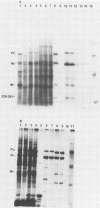
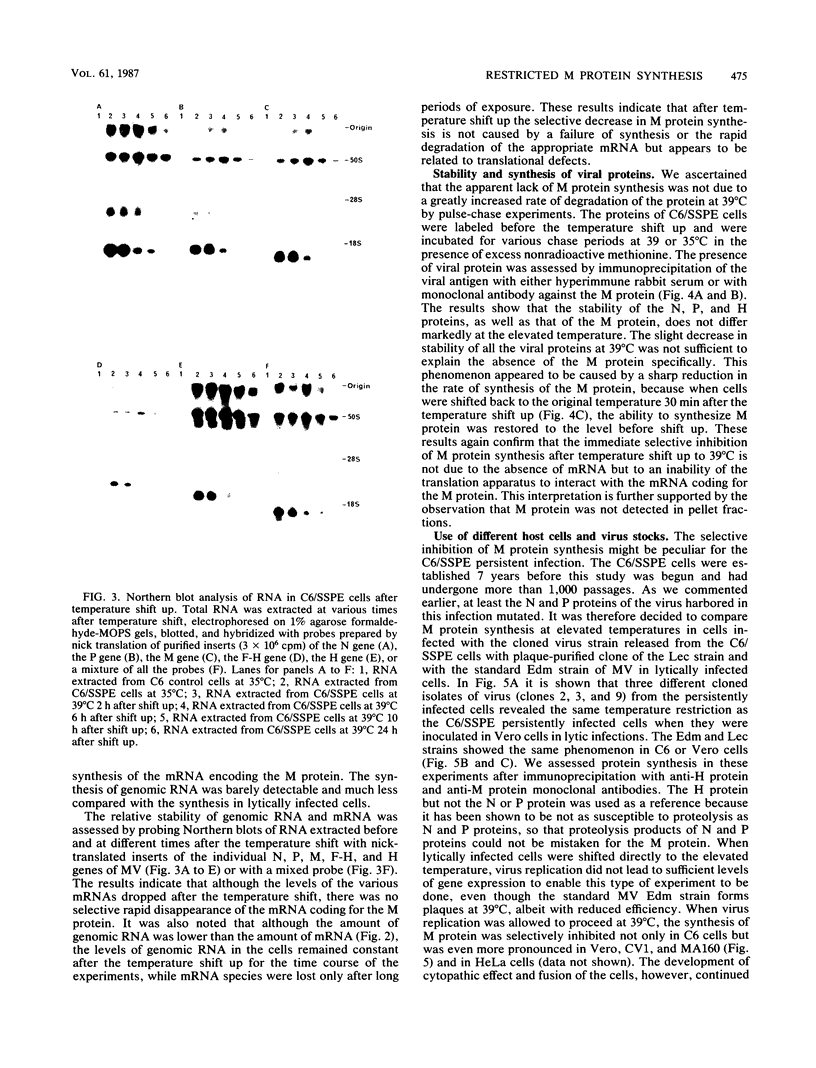
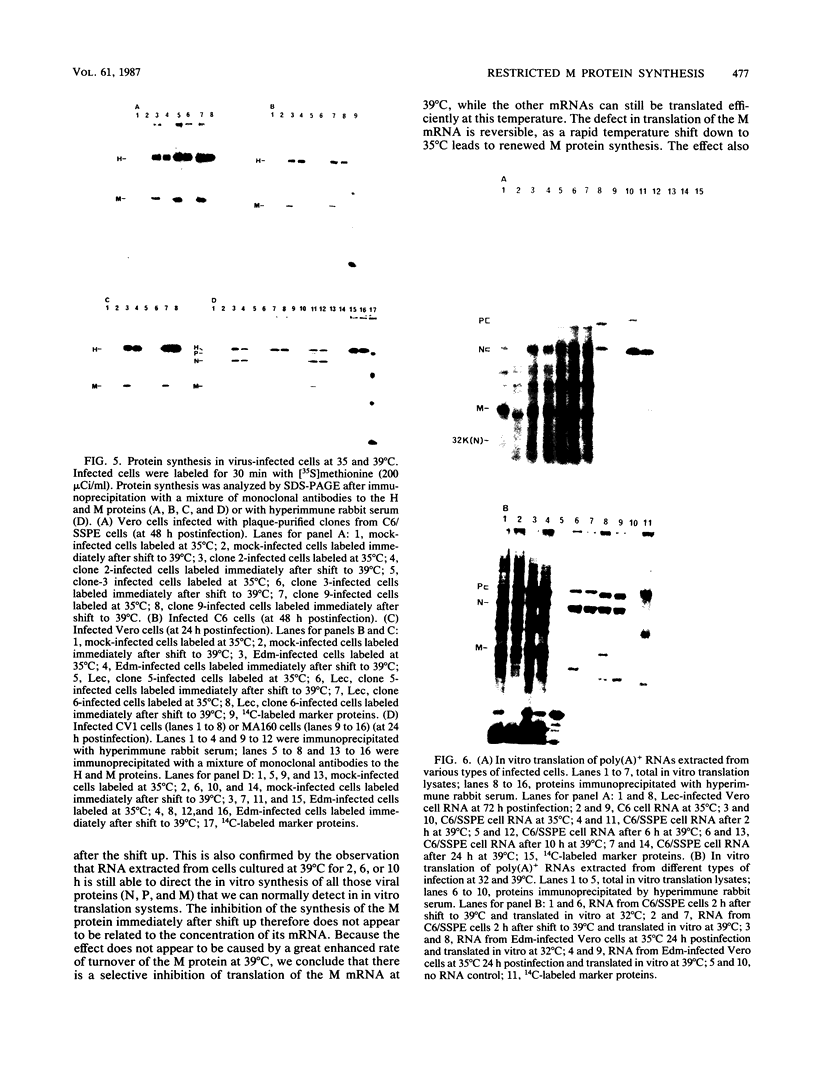
Abstract
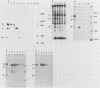
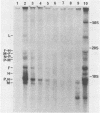
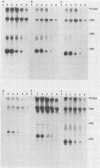
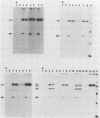
The elevation of culture temperatures of C6 cells that were persistently infected with the Lec strain of the subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) virus (C6/SSPE) resulted in immediate selective inhibition of membrane (M) protein synthesis. This phenomenon was confirmed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of total cytoplasmic lysates and immunoprecipitation with monoclonal antibody against the M protein in short-time labeling experiments. The synthesis of various viral mRNAs in the presence of actinomycin D decreased gradually at similar rates after a shift to 39 degrees C. No specific disappearance of the mRNA coding for the M protein was observed when viral RNAs isolated from the infected cells were compared before and after a shift up by Northern blot analysis. Results of pulse-chase experiments did not show any significant difference in M protein stability between 35 and 39 degrees C. This rapid block of M protein synthesis was observed not only in Vero cells that were lytically infected with plaque-purified clones from the Lec strain, clones isolated from C6/SSPE cells and the standard Edmonston strain of measles virus but also in CV1, MA160, and HeLa cells that were lytically infected with the Edmonston strain. Poly(A)+ RNAs that were extracted from C6/SSPE cells before and after a shift to 39 degrees C produced detectable phospho, nucleocapsid, and M proteins in cell-free translation systems at 32 degrees C. Even higher incubation temperatures did not demonstrate the selective depression of M protein synthesis described above in vitro. All these data indicate that M protein synthesis of measles virus is selectively suppressed at elevated temperatures because of an inability of the translation apparatus to interact with the M protein-encoded mRNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baczko K., Carter M. J., Billeter M., ter Meulen V. Measles virus gene expression in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Virus Res. 1984 Oct;1(7):585–595. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90015-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett P. N., Koschel K., Carter M., ter Meulen V. Effect of measles virus antibodies on a measles SSPE virus persistently infected C6 rat glioma cell line. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1411–1421. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Richardson C. D., Rozenblatt S., Lazzarini R. A. Matrix genes of measles virus and canine distemper virus: cloning, nucleotide sequences, and deduced amino acid sequences. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):408–416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.408-416.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Richardson C. D., Rozenblatt S. Positive identification of a measles virus cDNA clone encoding a region of the phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):939–942. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.939-942.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M. A., Baczko K., Schmid A., Ter Meulen V. Cloning of DNA corresponding to four different measles virus genomic regions. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):147–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. J., Willcocks M. M., Löffler S., Ter Meulen V. Comparison of lytic and persistent measles virus matrix proteins by competition radioimmunoassay. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1801–1805. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. J., Willcocks M. M., Löffler S., ter Meulen V. Relationships between monoclonal antibody-binding sites on the measles virus haemagglutinin. J Gen Virol. 1982 Nov;63(Pt 1):113–120. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. J., Willcocks M. M., ter Meulen V. Defective translation of measles virus matrix protein in a subacute sclerosing panencephalitis cell line. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):153–155. doi: 10.1038/305153a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervera M., Dreyfuss G., Penman S. Messenger RNA is translated when associated with the cytoskeletal framework in normal and VSV-infected HeLa cells. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90276-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Antiviral antibody reacting on the plasma membrane alters measles virus expression inside the cell. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):529–530. doi: 10.1038/279529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorecki M., Rozenblatt S. Cloning of DNA complementary to the measles virus mRNA encoding nucleocapsid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C. Measles virus polypeptides in infected cells studied by immune precipitation and one-dimensional peptide mapping. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):224–230. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.224-230.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Gantz D., Blum H., Stowring L., Ventura P., Geballe A., Moyer B., Brahic M. Combined macroscopic and microscopic detection of viral genes in tissues. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90462-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Gantz D., Eble B., Walker D., Stowring L., Ventura P., Blum H., Wietgrefe S., Zupancic M., Tourtellotte W. Natural history of restricted synthesis and expression of measles virus genes in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3020–3024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. False starts in translational control of gene expression. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):580–581. doi: 10.1038/316580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Chen S. N., Togashi T., Shesberadaran H., Johnson K. P. Five measles virus antigens demonstrated by use of mouse hybridoma antibodies in productively infected tissue culture cells. Arch Virol. 1982;71(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF01315171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Kristensson K., Brzosko W. J., Kapsenberg J. G. Measles virus matrix protein detected by immune fluorescence with monoclonal antibodies in the brain of patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):337–340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.337-340.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura H., Sato H., Tanaka J., Kamiya S., Yoshie T., Hatano M. Synthesis of M protein of HVJ (Sendai virus) in rat glial cells is selectively restricted at a non-permissive temperature. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):639–643. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R. The genetics of vesiculoviruses. Arch Virol. 1982;72(1-2):1–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01314447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. D., Berkovich A., Rozenblatt S., Bellini W. J. Use of antibodies directed against synthetic peptides for identifying cDNA clones, establishing reading frames, and deducing the gene order of measles virus. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):186–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.186-193.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins S. J., Rapp F. Inhibition of measles virus replication by cyclic AMP. Virology. 1980 Oct 30;106(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Gesang C., Lavie V., Neumann F. S. Cloning and characterization of DNA complementary to the measles virus mRNA encoding hemagglutinin and matrix protein. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):790–797. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.790-797.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainionpä R. Measles virus-specified polypeptides in infected cells. Arch Virol. 1979;60(3-4):239–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01317495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varsanyi T. M., Utter G., Norrby E. Purification, morphology and antigenic characterization of measles virus envelope components. J Gen Virol. 1984 Feb;65(Pt 2):355–366. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-2-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Meulen V., Löffler S., Carter M. J., Stephenson J. R. Antigenic characterization of measles and SSPE virus haemagglutinin by monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1981 Dec;57(Pt 2):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-2-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]