Abstract
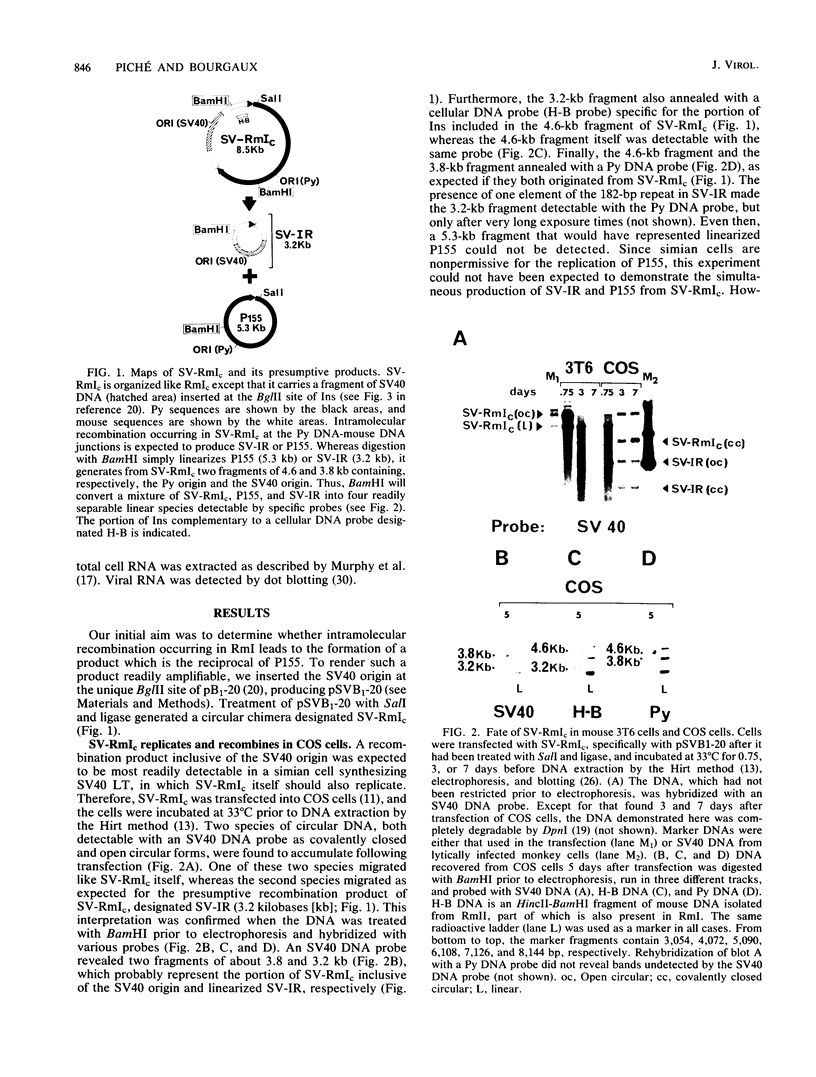
RmI, a circular chimera made of the polyomavirus (Py) genome with an insertion of mouse DNA (Ins), effectively undergoes intramolecular recombination in normal mouse cells, as indicated by the conversion of cloned RmI (RmIc) into unit-length Py DNA in transfected cultures. To follow the fate of the cellular component of RmI after recombination, the origin of simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA was inserted into the Ins region of RmIc, generating a new molecular species designated SV-RmIc. The recombination of SV-RmIc in simian cells synthesizing SV40 large T antigen gave rise to a molecule containing the SV40 origin, the reciprocal of unit-length Py DNA. However, SV-RmIc failed to yield unit-length Py DNA in murine cells unless Py large T antigen was provided in trans. In murine cells synthesizing SV40 large T antigen, the only detectable product from SV-RmIc contained only Py sequences, but was heterogeneous in size. These results and others also reported here strongly suggest that Py large T antigen plays a direct role in the resolution of RmI in murine cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abremski K., Hoess R., Sternberg N. Studies on the properties of P1 site-specific recombination: evidence for topologically unlinked products following recombination. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1301–1311. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Stringer J., Mitchison T., Sambrook J. Integration and excision of SV40 DNA from the chromosome of a transformed cell. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. Studies on simian virus 40 excision from cellular chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):709–719. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard L., Gelinas C., Asselin C., Bastin M. Tumorigenic activity of polyoma virus and SV40 DNAs in newborn rodents. Virology. 1984 May;135(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgaux P., Delbecchi L., Yu K. K., Herring E., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D. A mouse embryo cell line carrying an inducible, temperature-sensitive, polyoma virus genome. Virology. 1978 Jul 15;88(2):348–360. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgaux P., Sylla B. S., Chartrand P. Excision of polyoma virus DNA from that of a transformed mouse cell: identification of a hybrid molecule with direct and inverted repeat sequences at the viral-cellular joints. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):84–97. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90379-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman W., Yin S., Thio L. L., Landy A. Determinants of directionality in lambda site-specific recombination. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):699–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90477-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Grass D. S., Blanck G., Hoganson N., Manley J. L., Pollack R. E. A functional simian virus 40 origin of replication is required for the generation of a super T antigen with a molecular weight of 100,000 in transformed mouse cells. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):492–502. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.492-502.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbecchi L., Gendron D., Bourgaux P. Inducible permissive cells transformed by a temperature-sensitive polyoma virus: superinfection does not allow excision of the resident viral genome. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):196–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.196-206.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galup C., Herring-Gillam E., Sylla B. S., Bourgaux P. The temperature-sensitive defect in polyoma virus P155 mutant. Virus Res. 1984 Sep;1(6):469–475. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Ahrens B. SV40 early mutants that are defective for viral DNA synthesis but competent for transformation of cultured rat and simian cells. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):78–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., Clancy S., Calos M. P. Simian virus 40 replication in adenovirus-transformed human cells antagonizes gene expression. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):169–171. doi: 10.1038/317169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. D., Manley J. L. Repression of simian virus 40 early transcription by viral DNA replication in human 293 cells. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):172–175. doi: 10.1038/317172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manos M. M., Gluzman Y. Simian virus 40 large T-antigen point mutants that are defective in viral DNA replication but competent in oncogenic transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1125–1133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Bullock P., Botchan M. Simian virus 40 T antigen is required for viral excision from chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7534–7538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D., Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Willison K., Rigby P. W. Transcripts regulated during normal embryonic development and oncogenic transformation share a repetitive element. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):865–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piché A., Bourgaux P. Resolution of a polyomavirus-mouse hybrid replicon: release of genomic viral DNA. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):840–844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.840-844.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintel D., Bouck N., di Mayorca G. Separation of lytic and transforming functions of the simian virus 40 A region: two mutants which are temperature sensitive for lytic functions have opposite effects on transformation. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):518–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.518-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rautmann G., Glaichenhaus N., Nahgashfar Z., Breathnach R., Rassoulzadegan M. Complementation of a tsa mutant and replication of a recombinant DNA carrying the viral ori region in mouse cells transformed by polyoma virus. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):306–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Resolution of cointegrates between transposons gamma delta and Tn3 defines the recombination site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller A., Prives C. Simian virus 40 and polyomavirus large tumor antigens have different requirements for high-affinity sequence-specific DNA binding. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):532–545. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.532-545.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürmann C., Montenarh M., Kohler M., Henning R. Oligomerization of simian virus 40 tumor antigen may be involved in viral DNA replication. Virology. 1985 Oct 15;146(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Berg P. Homologous and nonhomologous recombination in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1040–1052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman D. J., Milman G. Short-term, high-efficiency expression of transfected DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1641–1643. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylla B. S., Huberdeau D., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D., Bourgaux P. Site-specific excision of integrated polyoma DNA. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):661–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90398-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verderame M. F., Pollack R. Expression of 100,000-Mr simian virus 40 (SV40) tumor antigen in mouse fibroblasts transfected with replication-defective SV40 genomes. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):857–863. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.857-863.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Gudewicz T., Porter T., White A., Wilson J. H. How damaged is the biologically active subpopulation of transfected DNA? Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):387–398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Vernaleone F., Wilson J. H. Topological requirements for homologous recombination among DNA molecules transfected into mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2080–2089. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]