Abstract
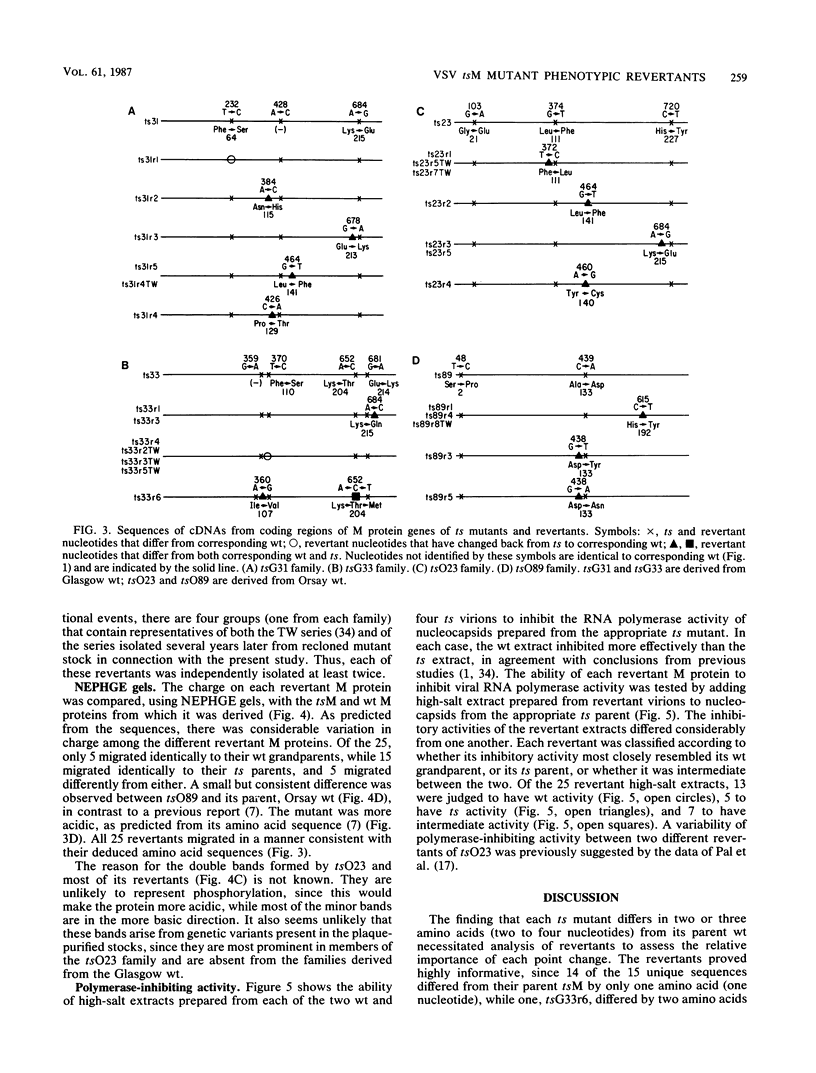
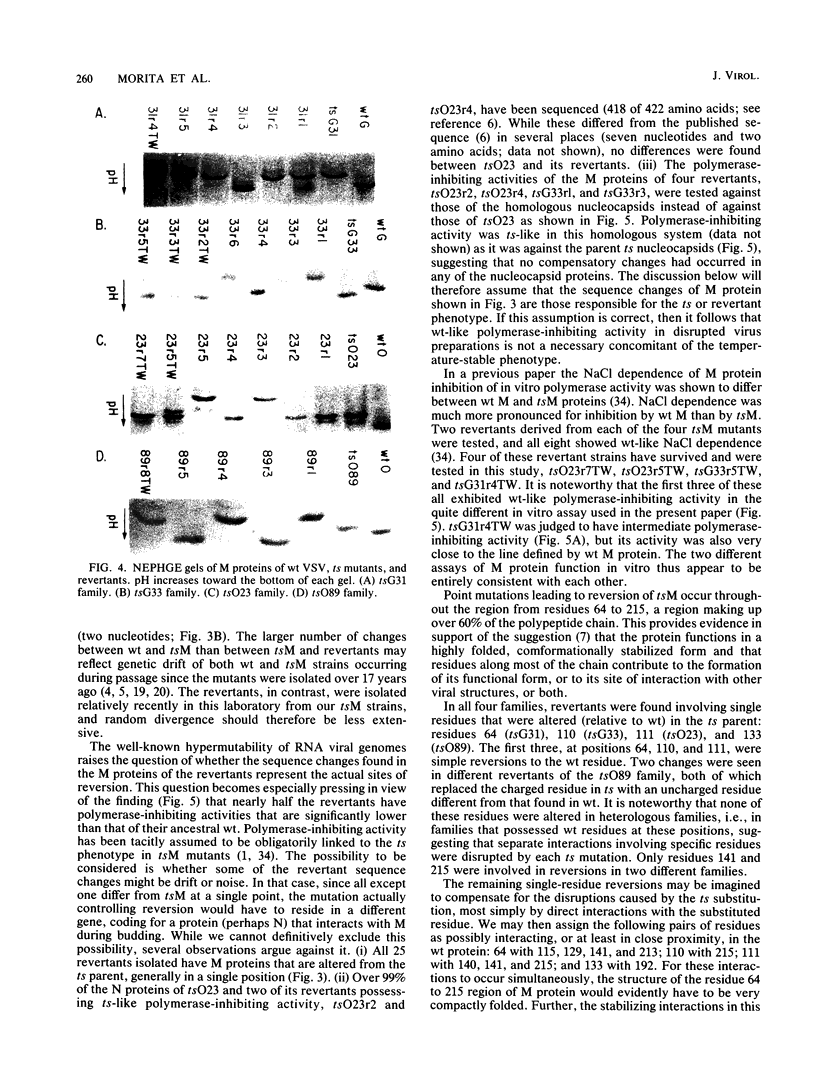
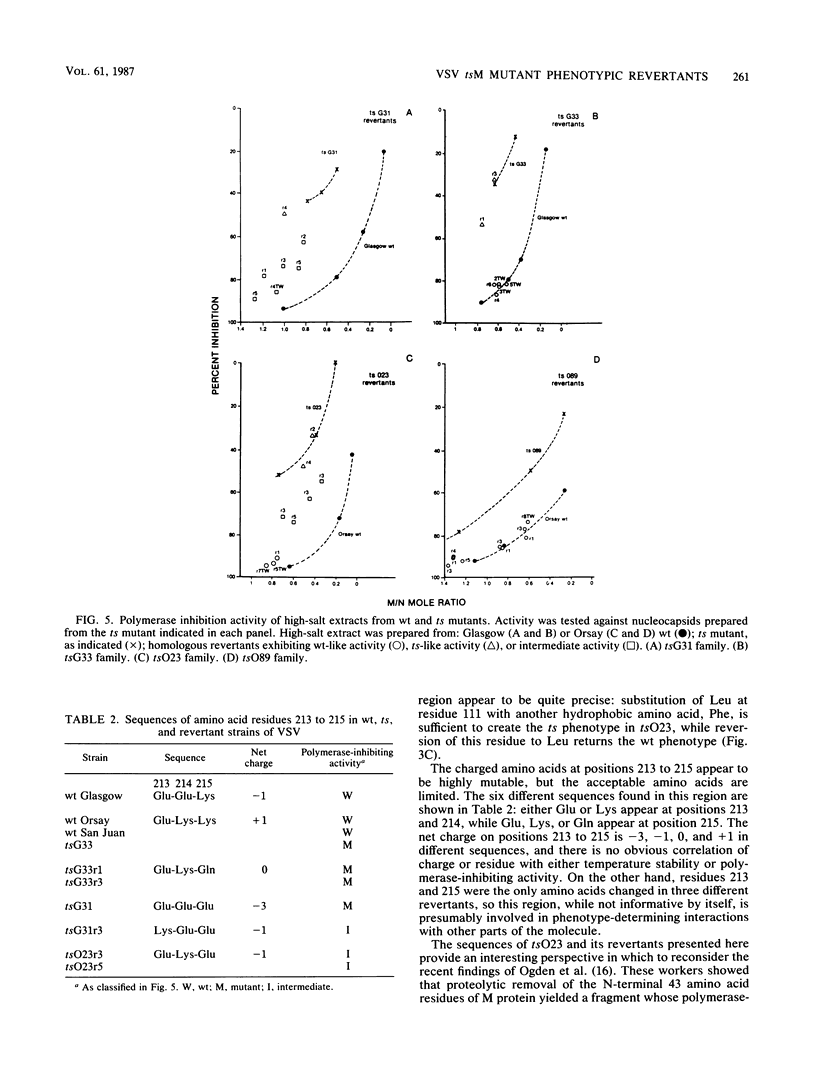
Twenty-five spontaneous temperature-stable revertants of four different temperature-sensitive (ts) M protein mutants (complementation group III: tsG31, tsG33, tsO23, and tsO89) were sequenced and tested for their ability to inhibit vesicular stomatitis virus RNA polymerase activity in vitro. Consensus sequences of the coding region of each M protein gene were determined, using total viral RNA as template. Fifteen different sequences were found among the 25 revertants; 14 differed from their ts parent by a single amino acid (one nucleotide), and 1 differed by two amino acids (two nucleotides). Amino acids were altered in various positions between residues 64 and 215, representing over 60% of the polypeptide chain. Resequencing of the Glasgow and Orsay wild types and the four ts mutants confirmed previously published differences (Y. Gopalakrishana and J. Lenard, J. Virol., 56:655-659, 1985), and one or two additional differences were found in each. The relative charges of the revertant M proteins, as determined by nonequilibrium pH gradient electrophoresis, were consistent with the deduced sequences in every case. The ability of each revertant M protein to inhibit the RNA polymerase activity of nucleocapsids prepared from its parent ts mutant was also tested. Only 13 of the 25 revertants had M protein with high (wild type-like) polymerase-inhibiting activity, while 5 had low (ts-like) activity, and 7 had intermediate activity, demonstrating that this property is not an essential concomitant of the temperature-stable phenotype. It is concluded that the high reversion frequency observed for these mutants arises from a very high incidence of pseudoreversion, i.e., many different molecular changes can repair the ts phenotype.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carroll A. R., Wagner R. R. Role of the membrane (M) protein in endogenous inhibition of in vitro transcription by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.134-142.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Little S. P., Hagen F. S., Huang A. S. The matrix (M) protein of vesicular stomatitis virus regulates transcription. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1455–1462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combard A., Printz Ane C. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus transcriptase complex by the virion envelope M protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 14;88(1):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91704-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A. Etude des mutants thermosensibles du virus de la stomatite vésiculaire. Mise au point d'un test de complémentation. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 May 5;268(18):2305–2308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A. Etude génétique du virus de la stomatite vésiculaire: classement de mutants thermosensibles spontanés en groupes de complémentation. J Gen Virol. 1970 Sep;8(3):187–195. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-8-3-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallione C. J., Greene J. R., Iverson L. E., Rose J. K. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus N and NS proteins. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):529–535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.529-535.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
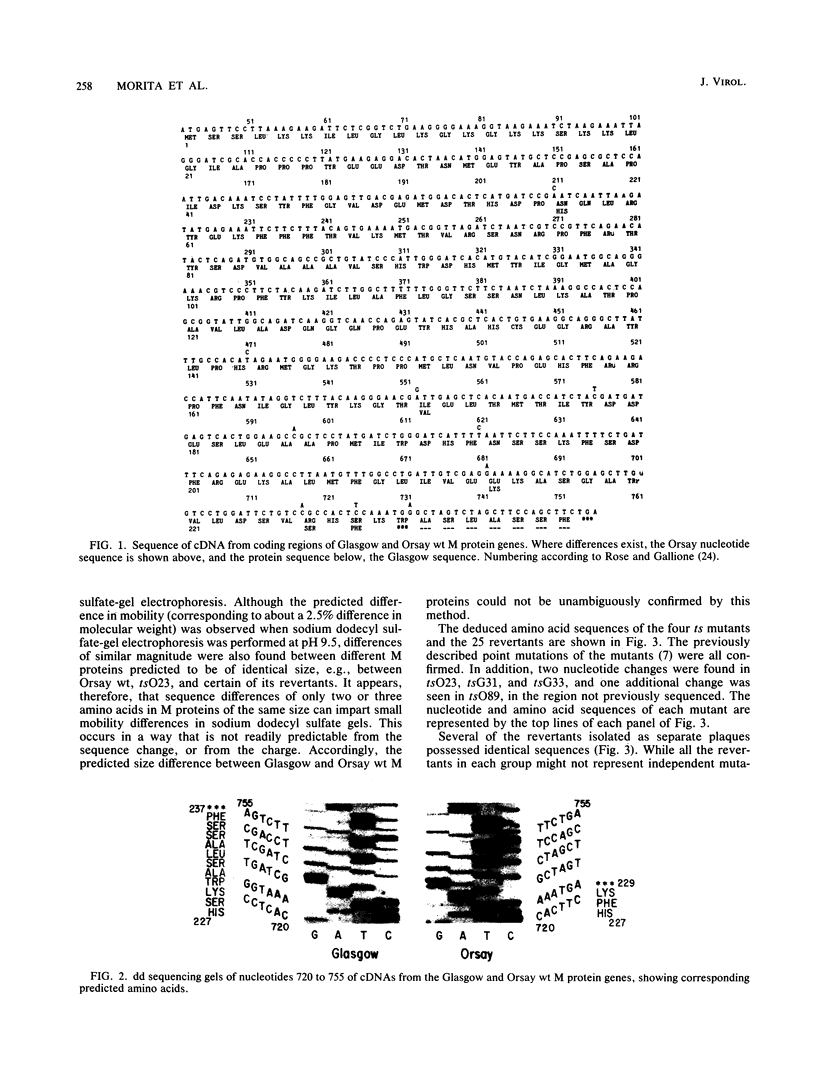
- Gopalakrishna Y., Lenard J. Sequence alterations in temperature-sensitive M-protein mutants (complementation group III) of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):655–659. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.655-659.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D., Lodish H. F., Baltimore D. Analysis of the defects of temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus: intracellular degradation of specific viral proteins. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1140–1148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1140-1148.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafay F. Envelope proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: effect of temperature-sensitive mutations in complementation groups III and V. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1220–1228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1220-1228.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinet C., Combard A., Printz-Ané C., Printz P. Envelope proteins and replication of vesicular stomatitis virus: in vivo effects of RNA+ temperature-sensitive mutations on viral RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):123–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.123-133.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. K., Lenard J. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus infection by spike glycoprotein. Evidence for an intracellular, G protein-requiring step. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):430–437. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Brown J. C. Role of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein in maintaining the viral nucleocapsid in the condensed form found in native virions. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):295–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.295-299.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Tobin G. J., McGowan J. J., Brown J. C. In vitro reassembly of vesicular stomatitis virus skeletons. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1055-1062.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
