Abstract
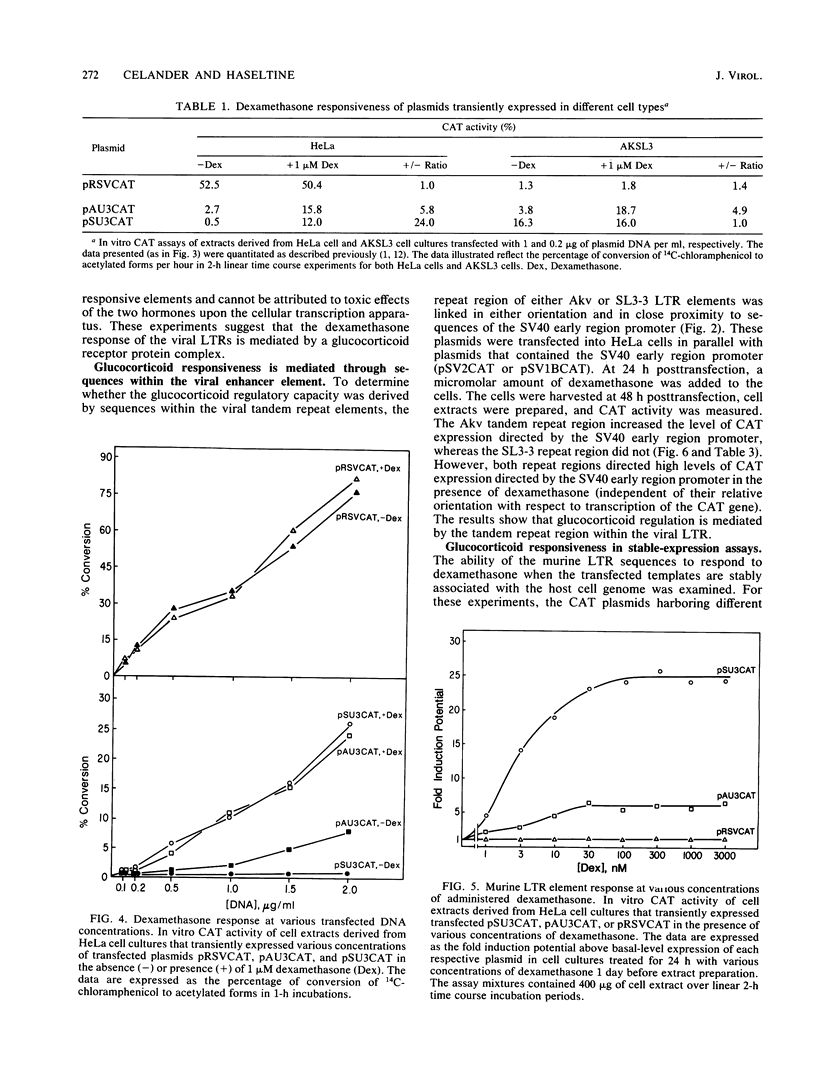
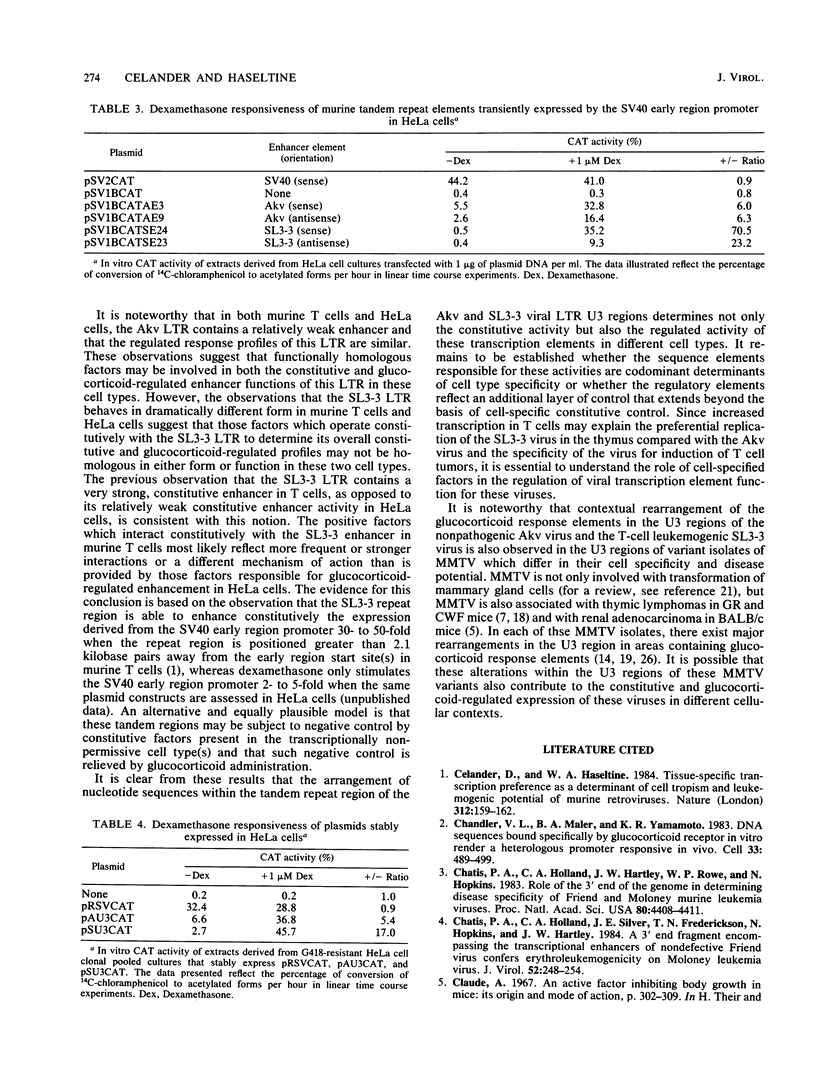
The transcriptional control region (the long terminal repeat, LTR) of the leukemogenic murine retrovirus SL3-3 contains a glucocorticoid-responsive consensus sequence, as does the corresponding region of the nonleukemogenic virus Akv. Dexamethasone increases gene expression directed by both LTR sequences. However, the responses of the LTRs of the two viruses to dexamethasone differ according to the cell line in which the response is measured. The results of these studies provide insights regarding differences in response to glucocorticoids dependent upon cell line and indicate that the glucocorticoid-responsive elements may compose one of the determinants of tissue specificity and pathogenicity of the murine retroviruses.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Celander D., Haseltine W. A. Tissue-specific transcription preference as a determinant of cell tropism and leukaemogenic potential of murine retroviruses. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):159–162. doi: 10.1038/312159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Silver J. E., Frederickson T. N., Hopkins N., Hartley J. W. A 3' end fragment encompassing the transcriptional enhancers of nondefective Friend virus confers erythroleukemogenicity on Moloney leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco D., Yamamoto K. R. Two different factors act separately or together to specify functionally distinct activities at a single transcriptional enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):993–1001. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekaban G. A., Ball J. K. Integration of type B retroviral DNA in virus-induced primary murine thymic lymphomas. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):784–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.784-792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Bourgeois S. A new determinant of glucocorticoid sensitivity in lymphoid cell lines. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):409–415. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Weissman S. M. Mouse mammary tumor virus-related sequences in mouse lymphocytes are inducible by 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):1000–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.1000-1004.