Abstract
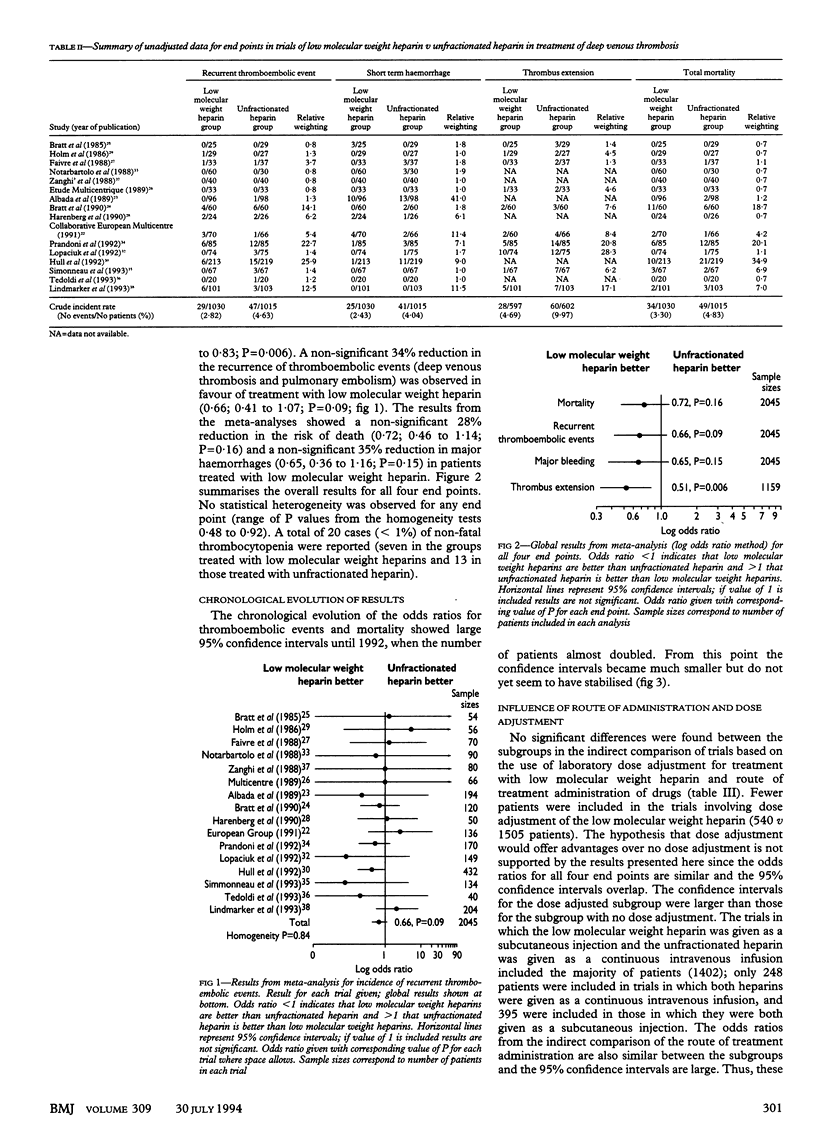
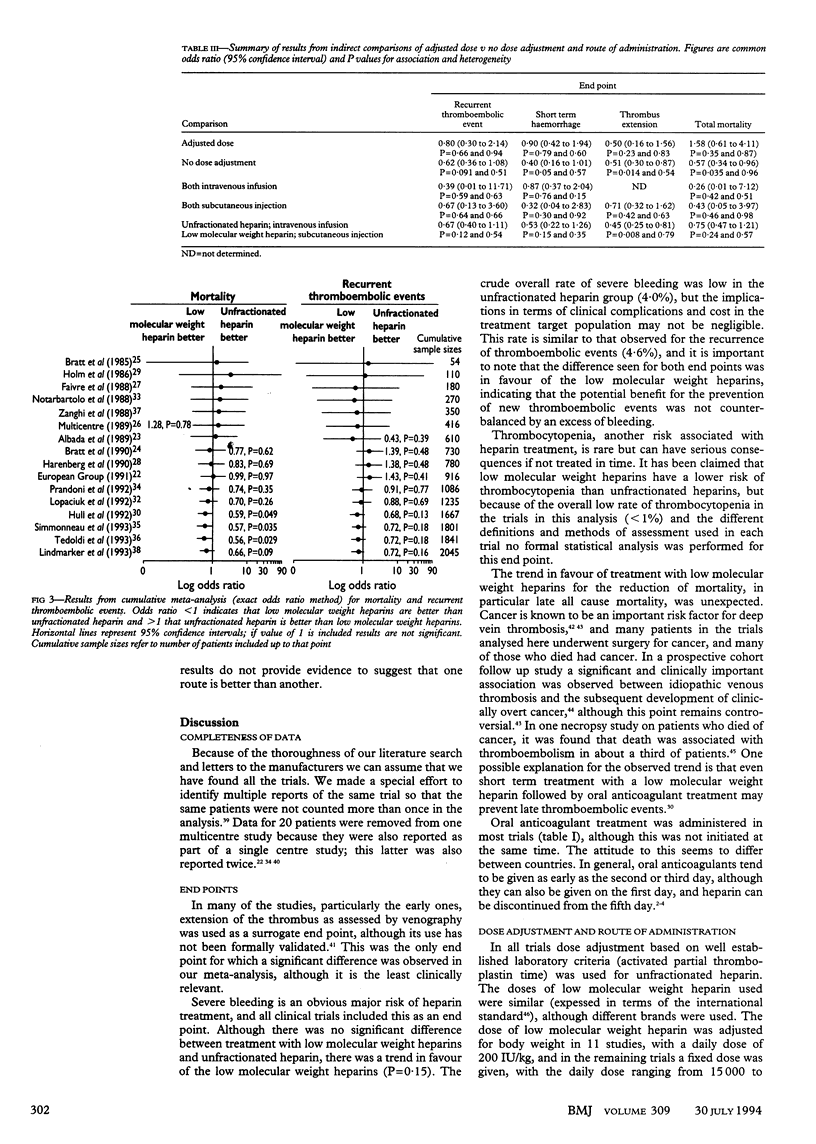
OBJECTIVE--To compare the efficacy and safety of low molecular weight heparins and unfractionated heparin in the initial treatment of deep venous thrombosis for the reduction of recurrent thromboembolic events, death, extension of thrombus, and haemorrhages. DESIGN--Meta-analysis of results from 16 randomised controlled clinical studies. SUBJECTS--2045 patients with established deep venous thrombosis. INTERVENTION--Treatment with low molecular weight heparins or unfractionated heparin. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Incidences of thromboembolic events (deep venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, or both); major haemorrhages; total mortality; and extension of thrombus. RESULTS--A significant reduction in the incidence of thrombus extension (common odds ratio 0.51, 95% confidence interval 0.32 to 0.83; P = 0.006) in favour of low molecular weight heparin was observed. Non-significant trends also in favour of the low molecular weight heparins were observed for the recurrence of thromboembolic events (0.66, 0.41 to 1.07; P = 0.09), major haemorrhages (0.65, 0.36 to 1.16; P = 0.15), and total mortality (0.72, 0.46 to 1.4; P = 0.16). CONCLUSIONS--Low molecular weight heparins seem to have a higher benefit to risk ratio than unfractionated heparin in the treatment of venous thrombosis. These results, however, remain to be confirmed by using clinical outcomes in suitably powered clinical trials.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albada J., Nieuwenhuis H. K., Sixma J. J. Treatment of acute venous thromboembolism with low molecular weight heparin (Fragmin). Results of a double-blind randomized study. Circulation. 1989 Oct;80(4):935–940. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.4.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnesen H., Heilo A., Jakobsen E., Ly B., Skaga E. A prospective study of streptokinase and heparin in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis. Acta Med Scand. 1978;203(6):457–463. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1978.tb14908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRITT D. W., JORDAN S. C. Anticoagulant drugs in the treatment of pulmonary embolism. A controlled trial. Lancet. 1960 Jun 18;1(7138):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. R., Stacey M. C., Jopp-McKay A. G., Hoskin S. E., Thompson P. J. Epidemiology of chronic venous ulcers. Br J Surg. 1991 Jul;78(7):864–867. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bara L., Samama M. The need for standardization of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) Thromb Haemost. 1986 Dec 15;56(3):418–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin J. A., Laird N. M., Sacks H. S., Chalmers T. C. A comparison of statistical methods for combining event rates from clinical trials. Stat Med. 1989 Feb;8(2):141–151. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780080202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissel J. P., Blanchard J., Panak E., Peyrieux J. C., Sacks H. Considerations for the meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Summary of a panel discussion. Control Clin Trials. 1989 Sep;10(3):254–281. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(89)90067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissel J. P., Bossard N. Registry of multicenter clinical trials. Twelfth and thirteenth report--1990-1991. The Council on Thrombosis and Haemostasis of the International Society and Federation of Cardiology. The Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Dec 7;68(6):752–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissel J. P., Collet J. P., Moleur P., Haugh M. Surrogate endpoints: a basis for a rational approach. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1992;43(3):235–244. doi: 10.1007/BF02333016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandjes D. P., Heijboer H., Büller H. R., de Rijk M., Jagt H., ten Cate J. W. Acenocoumarol and heparin compared with acenocoumarol alone in the initial treatment of proximal-vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Nov 19;327(21):1485–1489. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199211193272103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratt G., Aberg W., Johansson M., Törnebohm E., Granqvist S., Lockner D. Two daily subcutaneous injections of fragmin as compared with intravenous standard heparin in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT). Thromb Haemost. 1990 Dec 28;64(4):506–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratt G., Törnebohm E., Granqvist S., Aberg W., Lockner D. A comparison between low molecular weight heparin (KABI 2165) and standard heparin in the intravenous treatment of deep venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Dec 17;54(4):813–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. J., Kelton J. G., Hirsh J., Cerskus A., Santos A. V., Gent M. The relationship between the hemorrhagic and antithrombotic properties of low molecular weight heparin in rabbits. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1239–1245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DerSimonian R., Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986 Sep;7(3):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faivre R., Neuhart Y., Kieffer Y., Apfel F., Magnin D., Didier D., Toulemonde F., Bassand J. P., Maurat J. P. Un nouveau traitement des thromboses veineuses profondes: les fractions d'héparine de bas poids moléculaire. Etude randomisée. Presse Med. 1988 Feb 13;17(5):197–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman A. M., Bara L., Le Roux Y., Woler M., Chauliac F., Samama M. M. The antithrombotic activity and pharmacokinetics of enoxaparine, a low molecular weight heparin, in humans given single subcutaneous doses of 20 to 80 mg. J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;28(7):609–618. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1988.tb03184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallus A., Jackaman J., Tillett J., Mills W., Wycherley A. Safety and efficacy of warfarin started early after submassive venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. Lancet. 1986 Dec 6;2(8519):1293–1296. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. J., Seneff M., Gore J. M., Anderson F. A., Jr, Greene H. L., Wheeler H. B., Dalen J. E. Occult malignant neoplasm in patients with deep venous thrombosis. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Feb;147(2):251–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. R., Stanson A. W., Brown M. L., Hauser M. F., O'Fallon W. M., Anderson H. M., Kazmier F. J., Melton L. J., 3rd Deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Risk of subsequent malignant neoplasms. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Nov;147(11):1907–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harenberg J., Huck K., Bratsch H., Stehle G., Dempfle C. E., Mall K., Blauth M., Usadel K. H., Heene D. L. Therapeutic application of subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin in acute venous thrombosis. Haemostasis. 1990;20 (Suppl 1):205–219. doi: 10.1159/000216179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm H. A., Ly B., Handeland G. F., Abildgaard U., Arnesen K. E., Gottschalk P., Høeg V., Aandahl M., Haugen K., Laerum F. Subcutaneous heparin treatment of deep venous thrombosis: a comparison of unfractionated and low molecular weight heparin. Haemostasis. 1986;16 (Suppl 2):30–37. doi: 10.1159/000215355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommes D. W., Bura A., Mazzolai L., Büller H. R., ten Cate J. W. Subcutaneous heparin compared with continuous intravenous heparin administration in the initial treatment of deep vein thrombosis. A meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Feb 15;116(4):279–284. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-4-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. D., Raskob G. E., Pineo G. F., Green D., Trowbridge A. A., Elliott C. G., Lerner R. G., Hall J., Sparling T., Brettell H. R. Subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin compared with continuous intravenous heparin in the treatment of proximal-vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 9;326(15):975–982. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204093261502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. D., Raskob G. E., Rosenbloom D., Panju A. A., Brill-Edwards P., Ginsberg J. S., Hirsh J., Martin G. J., Green D. Heparin for 5 days as compared with 10 days in the initial treatment of proximal venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 3;322(18):1260–1264. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005033221802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J., Antman E. M., Jimenez-Silva J., Kupelnick B., Mosteller F., Chalmers T. C. Cumulative meta-analysis of therapeutic trials for myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 23;327(4):248–254. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207233270406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leizorovicz A., Haugh M. C., Chapuis F. R., Samama M. M., Boissel J. P. Low molecular weight heparin in prevention of perioperative thrombosis. BMJ. 1992 Oct 17;305(6859):913–920. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6859.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leizorovicz A., Haugh M., Boissel J. P. Meta-analysis and multiple publication of clinical trial reports. Lancet. 1992 Oct 31;340(8827):1102–1103. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad B., Sternby N. H., Bergqvist D. Incidence of venous thromboembolism verified by necropsy over 30 years. BMJ. 1991 Mar 23;302(6778):709–711. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6778.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopaciuk S., Meissner A. J., Filipecki S., Zawilska K., Sowier J., Ciesielski L., Bielawiec M., Glowinski S., Czestochowska E. Subcutaneous low molecular weight heparin versus subcutaneous unfractionated heparin in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis: a Polish multicenter trial. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jul 6;68(1):14–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEL N., HAENSZEL W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 Apr;22(4):719–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggioni A. P., Franzosi M. G., Santoro E., White H., Van de Werf F., Tognoni G. The risk of stroke in patients with acute myocardial infarction after thrombolytic and antithrombotic treatment. Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Sopravvivenza nell'Infarto Miocardico II (GISSI-2), and The International Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 2;327(1):1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207023270101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Soulen R. L., Atichartakarn V., Budzynski A. Z., Parulekar S., Kim J. R., Edward N., Zahavi J., Algazy K. M. Quantitative venographic assessment of deep vein thrombosis in the evaluation of streptokinase and heparin therapy. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 May;89(5):1018–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prandoni P., Lensing A. W., Büller H. R., Carta M., Cogo A., Vigo M., Casara D., Ruol A., ten Cate J. W. Comparison of subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin with intravenous standard heparin in proximal deep-vein thrombosis. Lancet. 1992 Feb 22;339(8791):441–445. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91054-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prandoni P., Vigo M., Cattelan A. M., Ruol A. Treatment of deep venous thrombosis by fixed doses of a low-molecular-weight heparin (CY216). Haemostasis. 1990;20 (Suppl 1):220–223. doi: 10.1159/000216180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonneau G., Charbonnier B., Decousus H., Planchon B., Ninet J., Sie P., Silsiguen M., Combe S. Subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin compared with continuous intravenous unfractionated heparin in the treatment of proximal deep vein thrombosis. Arch Intern Med. 1993 Jul 12;153(13):1541–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. G., Pocock S. J. Can meta-analyses be trusted? Lancet. 1991 Nov 2;338(8775):1127–1130. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91975-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf S., Peto R., Lewis J., Collins R., Sleight P. Beta blockade during and after myocardial infarction: an overview of the randomized trials. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;27(5):335–371. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(85)80003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanghi' M., Morici V., Costanzo M., Astuto L., Salanitri G. Deep vein thrombosis of the legs: new therapy by means of low molecular weight heparins. J Int Med Res. 1988 Nov-Dec;16(6):474–484. doi: 10.1177/030006058801600610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