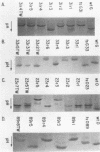
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Arnheiter H., Dubois-Dalcq M., Lazzarini R. A. Stereo images of vesicular stomatitis virus assembly. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):922–932. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.922-932.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden J. R., Pal R., Wagner R. R. Mapping regions of the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus which bind to ribonucleocapsids, liposomes, and monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):860–868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.860-868.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Grinnell B. W., Snyder R. M., Wagner R. R. Regulation of viral transcription by the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus probed by monoclonal antibodies and temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):386–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.386-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Grinnell B. W., Snyder R. M., Wiener J. R., Volk W. A., Wagner R. R. Monoclonal antibodies to the M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana serotype) and to a cDNA M gene expression product. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):298–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.298-306.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R. Conditional lethal mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;69:85–116. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50112-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R., Duncan I. B. Preliminary physiological characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1971 Jul;8(1):56–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.1.56-61.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R. Genetic characteristics of conditional lethal mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus induced by 5-fluorouracil, 5-azacytidine, and ethyl methane sulfonate. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):559–567. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.559-567.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K. Complete intergenic and flanking gene sequences from the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90515-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. M., Groppi V. E., Jr, Browning E. T. Resolution of basic cellular proteins including histone variants by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis: evaluation of lysine to arginine ratios and phosphorylation. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 15;103(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer T. J., Dickson C., Weiss R. A. Morphological and biochemical characterization of viral particles produced by the tsO45 mutant of vesicular stomatitis virus at restrictive temperature. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):185–195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.185-195.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer T. J., Lodish H. F. Noninfectious vesicular stomatitis virus particles deficient in the viral nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):443–447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.443-447.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D., Newcomb W. W., Brown J. C., Wall J. S., Hainfeld J. F., Trus B. L., Steven A. C. Mass and molecular composition of vesicular stomatitis virus: a scanning transmission electron microscopy analysis. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):598–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.598-607.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiang M., Monroe S. S., Schlesinger S. Studies of defective interfering RNAs of Sindbis virus with and without tRNAAsp sequences at their 5' termini. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.38-44.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Bennett P. L. Assembly of membrane glycoproteins studied by phenotypic mixing between mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus and retroviruses. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):252–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90518-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., Pal R., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Effect of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein on the lateral organization of lipid bilayers containing phosphatidylglycerol: use of fluorescent phospholipid analogues. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 17;24(26):7651–7658. doi: 10.1021/bi00347a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., Pal R., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Influence of the peripheral matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus on the membrane dynamics of mixed phospholipid vesicles: fluorescence studies. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2162–2170. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Lenard J. Interaction of wild-type and mutant M protein vesicular stomatitis virus with nucleocapsids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakowski J. J., Petri W. A., Jr, Wagner R. R. Role of matrix protein in assembling the membrane of vesicular stomatitis virus: reconstitution of matrix protein with negatively charged phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3902–3907. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]