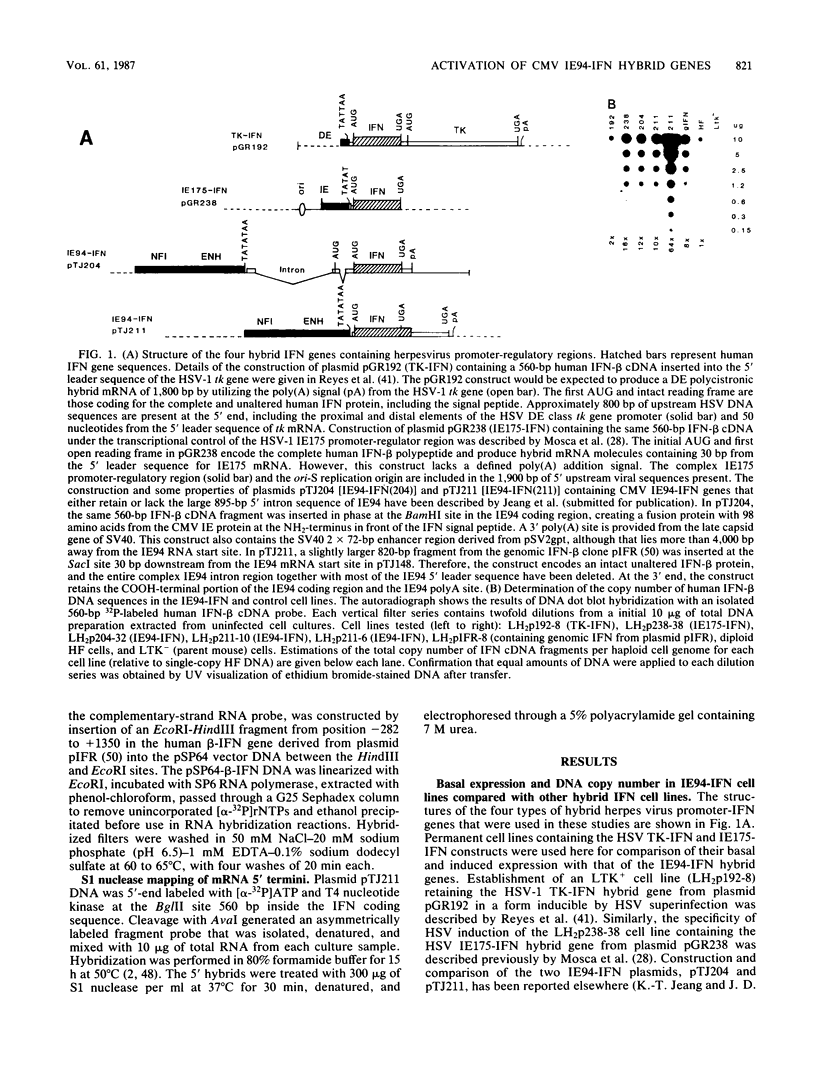
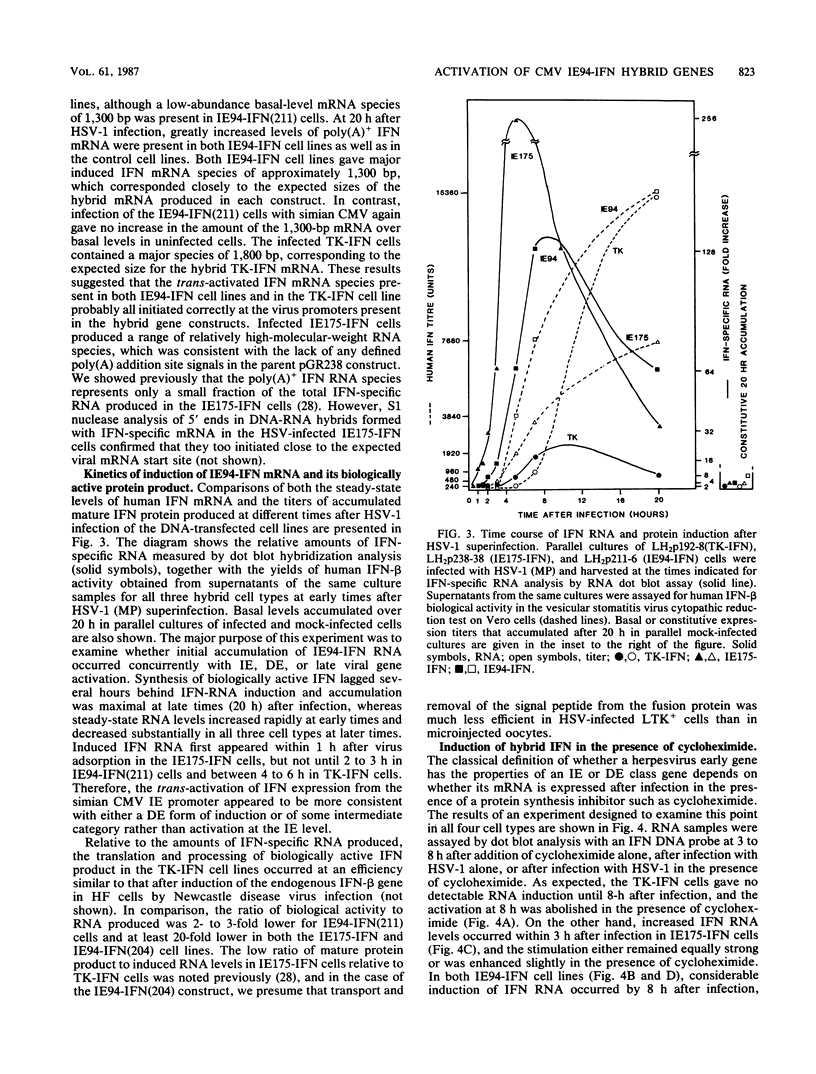
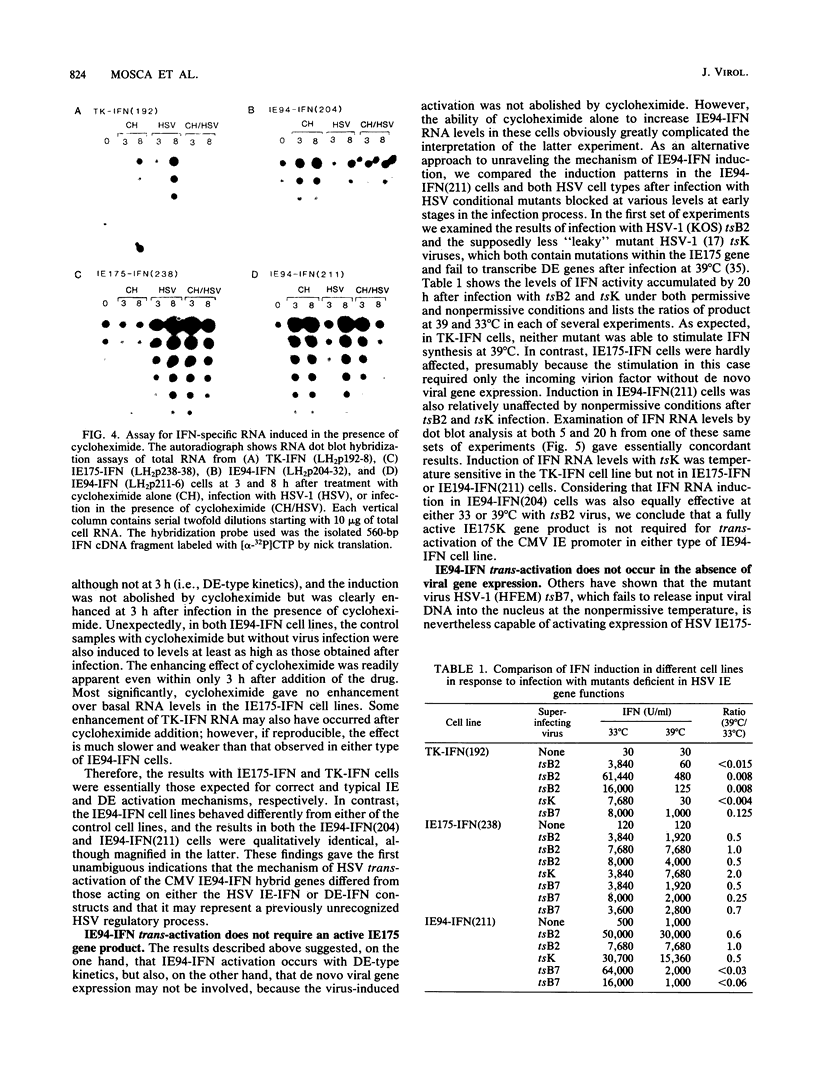
Abstract
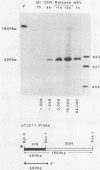
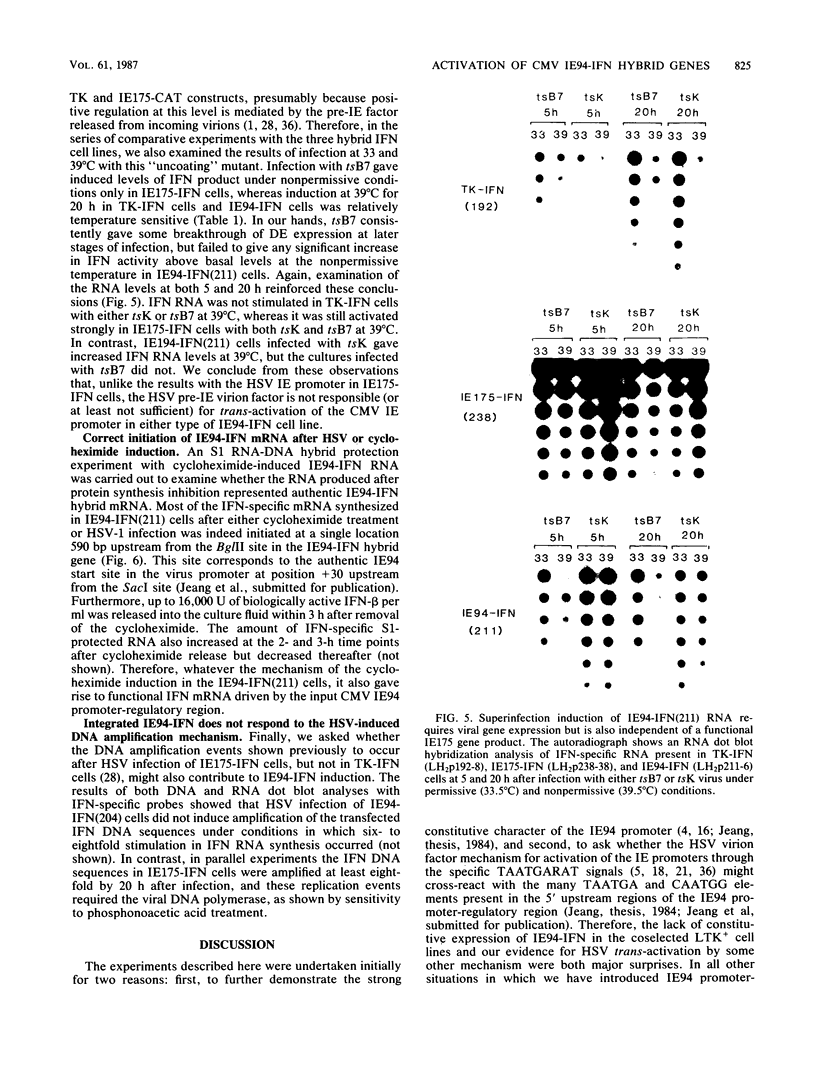
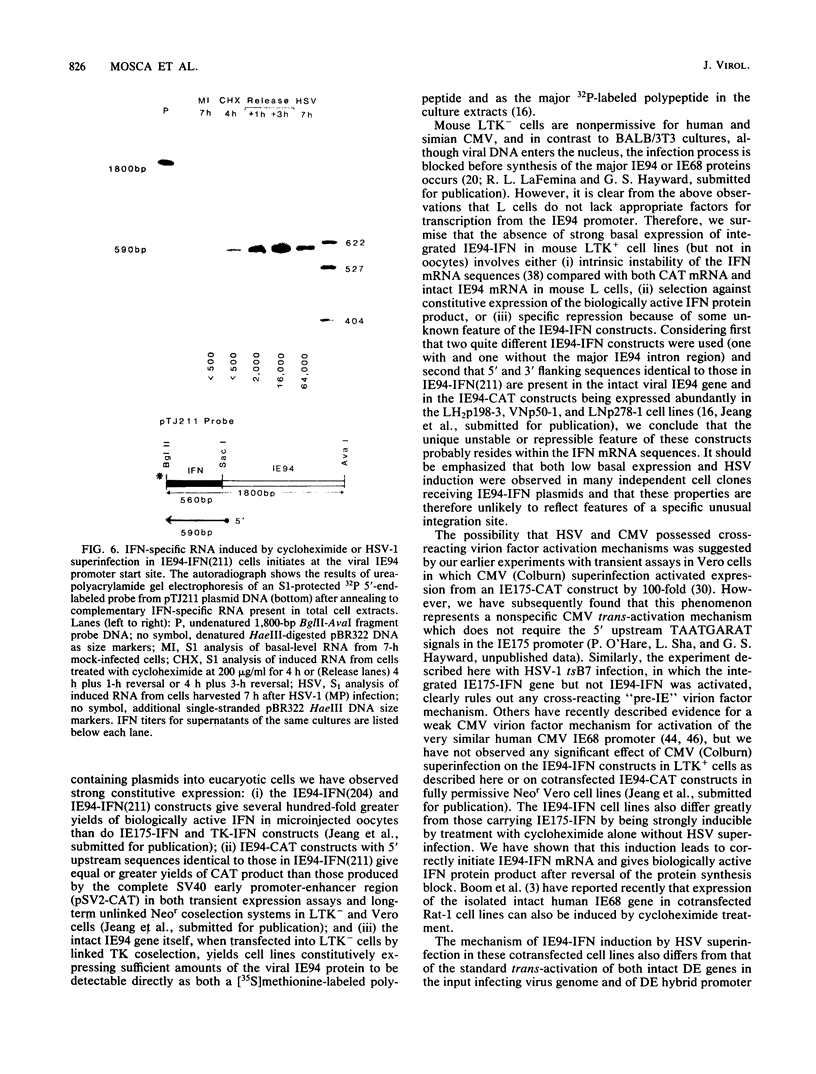
We have constructed stable DNA-transfected LTK+ cell lines containing two different coselected hybrid interferon (IFN) genes driven by the usually strong and constitutive promoter from the immediate-early 94K protein (IE94) gene of simian cytomegalovirus. Surprisingly, and unlike hybrid IE94-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene constructs, both of the IE94-IFN genes (one with and one without the complex spliced intron region) produced relatively low basal titers of biologically active human IFN in the mouse cell lines. However, IFN expression could be stimulated up to 120-fold by superinfection with herpes simplex virus (HSV), although not with cytomegalovirus. To examine the mechanism of this unexpected HSV induction process, we measured the levels of both IE94-IFN mRNA and IFN protein produced under various infection protocols. Compared with similar previously characterized cell lines containing hybrid IFN genes under the control of HSV IE or delayed-early (DE) promoters, activation of IFN expression first occurred at an intermediate time. Both IE94-IFN cell lines also produced an unusual pattern of response to infection with the HSV IE regulation-deficient mutants tsK and tsB7: stimulation of IFN synthesis occurred in the absence of a functional HSV IE175 (or ICP4) gene product, but did not occur in the absence of uncoating of virus capsids. Cycloheximide treatment (without virus infection) also gave a rapid 30-fold increase in steady-state levels of correctly initiated mRNA from both types of IE94-IFN hybrid genes, but had no effect on cells containing the IE175-IFN construct. Therefore, we conclude that the use of the IE94-IFN constructs identifies a novel HSV regulatory response that requires a previously unrecognized function of HSV and does not involve either IE175 or the pre-IE "virion factor" trans-activators that are known to stimulate transcription of HSV IE and DE genes, respectively.