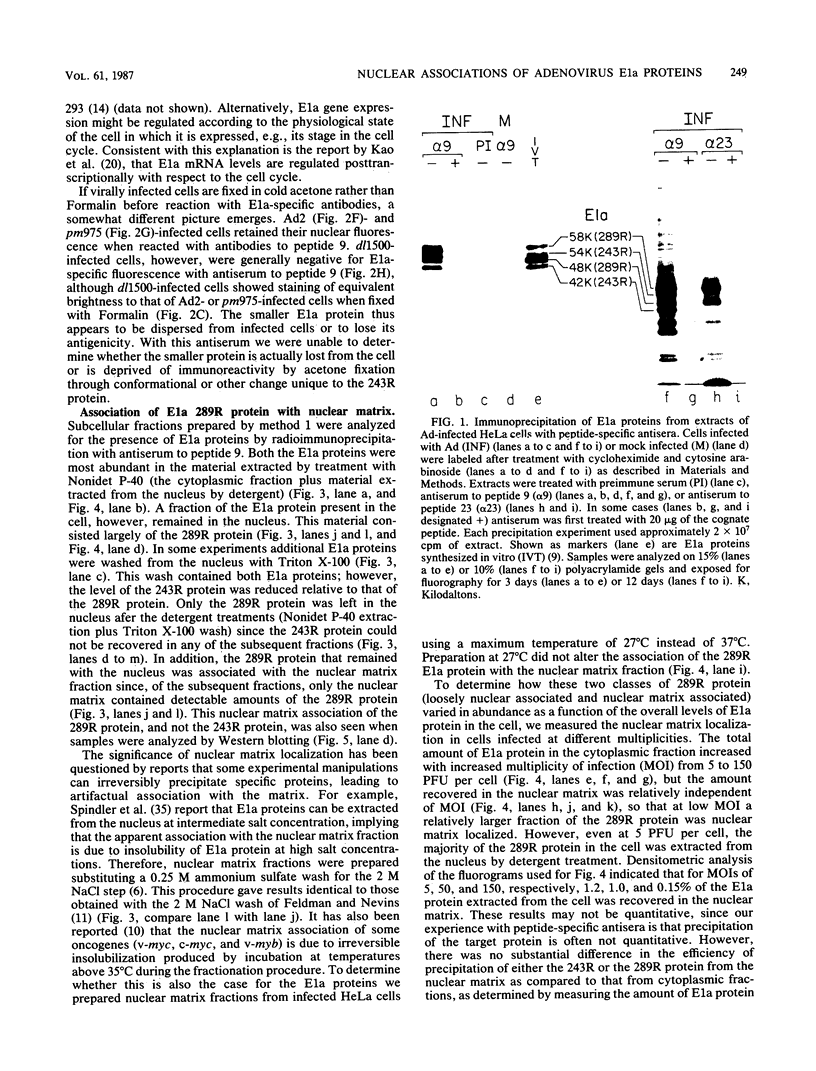
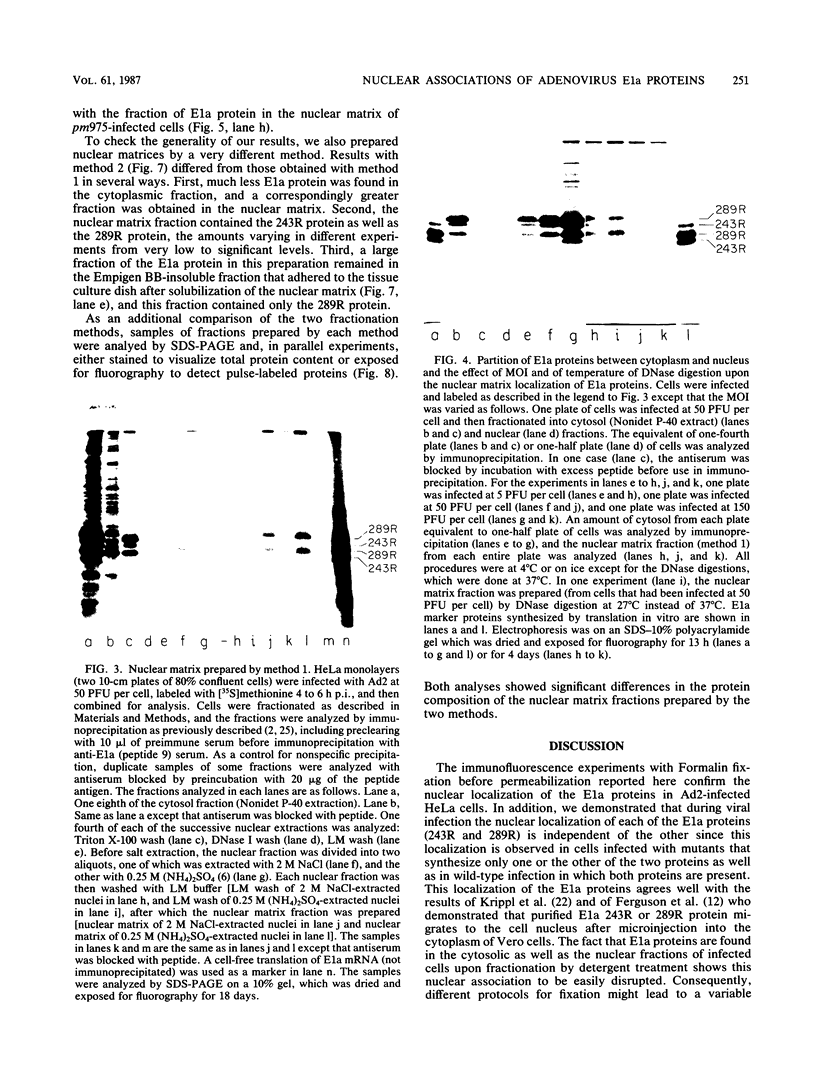
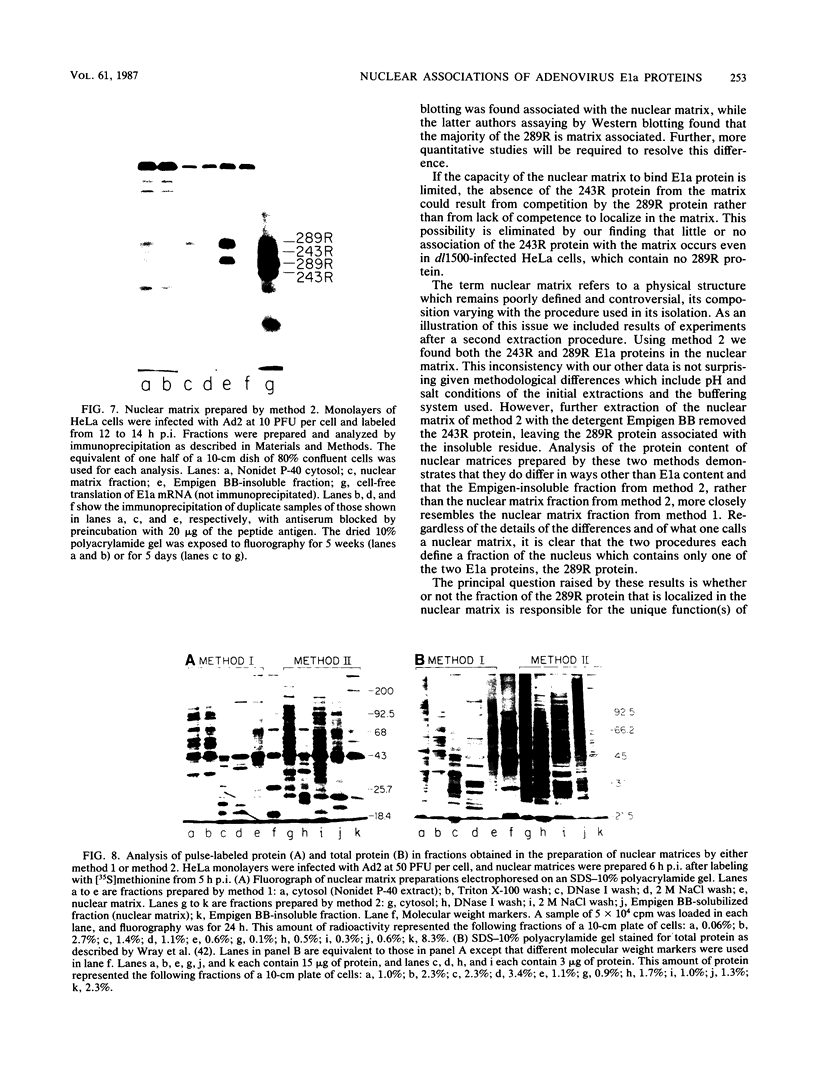
The localization in infected and transformed cells of the two major adenovirus type 2 E1a proteins, of 289 and 243 amino acid residues, was studied with antisera raised against synthetic peptides or a TrpE-E1a fusion protein. Both E1a proteins were detected only in the nucleus of infected cells as determined by immunofluorescence analysis of cells infected with wild-type virus or with the mutants pm975 or dl1500, which produce, respectively, only the 289-residue or only the 243-residue E1a protein. However, the 289-residue protein was more tightly associated with the nucleus than was the 243-residue protein, as determined by the stability of nuclear fluorescence to different fixation procedures and by the use of radioimmunoprecipitation and Western blot analysis to analyze fractions extracted from the nucleus by detergent and other treatments. The latter experiments revealed that only the 289-residue protein, and only a fraction of that protein present in the nucleus, is associated with the nuclear matrix, both in infected HeLa cells and in the transformed human cell line 293.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Processing of adenovirus 2-induced proteins. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.241-252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Schmitt R. C., Smart J. E., Lewis J. B. Early region 1B of adenovirus 2 encodes two coterminal proteins of 495 and 155 amino acid residues. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):387–396. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.387-396.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capco D. G., Wan K. M., Penman S. The nuclear matrix: three-dimensional architecture and protein composition. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):847–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90446-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey J. F., Evelegh C. M., Branton P. E., Bayley S. T. Peptide maps and N-terminal sequences of polypeptides from early region 1A of human adenovirus 5. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.30-37.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Tachibana C. Y., Abrams H. D., Hann S. R. V-myc- and c-myc-encoded proteins are associated with the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):114–126. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esche H., Mathews M. B., Lewis J. B. Proteins and messenger RNAs of the transforming region of wild-type and mutant adenoviruses. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):399–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Hancock D. C. Studies on the interaction of the human c-myc protein with cell nuclei: p62c-myc as a member of a discrete subset of nuclear proteins. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Localization of the adenovirus E1Aa protein, a positive-acting transcriptional factor, in infected cells infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):829–838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B., Krippl B., Andrisani O., Jones N., Westphal H., Rosenberg M. E1A 13S and 12S mRNA products made in Escherichia coli both function as nucleus-localized transcription activators but do not directly bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2653–2661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Tsukamoto A., Montell C., Berk A. J. Enhanced expression of adenovirus transforming proteins. