Abstract
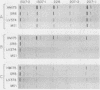
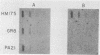
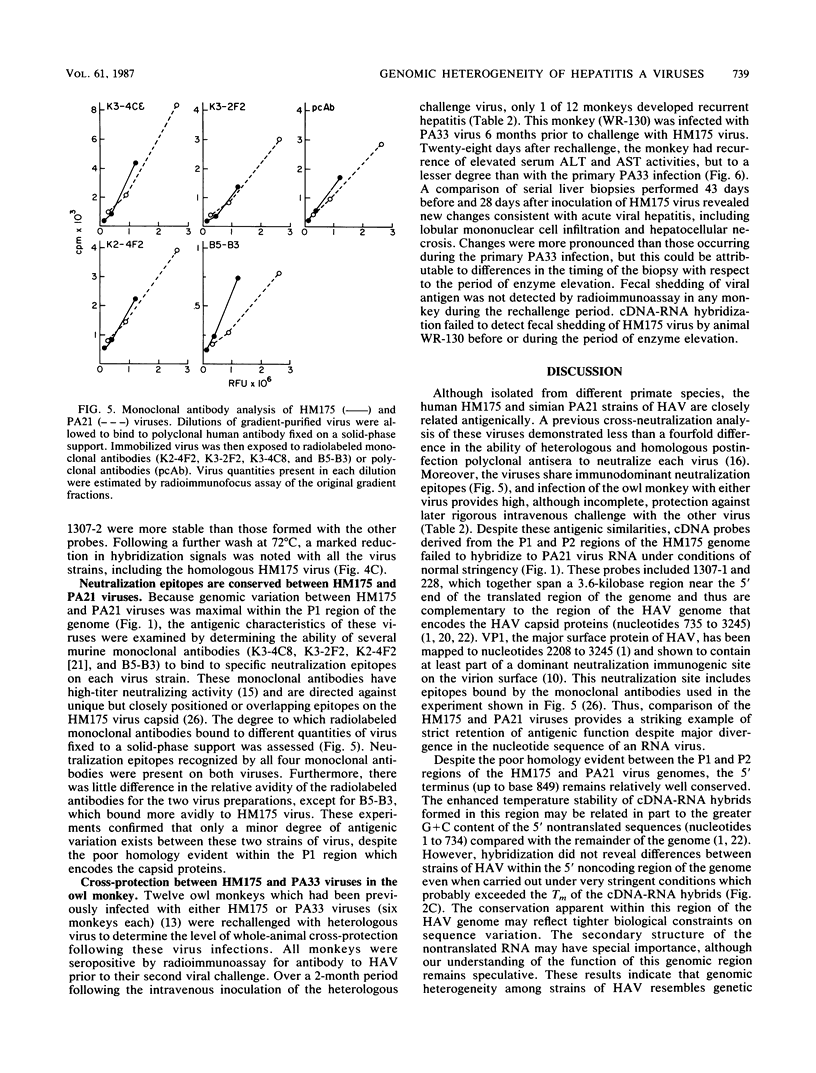
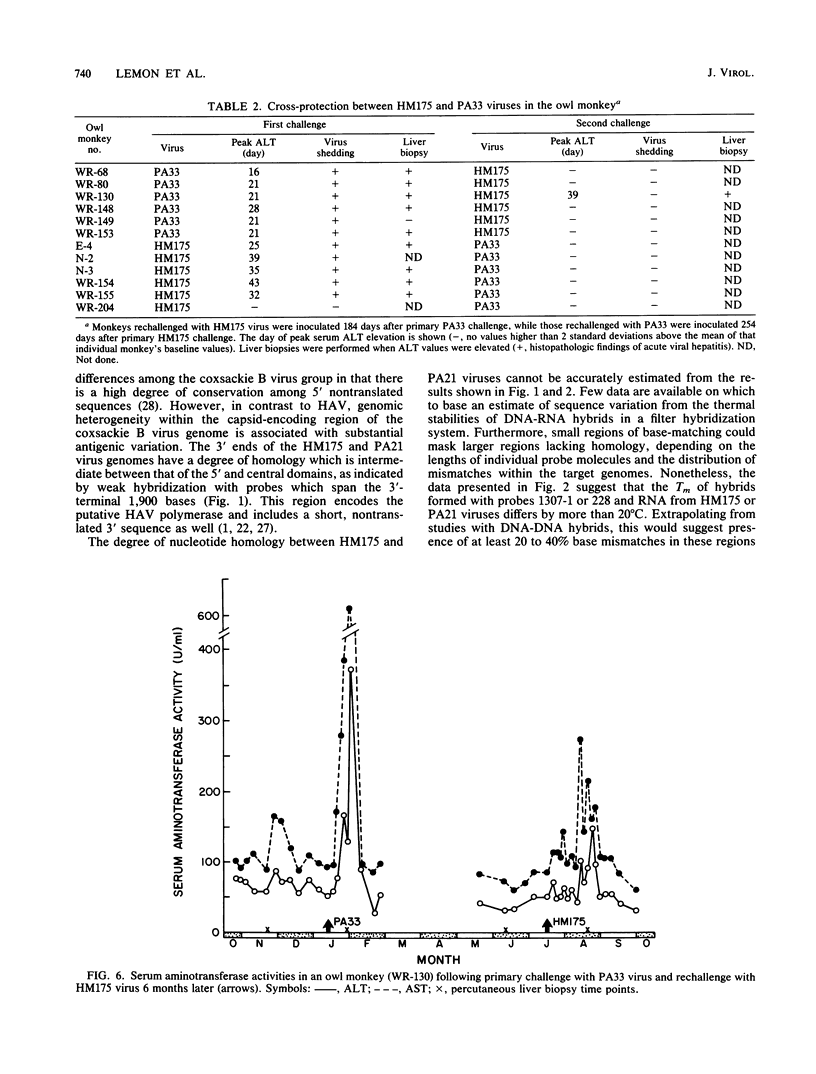
Cloned cDNA probes derived from the P1 and P2 regions of the genome of HM175 virus, a reference strain of human hepatitis A virus (HAV), failed to hybridize under standard stringency criteria with RNA from PA21 and PA33 viruses, two epizootiologically related HAV strains recovered from naturally infected New World owl monkeys. Hybridization of these probes to PA21 RNA was only evident under reduced stringency conditions. However, cDNA representing the 5' nontranslated region of the HM175 genome hybridized equally to HM175 and PA21 RNA under standard stringency conditions, while a probe derived from the 3' 1,400 bases of the genome yielded a reduced hybridization signal with PA21 RNA. In contrast, no differences could be discerned between HM175 virus and three other HAV strains of human origin (GR8, LV374, and MS1) in any region of the genome, unless increased stringency conditions were used. These results suggest that PA21 and PA33 are unique among HAV isolates and may represent a virus native to the owl monkey. Despite extremely poor homology within the P1 region, which encodes capsid polypeptides, monoclonal antibody analysis confirmed that the immunodominant neutralization epitopes of HAV were highly conserved between HM175 and PA21 viruses. Furthermore, experimental challenge of the owl monkey with successive PA33 and HM175 inocula confirmed a high but incomplete degree of cross-protection. Only one of six monkeys previously infected with PA33 developed recurrent hepatitis 28 days after intravenous HM175 challenge, while none of six monkeys previously infected with HM175 had demonstrable hepatitis following PA33 challenge. These data provide molecular evidence for the existence of HAV strains unique to nonhuman primate species and indicate that strict conservation of antigenic function may accompany substantial genetic divergence in HAV.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baroudy B. M., Ticehurst J. R., Miele T. A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Purcell R. H., Feinstone S. M. Sequence analysis of hepatitis A virus cDNA coding for capsid proteins and RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2143–2147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltz G. A., Jacobs K. A., Eickbush T. H., Cherbas P. T., Kafatos F. C. Isolation of multigene families and determination of homologies by filter hybridization methods. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:266–285. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binn L. N., Bancroft W. H., Lemon S. M., Marchwicki R. H., LeDuc J. W., Trahan C. J., Staley E. C., Keenan C. M. Preparation of a prototype inactivated hepatitis A virus vaccine from infected cell cultures. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):749–756. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binn L. N., Lemon S. M., Marchwicki R. H., Redfield R. R., Gates N. L., Bancroft W. H. Primary isolation and serial passage of hepatitis A virus strains in primate cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):28–33. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.28-33.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs J. D., Melnick J. L., Conrad M. E., Felsher B. F. Viral hepatitis. Clinical and tissue culture studies. JAMA. 1970 Nov 9;214(6):1041–1046. doi: 10.1001/jama.214.6.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. S., Heisey G. B. Wild Malaysian cynomolgus monkeys are exposed to hepatitis A virus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Sep;33(5):940–944. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J. W., Kalter S. S. Hepatitis A and B: serologic survey of human and nonhuman primate sera. Lab Anim Sci. 1980 Jun;30(3):541–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gust I. D., Lehmann N. I., Crowe S., McCrorie M., Locarnini S. A., Lucas C. R. The origin of the HM175 strain of hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):365–367. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J., Spindler K., Horodyski F., Grabau E., Nichol S., VandePol S. Rapid evolution of RNA genomes. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1577–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.7041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. V., Stanton L. W., Tomassini J. E., Long W. J., Scolnick E. M. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to hepatitis A virus: partial localization of a neutralizing antigenic site. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):465–473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.465-473.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. W., Newbold J. E., Lemon S. M. Combined immunoaffinity cDNA-RNA hybridization assay for detection of hepatitis A virus in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):984–989. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.984-989.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lednar W. M., Lemon S. M., Kirkpatrick J. W., Redfield R. R., Fields M. L., Kelley P. W. Frequency of illness associated with epidemic hepatitis A virus infections in adults. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Aug;122(2):226–233. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Binn L. N. Antigenic relatedness of two strains of hepatitis A virus determined by cross-neutralization. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):418–420. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.418-420.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Binn L. N., Marchwicki R. H. Radioimmunofocus assay for quantitation of hepatitis A virus in cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):834–839. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.834-839.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Binn L. N. Serum neutralizing antibody response to hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1033–1039. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Brown C. D., Brooks D. S., Simms T. E., Bancroft W. H. Specific immunoglobulin M response to hepatitis A virus determined by solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):927–936. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.927-936.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., LeDuc J. W., Binn L. N., Escajadillo A., Ishak K. G. Transmission of hepatitis A virus among recently captured Panamanian owl monkeys. J Med Virol. 1982;10(1):25–36. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890100105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M. Type A viral hepatitis. New developments in an old disease. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 24;313(17):1059–1067. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510243131706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linemeyer D. L., Menke J. G., Martin-Gallardo A., Hughes J. V., Young A., Mitra S. W. Molecular cloning and partial sequencing of hepatitis A viral cDNA. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):247–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.247-255.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor A., Kornitschuk M., Hurrell J. G., Lehmann N. I., Coulepis A. G., Locarnini S. A., Gust I. D. Monoclonal antibodies against hepatitis A virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1237–1243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1237-1243.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najarian R., Caput D., Gee W., Potter S. J., Renard A., Merryweather J., Van Nest G., Dina D. Primary structure and gene organization of human hepatitis A virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2627–2631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Ittensohn O. L., Villarejos V. M., Arguedas J. A., Hilleman M. R. Etiologic relationship of marmoset-propagated CR326 hepatitis A virus to hepatitis in man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Apr;142(4):1257–1267. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakela J., Fay O. H., Stevenson D., Gordon I., Mosley J. W. Similarities of two hepatitis A virus strains. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;54(5):561–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticehurst J. R., Racaniello V. R., Baroudy B. M., Baltimore D., Purcell R. H., Feinstone S. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of hepatitis A virus cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5885–5889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy S. A comparison of genomic homologies among the coxsackievirus B group: use of fragments of the cloned coxsackievirus B3 genome as probes. J Gen Virol. 1984 Dec;65(Pt 12):2167–2172. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-12-2167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitz M., Siegl G. Variation among hepatitis A virus strains. I. Genomic variation detected by T1 oligonucleotide mapping. Virus Res. 1985 Dec;4(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]