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom R., Geelen J. L., Sol C. J., Raap A. K., Minnaar R. P., Klaver B. P., van der Noordaa J. Establishment of a rat cell line inducible for the expression of human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene products by protein synthesis inhibition. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):851–859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.851-859.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activation of immediate-early, early, and late promoters by temperature-sensitive and wild-type forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 protein ICP4. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1997–2008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis D., Smiley J. R. Transactivation of a late herpes simplex virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):544–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Activation of cellular promoters during herpes virus infection of biochemically transformed cells. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1973–1980. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03880.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Draper K. G., Wagner E. K. Uninfected cell polymerase efficiently transcribes early but not late herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6139–6143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Identification of immediate early genes from herpes simplex virus that transactivate the virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5265–5269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris-Hamilton E., Bachenheimer S. L. Accumulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNAs of different kinetic classes in the cytoplasm of infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):144–151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.144-151.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Sinden R. R., Sadler J. R. Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 induce shutoff of host protein synthesis by different mechanisms in Friend erythroleukemia cells. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):241–250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.241-250.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Chin G., Hayward G. S. Characterization of cytomegalovirus immediate-early genes. I. Nonpermissive rodent cells overproduce the IE94K protein form CMV (Colburn). Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Gibson W. A cycloheximide-enhanced protein in cytomegalovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):362–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. Replicative forms of human cytomegalovirus DNA with joined termini are found in permissively infected human cells but not in non-permissive Balb/c-3T3 mouse cells. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):373–389. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R., Hayward G. S. Constitutive and retinoic acid-inducible expression of cytomegalovirus immediate-early genes in human teratocarcinoma cells. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):434–440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.434-440.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaThangue N. B., Shriver K., Dawson C., Chan W. L. Herpes simplex virus infection causes the accumulation of a heat-shock protein. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):267–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. C., Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Transcriptional regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene is mediated through an enhancer-type sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung W. C., Dimock K., Smiley J. R., Bacchetti S. Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase transcripts are absent from both nucleus and cytoplasm during infection in the presence of cycloheximide. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):361–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.361-365.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Differentiation between alpha promoter and regulator regions of herpes simplex virus 1: the functional domains and sequence of a movable alpha regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: the alpha 27 gene promoter-thymidine kinase chimera is positively regulated in converted L cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1015-1023.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton M. H., Reyes G. R., Ciufo D. M., Buchan A., Macnab J. C., Hayward G. S. Expression of cloned herpesvirus genes. I. Detection of nuclear antigens from herpes simplex virus type 2 inverted repeat regions in transfected mouse cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1091–1101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1091-1101.