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):276–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.276-285.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoyle R. A., Osheroff W. P., Rossini M. Two functions encoded by adenovirus early region 1A are responsible for the activation and repression of the DNA-binding protein gene. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):707–713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03687.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley K. P., Overhauser J., Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S., Jones N. C. Transformation properties of type 5 adenovirus mutants that differentially express the E1A gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5734–5738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for adenovirus early region 1A proteins: extensive heterogeneity in early region 1A products. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):533–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.533-546.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter M. L., Lewis J. B. Adenovirus type 2 early proteins synthesized in vitro and in vivo: identification in infected cells of the 38,000- to 50,000- molecular-weight protein encoded by the left end of the adenovirus type 2 genome. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):736–749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.736-749.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz D. R., Chinnadurai G. Immortalization of rat embryo fibroblasts by an adenovirus 2 mutant expressing a single functional E1a protein. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):358–363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.358-363.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao H. T., Capasso O., Heintz N., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle control of the human HSP70 gene: implications for the role of a cellular E1A-like function. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):628–633. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W. J., Greene G. L. Monoclonal antibodies localize oestrogen receptor in the nuclei of target cells. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):745–747. doi: 10.1038/307745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krippl B., Ferguson B., Rosenberg M., Westphal H. Functions of purified E1A protein microinjected into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6988–6992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W. Proteins encoded near the adenovirus late messenger RNA leader segments. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):112–123. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Fahnestock M. L., Hardy M. M., Anderson C. W. Presence in infected cells of nonvirion proteins encoded by adenovirus messenger RNAs of the major late transcription regions L0 and L1. Virology. 1985 Jun;143(2):452–466. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90385-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Courtois G., Eng C., Berk A. Complete transformation by adenovirus 2 requires both E1A proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Resolving the functions of overlapping viral genes by site-specific mutagenesis at a mRNA splice site. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):380–384. doi: 10.1038/295380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne T. F., Gaynor R. B., Berk A. J. The TATA homology and the mRNA 5' untranslated sequence are not required for expression of essential adenovirus E1A functions. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Graham F. L., Branton P. E. Intracellular localization of adenovirus type 5 tumor antigens in productively infected cells. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):456–468. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Lewis J. B., Mathews M. B., Harter M. L., Anderson C. W. Adenovirus type 2 early proteins: assignment of the early region 1A proteins synthesized in vivo and in vitro to specific mRNAs. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):703–713. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Berk A. J. Rapid intracellular turnover of adenovirus 5 early region 1A proteins. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):706–710. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.706-710.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Eng C. Y., Berk A. J. An adenovirus early region 1A protein is required for maximal viral DNA replication in growth-arrested human cells. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):742–750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.742-750.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Rosser D. S., Berk A. J. Analysis of adenovirus transforming proteins from early regions 1A and 1B with antisera to inducible fusion antigens produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):132–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.132-141.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staufenbiel M., Deppert W. Nuclear matrix preparations from liver tissue and from cultured vertebrate cells: differences in major polypeptides. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;31(2):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Scheidtmann K. H., Carbone A., Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Antibodies specific for the carboxy- and amino-terminal regions of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5197–5200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welshons W. V., Lieberman M. E., Gorski J. Nuclear localization of unoccupied oestrogen receptors. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):747–749. doi: 10.1038/307747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberg G., Shenk T. Dissection of overlapping functions within the adenovirus type 5 E1A gene. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1907–1912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Rowe D. T., Tremblay M. L., McDermott M., Branton P. E. Identification of human adenovirus early region 1 products by using antisera against synthetic peptides corresponding to the predicted carboxy termini. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1003–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1003-1013.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]