Abstract
A malignant glioma cell line was infected with the human T-lymphotropic virus type IIIB isolate of the human immunodeficiency virus. Infection appeared to be latent rather than productive. Through contact with monocytic or lymphoid cells, the virus present in the glioma cells could be transmitted and gave rise to a fully productive infection.
Full text
PDF
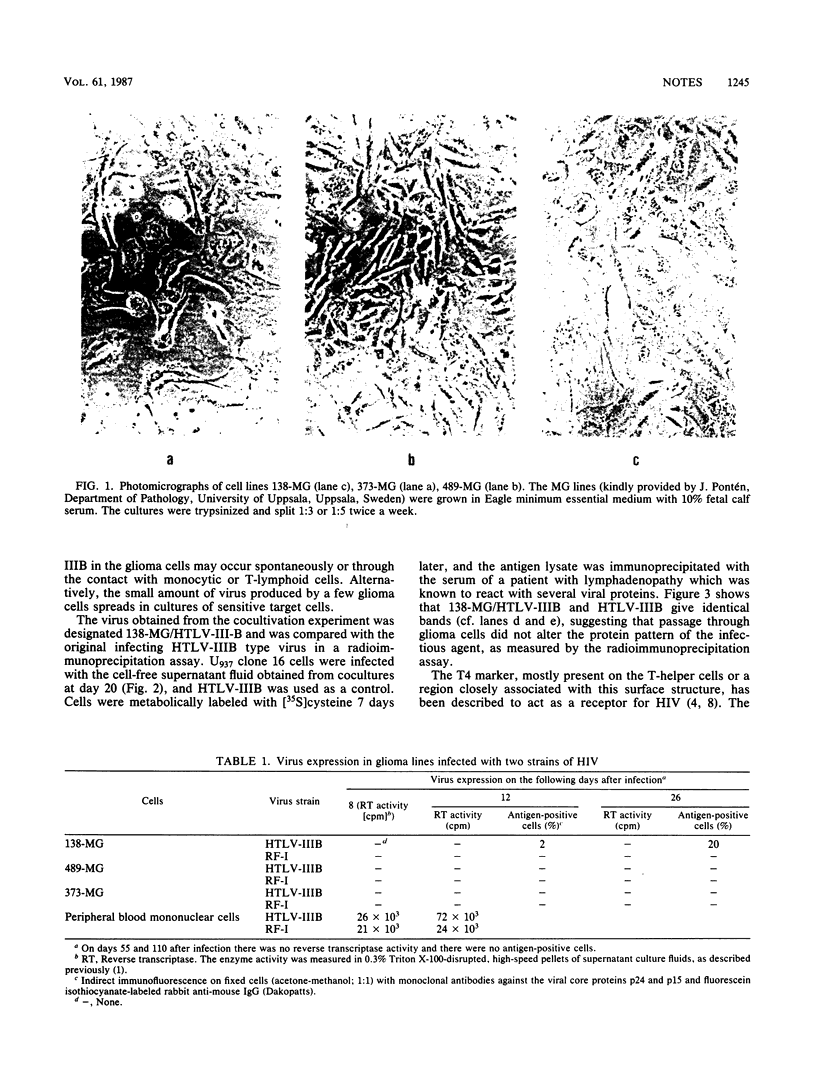
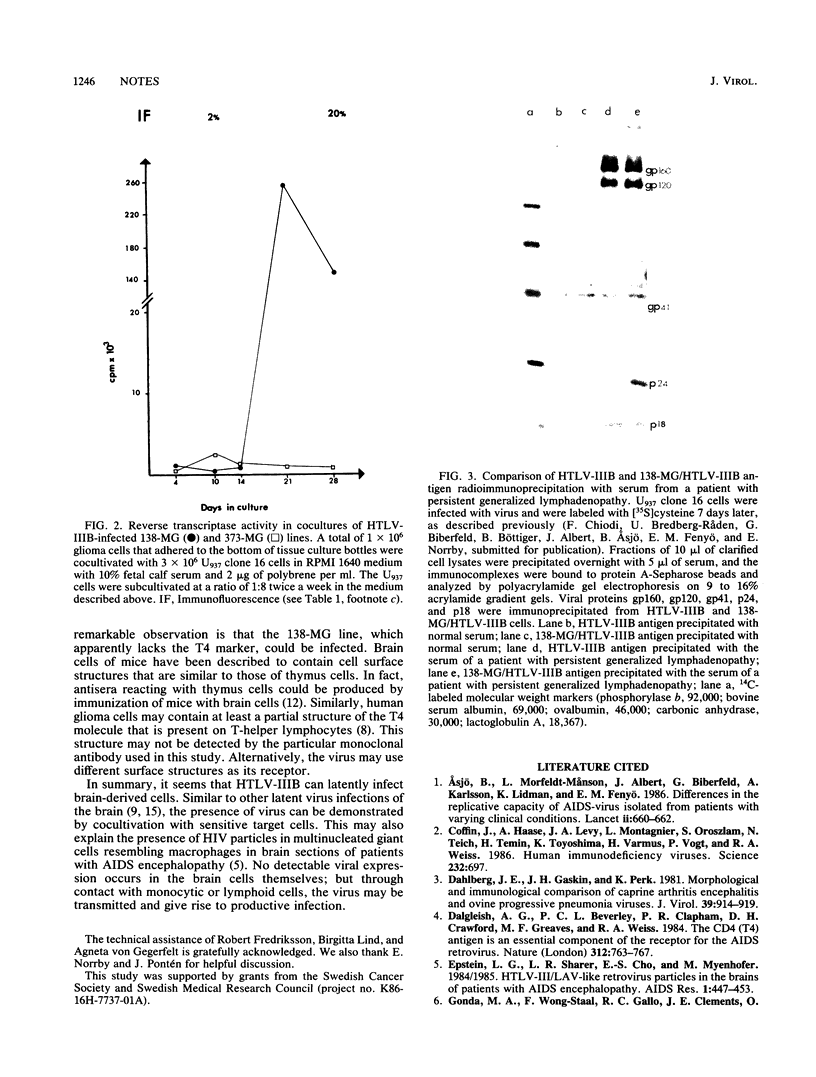

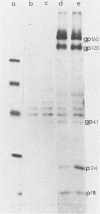
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asjö B., Morfeldt-Månson L., Albert J., Biberfeld G., Karlsson A., Lidman K., Fenyö E. M. Replicative capacity of human immunodeficiency virus from patients with varying severity of HIV infection. Lancet. 1986 Sep 20;2(8508):660–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J., Haase A., Levy J. A., Montagnier L., Oroszlan S., Teich N., Temin H., Toyoshima K., Varmus H., Vogt P. Human immunodeficiency viruses. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):697–697. doi: 10.1126/science.3008335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Gaskin J. M., Perk K. Morphological and immunological comparison of caprine arthritis encephalitis and ovine progressive pneumonia viruses. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):914–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.914-919.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. G., Sharer L. R., Cho E. S., Myenhofer M., Navia B., Price R. W. HTLV-III/LAV-like retrovirus particles in the brains of patients with AIDS encephalopathy. AIDS Res. 1984;1(6):447–454. doi: 10.1089/aid.1.1983.1.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda M. A., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Clements J. E., Narayan O., Gilden R. V. Sequence homology and morphologic similarity of HTLV-III and visna virus, a pathogenic lentivirus. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):173–177. doi: 10.1126/science.2981428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T. The slow infection caused by visna virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;72:101–156. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66289-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N., Georgsson G., Pálsson P. A., Najjar J. A., Lutley R., Pétursson G. Experimental visna in Icelandic sheep: the prototype lentiviral infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):75–82. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Cho E. S., Petito C. K., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):525–535. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Jordan B. D., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: I. Clinical features. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):517–524. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oger J., Szuchet S., Antel J., Arnason B. G. A monoclonal antibody against human T suppressor lymphocytes binds specifically to the surface of cultured oligodendrocytes. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):66–68. doi: 10.1038/295066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P. On the fragmentation of monoclonal IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b from BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2895–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petito C. K., Navia B. A., Cho E. S., Jordan B. D., George D. C., Price R. W. Vacuolar myelopathy pathologically resembling subacute combined degeneration in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1985 Apr 4;312(14):874–879. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198504043121402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontén J., Macintyre E. H. Long term culture of normal and neoplastic human glia. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;74(4):465–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb03502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pétursson G., Nathanson N., Georgsson G., Panitch H., Pálsson P. A. Pathogenesis of visna. I. Sequential virologic, serologic, and pathologic studies. Lab Invest. 1976 Oct;35(4):402–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider W. D., Simpson D. M., Nielsen S., Gold J. W., Metroka C. E., Posner J. B. Neurological complications of acquired immune deficiency syndrome: analysis of 50 patients. Ann Neurol. 1983 Oct;14(4):403–418. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark B., Pontén J., Hugosson R. Determinants for the establishment of permanent tissue culture lines from human gliomas. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1973 Nov;81(6):791–805. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb03573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]