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalides R., Wagenaar E., Hilkens J., Hilgers J., Groner B., Hynes N. E. Acquisition of proviral DNA of mouse mammary tumor virus in thymic leukemia cells from GR mice. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):819–829. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.819-829.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalides R., Wagenaar E., Weijers P. Rearrangements in the long terminal repeat of extra mouse mammary tumor proviruses in T-cell leukemias of mouse strain GR result in a novel enhancer-like structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):823–830. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Heber A., Schmid W., Danesch U., Posseckert G., Beato M., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the transcriptional enhancer of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. H., Long C. A., Vaidya A. B., Sheffield J. B., Dion A. S., Lasfargues E. Y. Mammary tumor viruses. Adv Cancer Res. 1979;29:347–418. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60850-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overhauser J., Fan H. Generation of glucocorticoid-responsive Moloney murine leukemia virus by insertion of regulatory sequences from murine mammary tumor virus into the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):133–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.133-144.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Lenz J., Ruprecht R., Cloyd M. W. Tissue selectivity of murine leukemia virus infection is determined by long terminal repeat sequences. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):862–866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.862-866.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellinger R. J., Garcia M., Vessaz A., Diggelmann H. Exogenous mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA isolated from a kidney adenocarcinoma cell line contains alterations in the U3 region of the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.1-11.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