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Pitha P. M. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of exogenous human beta interferon gene in simian cells defective in interferon synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2279–2283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Reyes G. R., Pitha P. M., Hayward G. S. Differential activation of hybrid genes containing herpes simplex virus immediate-early or delayed-early promoters after superinfection of stable DNA-transfected cell lines. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):867–878. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.867-878.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Requirement of protein synthesis for the degradation of host mRNA in Friend erythroleukemia cells infected wtih herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):619–627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.619-627.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Expression of recombinant genes containing herpes simplex virus delayed-early and immediate-early regulatory regions and trans activation by herpesvirus infection. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.522-531.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson R. H., Bacchetti S., Smiley J. R. Cells that constitutively express the herpes simplex virus immediate-early protein ICP4 allow efficient activation of viral delayed-early genes in trans. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):414–421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.414-421.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G., Stow N. D. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.708-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Knipe D. M. Stimulation of expression of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein by two viral functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):957–963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Analysis of interferon mRNA in human fibroblast cells induced to produce interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7426–7430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus mutants defective in the virion-associated shutoff of host polypeptide synthesis and exhibiting abnormal synthesis of alpha (immediate early) viral polypeptides. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):498–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.498-512.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., Gavis E. R., Buchan A., Raj N. B., Hayward G. S., Pitha P. M. Expression of human beta-interferon cDNA under the control of a thymidine kinase promoter from herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):598–601. doi: 10.1038/297598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., Jeang K. T., Hayward G. S. Transfection with the isolated herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase genes. I. Minimal size of the active fragments from HSV-1 and HSV-2. J Gen Virol. 1982 Oct;62(Pt 2):191–206. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-2-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Holland L. E., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Expression of herpes simplex virus beta and gamma genes integrated in mammalian cells and their induction by an alpha gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2028–2044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Roizman B. gamma 2-Thymidine kinase chimeras are identically transcribed but regulated a gamma 2 genes in herpes simplex virus genomes and as beta genes in cell genomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):518–528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus gene expression: alpha and beta promoters are trans activated by viral functions in permissive human fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.135-143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Roehr T. J. Activation of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus by cis-acting elements in the promoter-regulatory sequence and by virus-specific trans-acting components. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):431–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.431-441.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. Replication origins and a sequence involved in coordinate induction of the immediate-early gene family are conserved in an intergenic region of herpes simplex virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):2061–2079. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]